What Is Debt-to-Income Ratio?
Quick Answer
Your debt-to-income ratio indicates how much of your monthly income goes to pay debt obligations. It's an important indicator of how well you're able to manage your monthly payments.

Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is the total of your monthly debt payments divided by your gross monthly income. DTI is one of many factors lenders consider to determine your eligibility for a loan or a credit card.
Even if you're not planning to borrow money, you can use the metric to evaluate your debt situation and decide which steps you can take, if any, to improve your overall financial health.
What Is a Debt-to-Income Ratio?
The debt-to-income ratio is a simple formula that shows lenders how much of your income goes toward monthly debt payments. With most types of loans, lenders include all of your debt payments in the DTI calculation.
With mortgage loans, however, lenders typically calculate two forms of your DTI:
- Front-end DTI: Examines how much of your gross income goes toward housing costs, including mortgage payments, property taxes and homeowners insurance.
- Back-end DTI: Compares your gross income to all monthly debt payments, including housing, credit cards, auto loans, student loans and any other type of debt.
How Do I Calculate My Debt-to-Income Ratio?
To determine your DTI, first add up all of your monthly debt payments (use minimum payments for revolving credit such as credit cards). Then, divide the sum by your gross monthly income. That's your income before taxes and other deductions are taken out. Last, multiply by 100 to express your DTI as a percentage.
Here's the debt-to-income ratio formula:
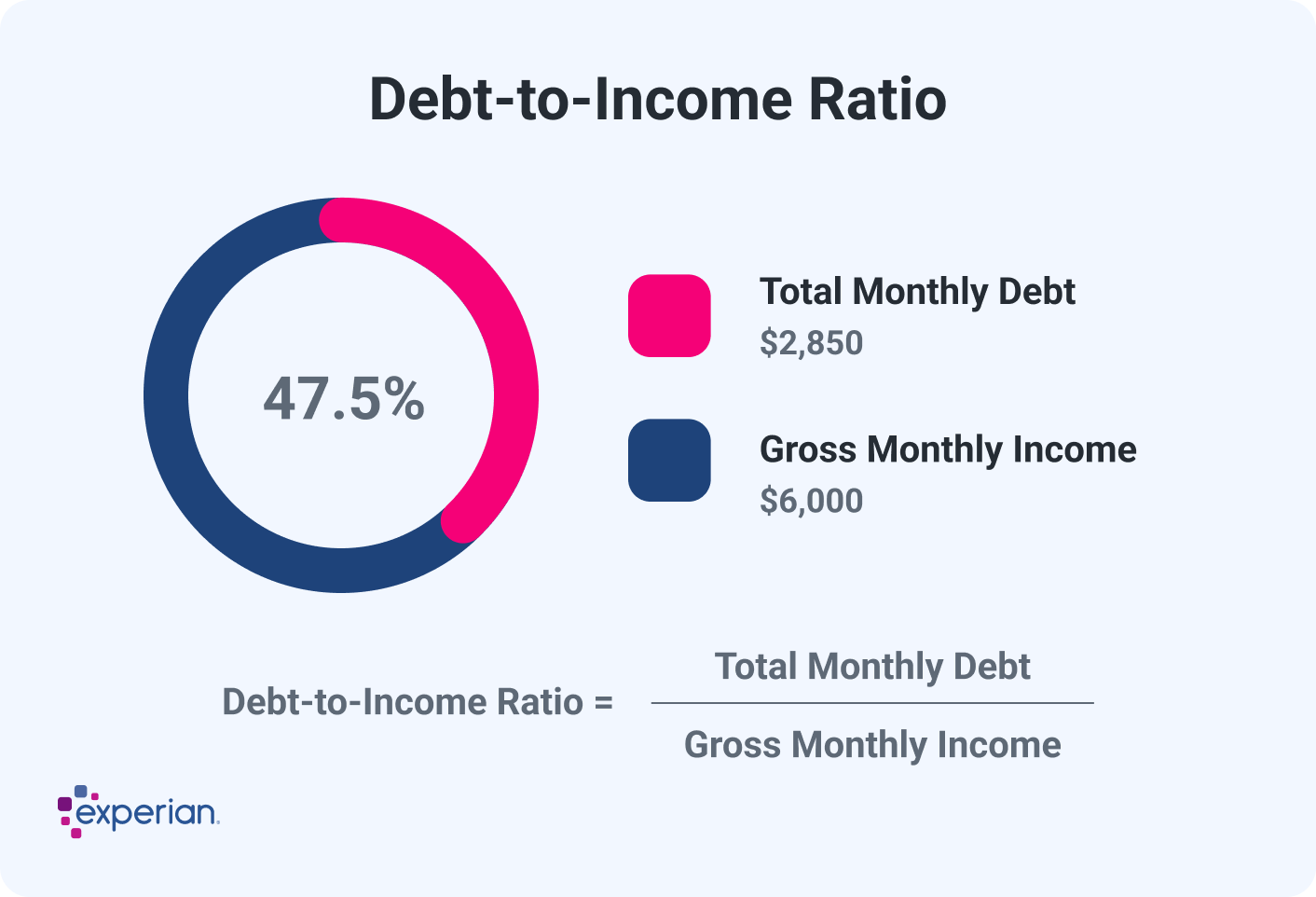
Example: Let's say you earn $6,000 a month before taxes, and you have the following monthly payments:
- Mortgage loan: $1,600
- Auto loan: $500
- Student loans: $350
- Credit cards: $400
To calculate your front-end DTI, simply divide your mortgage payment of $1,600 by your monthly income of $6,000. Multiply the resulting decimal by 100 to find your DTI ratio of 26.67%. (This calculation assumes you pay property taxes and home insurance as part of your mortgage payment.)
For your back-end DTI, adding up all of your debt payments will give you a sum of $2,850. You'll then divide that by $6,000, which equals 0.475. Then, multiply by 100, giving you a ratio of 47.5%.
What's a Good Debt-to-Income Ratio?
A back-end DTI of 35% or less generally indicates that you're managing your debt payments comfortably and have enough cash flow left over for other expenses and financial goals.
That said, you can typically still get approved for a loan if you have a DTI of 50% or less. Some lenders may be willing to go higher than 50%, but interest rates and fees may be high if you can get approved.
If you're planning to apply for a mortgage loan, here are some guidelines to consider:
| Loan Type | Max Front-End DTI | Preferred Back-End DTI | Max Back-End DTI |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional loan | 28% — 35% | 36% — 43% | 50% |
| FHA loan | 31% | 43% | 57% |
| USDA loan | 34% | 41% | 44% |
| VA loan | N/A | 41% | 65% |
Why Is Debt-to-Income Ratio Important?
Where your DTI stands can have implications not only on your ability to obtain credit but also on your general financial well-being. More specifically, here are some reasons why your DTI matters.
Lenders Use It to Evaluate Your Creditworthiness
Creditors will use your DTI, along with your income, credit score, credit history and other factors, to determine whether to approve your credit application, how much you can borrow and what your loan terms will look like.
Higher DTIs typically result in higher interest rates and fees and may even cause your application to be denied.
Learn more: Things Lenders Look at Besides Your Credit Score
It Can Affect Which Loans You Can Get
Lenders typically have set guidelines for the maximum DTI they'll accept. If you have a DTI in the mid to upper 40% range, for instance, you may still be able to get a credit card, an auto loan, a student loan or a personal loan.
Additionally, some mortgage lenders may be willing to work with you. However, mortgage lenders with lower DTI thresholds may deny your application. And if your DTI is above 50%, your credit options may be significantly limited.
It Can Impact Other Financial Goals
The more debt you carry, the less disposable income you have to put toward your emergency fund, retirement plan or other financial goals.
If you spend more than 50% of your monthly income on debt payments, for instance, you may have a hard time keeping up with your obligations.
Learn more: Steps to Setting Up a Debt Repayment Plan
Does Your Debt-to-Income Ratio Impact Your Credit?
Your debt-to-income ratio has no impact on your credit score, particularly because your income isn't a factor in credit-scoring models. That said, your monthly debt payments do appear on your credit reports, which is how lenders are able to calculate the ratio.
Although your DTI doesn't directly affect your credit, lowering your ratio can indirectly improve your credit score.
For example, if you paid off a credit card balance, you'd simultaneously lower your DTI and your credit utilization rate, which is a crucial factor in your FICO® ScoreΘ. Also, if you were to pay off a loan, reducing the total amount you owe could also positively impact your credit.
How to Lower Your Debt-to-Income Ratio
Whether you're planning to apply for credit or you simply want to improve your financial situation, here are some steps you can take to reduce your DTI:
- Minimize credit card use. Credit cards are a form of revolving credit, so it's possible to have a monthly payment show up on your credit reports even if you pay your balance in full each month. Consider paying off your credit card balances and minimizing use for a month or two before applying for a loan to keep your DTI low.
- Pay off small loan balances. If you have a loan with a relatively low remaining balance, using some of your savings to pay it off can help reduce your DTI. If you're applying for a conventional mortgage loan, though, lenders will typically exclude a loan payment from your DTI if you have 10 or fewer months of remaining payments.
- Avoid unnecessary debt. Try to avoid taking on new debt unless it's absolutely necessary. If you do need to borrow money, try to take steps to minimize how much you borrow to keep your monthly payment low.
- Consider debt consolidation. If you have a lot of high-interest debt, a debt consolidation loan can allow you to combine multiple payments into one, making it easier to pay down debt faster and potentially even give you a lower monthly payment in the meantime.
- Increase your income. Look for opportunities to earn more money. Options may include asking for a raise, requesting overtime hours, switching to a higher-paying position, getting a second job or taking on a side hustle.
Work to Improve Your Credit While Reducing Your DTI
In addition to eliminating debt to shrink your debt-to-income ratio, it's also important to build and maintain a good credit score. In fact, having a great credit score can help make up for a higher DTI if you don't have time to reduce the ratio.
As you consider ways to improve your credit, you can sign up with Experian to get free access to your Experian credit report and FICO® Score. While your score alone can give you a general sense of your credit health, your report can give you more insights into what's influencing your score.
You can then use these insights to determine which steps to take to increase your score over time. As you do, Experian can also provide you with real-time alerts when changes are made to your report, making it easier to track your progress and attend to potential issues as they arise.
Find out what debts you owe
Your free credit report lists all your debts, such as credit card balances and loans, helping you create a plan to tackle your debt and improve your financial health.
Review your creditAbout the author
Ben Luthi has worked in financial planning, banking and auto finance, and writes about all aspects of money. His work has appeared in Time, Success, USA Today, Credit Karma, NerdWallet, Wirecutter and more.
Read more from Ben