Tag: fraud prevention

Financial institutions have long relied on anti-money laundering (AML) and anti-fraud systems to protect themselves and their customers. These departments and systems have historically operated in siloes, but that’s no longer best practice. Now, a new framework that integrates fraud and AML, or FRAML, is taking hold as financial institutions see the value of sharing resources to fight fraud and other financial crimes. You don’t need to keep them separated For fraudsters, fraud and money laundering go hand-in-hand. By definition, someone opening an account and laundering money is committing a crime. The laundered funds are also often from illegal activity — otherwise, they wouldn’t need to be laundered. For financial institutions, different departments have historically owned AML and anti-fraud programs. In part, because AML and fraud prevention have different goals: AML is about staying compliant: AML is often owned by an organization’s compliance department, which ensures the proper processes and reporting are in place to comply with relevant regulations. Fraud is about avoiding losses: The fraud department identifies and stops fraudulent activity to help protect the organization from reputational harm and fraud losses. As fraudsters’ operations become more complex, the traditional separation of the two departments may be doing more harm than good. Common areas of focus There has always been some overlap in AML and fraud prevention. After all, an AML program can stop criminals from opening or using accounts that could lead to fraud losses. And fraud departments might stop suspicious activity that’s a criminal placing or layering funds. While AML and fraud both involve ongoing account monitoring, let’s take a closer look at similarities during the account creation: Verifying identities: Financial institutions’ AML programs must include know your customer (KYC) procedures and a Customer Identification Program (CIP). Being able to verify the identity of a new customer can be important for tracing transactions back to an individual or entity later. Similarly, fraud departments want to be sure there aren’t any red flags when opening a new account, such as a connection between the person or entity and previous fraudulent activity. Preventing synthetic identity fraud: Criminals may try to use synthetic identities to avoid triggering AML or fraud checks. Synthetic identity fraud has been a growing problem, but the latest solutions and tools can help financial institutions stop synthetic identity fraud across the customer lifecycle. Detecting money mules: Some criminals recruit money mules rather than using their own identity or creating a synthetic identity. The mules are paid to use their legitimate bank account to accept and transfer funds on behalf of the criminal. In some cases, the mule is an unwitting victim of a scam and an accomplice in money laundering. Although the exact requirements, tools, processes, and reports for AML and fraud differ, there’s certainly one commonality — identify and stop bad actors. Interactive infographic: Building a multilayered fraud and identity strategy The win-win of the FRAML approach Aligning AML and fraud could lead to cost savings and benefits for the organization and its customers in many ways. Save on IT costs: Fraud and AML teams may benefit from similar types of advanced analytics for detecting suspicious activity. In 2023, around 60 percent of businesses were using or trying to use machine learning (ML) in their fraud strategies, but a quarter said cost was impeding implementation.1 If fraud and AML can share IT resources and assets, they might be able to better afford the latest ML and AI solutions. Avoid duplicate work: Cost savings can also happen if you can avoid having separate AML and fraud investigations into the same case. The diverse backgrounds and approaches to investigations may also lead to more efficient and successful outcomes. Get a holistic view of customers: Sharing information about customers and accounts also might help you more accurately assess risk and identify fraud groups. Improve your customer experience: Shared data can also reduce customer outreach for identity or transaction verifications. Creating a single view of each account or customer can also improve customer onboarding and account monitoring, leading to fewer false positives and a better customer experience. Some financial institutions have implemented collaboration with the creation of a new team, sometimes called the financial crimes unit (FCU). Others may keep the departments separate but develop systems for sharing data and resources. Watch the webinar: Fraud and identity challenges for Fintechs How Experian can help Creating new systems and changing company culture doesn’t happen overnight, but the shift toward collaboration may be one of the big trends in AML and fraud for 2024. As a leader in identity verification and fraud prevention, Experian can offer the tools and strategies that organizations need to update their AML and fraud processes across the entire customer lifecycle. CrossCore® is our integrated digital identity and fraud risk platform which enables organizations to connect, access, and orchestrate decisions that leverage multiple data sources and services. CrossCore cloud platform combines risk-based authentication, identity proofing and fraud detection, which enables organizations to streamline processes and quickly respond to an ever-changing environment. In its 2023 Fraud Reduction Intelligence Platforms (FRIP), Kuppinger Cole wrote, “Once again, Experian is a Leader in Fraud Reduction Intelligence Platforms. Any organizations looking for a full-featured FRIP service with global support should consider Experian CrossCore.” Learn more about Experian’s AML and fraud solutions. 1. Experian (2023). Experian's 2023 Identity and Fraud Report

Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures are a requirement for banks and other financial institutions to collect and verify the identity of their customers. When a bank verifies the identity of another organization or its owners, the process may be called Know Your Business (KYB) instead. As part of banks’ anti-money laundering (AML) programs, KYC can help stop corruption, money laundering and terrorist financing. Creating and maintaining KYC programs is also important for regulatory compliance, reputation management and fraud prevention. READ: How to Build a Know Your Customer Checklist – Everything You Need to Know The three components of KYC programs Banks can largely determine how to set up their KYC and AML programs within the applicable regulatory guidelines. In the United States, KYC needs to happen when banks initially onboard a new customer. But it’s not a one-and-done event—ongoing customer and transaction monitoring is also important. Customer Identification Program (CIP) Creating a robust Customer Identification Program (CIP) is an essential part of KYC. At a minimum, a bank’s CIP requires it to collect the following information from new customers: Name Date of birth Address Identification number, such as a Social Security number (SSN) or Employer Identification Number (EIN) Banks' CIPs also have to use risk-based procedures to verify customers’ identities and form a reasonable belief that they know the customer's true identity.1 This might involve comparing the information from the application to the customer’s government-issued ID, other identifying documents and authoritative data sources, such as credit bureau databases. Additionally, the bank's CIP will govern how the bank: Retains the customer’s identifying information Compares customer to government lists Provides customers with adequate notices Banks can create CIPs that meet all the requirements in various ways, and many use third-party solutions to quickly collect data, detect forged or falsified documents and verify the provided information. INFOGRAPHIC: Streamlining the Digital Onboarding Process: Beating Fraud at its Game Customer due diligence (CDD) CIP and CDD overlap, but the CIP primarily verifies a customer’s identity while customer due diligence (CDD) helps banks understand the risk that each customer poses. To do this, banks try to understand what various types of customers do, what those customers’ normal banking activity looks like, and in contrast, what could be unusual or suspicious activity. Financial institutions can use risk ratings and scores to evaluate customers and then use simplified, standard or enhanced due diligence (EDD) processes based on the results. For example, customers who might pose a greater risk of laundering money or financing terrorism may need to undergo additional screenings and clarify the source of their funds. Ongoing monitoring Ongoing or continuous monitoring of customers’ identities and transactions is also important for staying compliant with AML regulations and stopping fraud. The monitoring can help banks spot a significant change in the identity of the customer, beneficial owner or account, which may require a new KYC check. Unusual transactions can also be a sign of money laundering or fraud, and they may require the bank to file a suspicious activity report (SAR). Why is KYC important in banking? Understanding and implementing KYC processes can be important for several reasons: Regulatory compliance: Although the specific laws and rules can vary by country or region, many banks are required to have AML procedures, including KYC. The fines for violating AML regulations can be in the hundreds of millions— a few banks have been fined over $1 billion for lax AML enforcement and sanctions breaching. Reputation management: In some cases, enforcement actions and fines were headline news. Banks that don’t have robust KYC procedures in place risk losing their customers' trust and respect. Fraud prevention: In addition to the regulatory requirements, KYC policies and systems can also work alongside fraud management solutions for banks. Identity verification at onboarding can help banks identify synthetic identities attempting to open money mule accounts or take out loans. Ongoing monitoring can also be important for identifying long-term fraud schemes and large fraud rings. ON-DEMAND WEBINAR: Fraud Strategies for a Positive Customer Experience KYC in a digital-first world Many financial institutions have been going through digital transformations. Part of that journey is updating the systems and tools in place to meet the expectations of customers and regulators. An Experian survey found that about half of consumers (51 percent) consider abandoning the creation of a new account because of friction or a less-than-positive experience — that increased to 69 percent for high-income households.2 The survey wasn’t specific to financial services, but friction could be a problem for banks wanting to attract new account holders. Just as access to additional data sources and machine learning help automate underwriting, financial institutions can use technological advances to add an appropriate amount of friction based on various risk signals. Some of these can be run in the background, such as an electronic Consent Based Social Security Number Verification (eCBSV) check to verify the customer’s name, SSN and date of birth match the Social Security Administration’s records. Others may require more customer involvement, such as taking a selfie that’s then compared to the image on their photo ID — Experian CrossCore® Doc Capture enables this type of verification. Experian is a leader in identity and data management Experian's identity verification solutions use proprietary and third-party data to help banks manage their KYC procedures, including identity verification and Customer Identification Programs. By bundling identity verification with fraud assessment, banks can stop fraudsters while quickly resolving identity discrepancies. The automated processes also allow you to offer a low-friction identity verification experience and use step-up authentications as needed. Learn more about Experian’s identity solutions. 1FDIC (2021). Customer Identification Program 2Experian (2023). Experian's 2023 Identity and Fraud Report

Ensuring the reliability of tenant applications is paramount to running a successful property management business. But with an exponential rise in prospective residents using fake financial documents to inflate income and employment status, how do property managers navigate and detect fake paystubs without stepping on a landmine of liability? The marketplace of deception Paystub generator websites As you embrace the commitment to diligence, be aware that some legitimate websites can be unknowingly used by fraudsters to create counterfeit financial documents. Knowledge is your ally here. At the touch of a button, even the minimally tech inclined can produce pay stubs that appear convincing. There are dozens of sites that offer paystub generator software, including: Design and editing software websites that are accessible to people beyond just creative professionals. Popular e-commerce platform stores that host apps capable of creating paystubs. Mobile app stores that allow users to download apps for use on all major mobile devices. Key indicators of a fake paystub Remember, as a property manager or owner, you are responsible for scrutinizing these documents to protect your business interests. Use your awareness to be vigilant, verifying every piece of information to ensure the credibility of prospective tenants. While some of these falsified paystubs may appear to be legitimate, they are usually not perfect. Here are some quick checks which may help you spot a fake or trigger a deeper review quickly. Watch out for elusive typos Erroneous spelling, particularly in company names and financial terms, is a big red flag. Keep your eyes peeled for these unruly characters. Distorted watermarks A legitimate paystub should carry official watermarks or specific symbols that indicate its authenticity. However, be on the lookout for watermarks that seem off — sometimes, they're too conspicuous or amateurish, which can be a tell-tale sign of forgery. Authentic watermarks should be subtle and consistent with the company's brand. Crunching the numbers Inaccurate calculations can unravel a fake paystub. If the numbers just don't add up or pay dates vary inexplicably, you should investigate further. Inconsistent font Professional payroll systems stick to a consistent font. If you notice various font styles and sizes, it's worth investigating further. Authenticity lies in uniformity. Going logo-less? A missing company logo, or one that looks like it was copied from a low-resolution image on the internet, should trigger suspicion. Unusual tax deductions Abnormal tax deductions could indicate someone's fiddling with the figures. Brush up on your tax knowledge or consult with an expert if something seems off-the-wall. Final food for thought Remember, having the right knowledge and tools empowers you to make informed decisions, safeguarding your property from potential fraudsters. Be diligent, stay informed, and leverage technology to support your processes. Action steps to take today Educate your team: Make sure everyone involved in the application review process knows what to look for. Develop a standard operating procedure: Update your existing (or develop) Standard Operating Procedures: As new ways of gaming the system arise, make sure your particular procedures are keeping up with the times. For example, include steps for the following: Understand tenant screening laws in your area. Create consistent resident screening criteria. Check credit report and background. Verify employment and income. Review rental history and evictions (if any). Check criminal record with multi-state search. Interview residents before signing a lease. Follow a consistent policy when accepting or rejecting applicants. Embrace technology: Income and employment verification solutions can verify income directly from a trusted data source and avoid the paystub predicament altogether. Consider implementing a verification system that leaves no room for guesswork. Our verification solution, Experian VerifyTM, provides accurate, efficient, and compliant income and employment verification services. With Experian Verify, property managers can navigate the complexities of tenant-related income and employment verification with ease, ensuring they are adhering to Fair Housing laws and detecting fraudulent behavior. To learn more about how Experian Verify can benefit your property business, please contact us and visit us online. Learn more

In the ever-expanding financial crime landscape, envision the most recent perpetrator targeting your organization. Did you catch them? Could you recover the stolen funds? Now, picture that same individual attempting to replicate their scheme at another establishment, only to be thwarted by an advanced system flagging their activity. The reason? Both companies are part of an anti-fraud data consortium, safeguarding financial institutions (FIs) from recurring fraud. In the relentless battle against fraud and financial crime, FIs find themselves at a significant disadvantage due to stringent regulations governing their operations. Criminals, however, operate without boundaries, collaborating across jurisdictions and international borders. Recognizing the need to level the playing field, FIs are increasingly turning to collaborative solutions, such as participation in fraud consortiums, to enhance their anti-fraud and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) efforts. Understanding consortium data for fraud prevention A fraud consortium is a strategic alliance of financial institutions and service providers united in the common goal of comprehensively understanding and combatting fraud. As online transactions surge, so does the risk of fraudulent activities. However, according to Experian’s 2023 U.S. Identity and Fraud Report, 55% of U.S. consumers reported setting up a new account in the last six months despite concerns around fraud and online security. The highest account openings were reported for streaming services (43%), social media sites and applications (40%), and payment system providers (39%). Organizations grappling with fraud turn to consortium data as a robust defense mechanism against evolving fraud strategies. Consortium data for fraud prevention involves sharing transaction data and information among a coalition of similar businesses. This collaborative approach empowers companies with enhanced data analytics and insights, bolstering their ability to combat fraudulent activities effectively. The logic is simple: the more transaction data available for analysis by artificial-intelligence-powered systems, the more adept they become at detecting and preventing fraud by identifying patterns and anomalies. Advantages of data consortiums for fraud and AML teams Participation in an anti-fraud data consortium provides numerous advantages for a financial institution's risk management team. Key benefits include: Case management resolution: Members can exchange detailed case studies, sharing insights on how they responded to specific suspicious activities and financial crime incidents. This collaborative approach facilitates the development of best practices for incident handling. Perpetrator IDs: Identifying repeat offenders becomes more efficient as consortium members share data on suspicious activities. Recognizing patterns in names, addresses, device fingerprints, and other identifiers enables proactive prevention of financial crimes. Fraud trends: Consortium members can collectively analyze and share data on the frequency of various fraud attempts, allowing for the calibration of anti-fraud systems to effectively combat prevalent types of fraud. Regulatory changes: Staying ahead of evolving financial regulations is critical. Consortiums enable FIs to promptly share updates on regulatory changes, ensuring quick modifications to anti-fraud/AML systems for ongoing compliance. Who should join a fraud consortium? A fraud consortium can benefit any organization that faces fraud risks and challenges, especially in the financial industry. However, some organizations may benefit more, depending on their size, type, and fraud exposure. Some of the organizations that should consider joining a fraud consortium are: Financial institutions: Banks, credit unions, and other financial institutions are prime targets for fraudsters, who use various methods such as identity theft, account takeover, card fraud, wire fraud, and loan fraud to steal money and information from them. Fintech companies: Fintech companies are innovative and disruptive players in the financial industry, who offer new and alternative products and services such as digital payments, peer-to-peer lending, crowdfunding, and robot-advisors. Online merchants: Online merchants are vulnerable to fraudsters, who use various methods such as card-not-present fraud, friendly fraud, and chargeback fraud to exploit their online transactions and payment systems. Why partner with Experian? What companies need is a consortium that allows FIs to collaboratively research anti-fraud and AML information, eliminating the need for redundant individual efforts. This approach promotes tighter standardization of anti-crime procedures, expedited deployment of effective anti-fraud/AML solutions, and a proactive focus on preventing financial crime rather than reacting to its aftermath. Experian Hunter is a sophisticated global application fraud and risk management solution. It leverages detection rules to screen incoming application data for identifying and preventing fraudulent activities. It matches incoming application data against multiple internal and external data sources, shared fraud databases and dedicated watch lists. It uses client-flexible matching rules to crossmatch data sources for highlighting data anomalies and velocity attempts. In addition, it looks for connections to previous suspected and known fraudulent applications. Hunter generates a fraud score to indicate a fraud risk level used to prioritize referrals. Suspicious applications are moved into the case management tool for further investigation. Overall, Hunter prevents application fraud by highlighting suspicious applications, allowing you to investigate and prevent fraud without inconveniencing genuine customers. To learn more about our fraud management solutions, visit us online or request a call. Learn more This article includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information.

This article was updated on March 4, 2024. If you steal an identity to commit fraud, your success is determined by how long it takes the victim to find out. That window gets shorter as businesses get better at knowing when and how to reach an identity owner when fraud is suspected. In response, frustrated fraudsters have been developing techniques to commit fraud that does not involve a real identity, giving them a longer run-time and a bigger payday. That's the idea behind synthetic identity (SID) fraud — one of the fastest-growing types of fraud. Defining synthetic identity fraud Organizations tend to have different definitions of synthetic identity fraud, as a synthetic identity will look different to the businesses it attacks. Some may see a new account that goes bad immediately, while others might see a longer tenured account fall delinquent and default. The qualifications of the synthetic identity also change over time, as the fraudster works to increase the identity’s appearance of legitimacy. In the end, there is no person to confirm that fraud has occurred, in the very best case, identifying a synthetic identity is inferred and verified. As a result, inconsistent reporting and categorization can make tracking and fighting SID fraud more difficult. To help create a more unified understanding and response to the issue, the Federal Reserve and 12 fraud experts worked together to develop a definition. In 2021, the Boston Federal Reserve published the result, “Synthetic identity fraud is the use of a combination of personally identifiable information to fabricate a person or entity to commit a dishonest act for personal or financial gain."1 To break down the definition, personally identifiable information (PII) can include: Primary PII: Such as a name, date of birth (DOB), Social Security number (SSN) or another government-issued identifier. When combined, these are generally unique to a person or entity. Secondary PII: Such as an address, email, phone number or device ID. These elements can help verify a person or entity's identity. Synthetic identities are created when fraudsters establish an identity from scratch using fake PII. Or they may combine real and fake PII (I.e., a stolen SSN with a fake name and DOB) to create a new identity. Additionally, fraudsters might steal and use someone's SSN to create an identity - children, the elderly and incarcerated people are popular targets because they don't commonly use credit.4 But any losses would still be tied to the SID rather than the victim. Exploring the Impact of SID fraud The most immediate and obvious impact of SID fraud is the fraud losses. Criminals may create a synthetic identity and spend months building up its credit profile, opening accounts and increasing credit limits. The identities and behaviors are constructed to look like legitimate borrowers, with some having a record of on-time payments. But once the fraudster decides to monetize the identity, they can apply for loans and max out credit cards before ‘busting out’ and disappearing with the money. Aite-Novaric Group estimates that SID fraud losses totaled $1.8 billion in 2020 and will increase to $2.94 billion in 2024.2 However, organizations that do not identify SIDs may classify a default as a credit loss rather than a fraud loss. By some estimates, synthetic identity fraud could account for up to 20 percent of loan and credit card charge-offs, meaning the annual charge-off losses in the U.S. could be closer to $11 billion.3 Additionally, organizations lose time and resources on collection efforts if they do not identify the SID fraud. Those estimates are only for unsecured U.S. credit products. But fraudsters use synthetic identities to take out secured loans, including auto loans. As part of schemes used to steal relief funds during the pandemic, criminals used synthetic identities to open demand deposit accounts to receive funds. These accounts can be used to launder money from other sources and commit peer-to-peer payment fraud. Deposit account holders are also a primary source of cross-marketing for some financial institutions. Criminals can take advantage of vulnerable onboarding processes for deposit accounts where there’s low risk to the institution and receive offers for lending products. Building a successful SID prevention strategy Having an effective SID prevention strategy is more crucial than ever for organizations. Aside from fraud losses, consumers listed identity theft as their top concern when conducting activities online. And while 92% of businesses have an identity verification strategy in place, 63% of consumers are "somewhat confident" or "not very confident" in businesses' ability to accurately identify them online. Read: Experian's 2023 Identity and Fraud Report Many traditional fraud models and identity verification methods are not designed to detect fake people. And even a step up to a phone call for verification isn't enough when the fraudster will be the one answering the phone. Criminals also quickly respond when organizations update their fraud detection methods by looking for less-protected targets. Fraudsters have even signed their SIDs up for social media accounts and apps with low verification hurdles to help their SIDs pass identity checks.5 Understand synthetic identity risks across the lifecycle Synthetic Identities are dynamic. When lending criteria is tightened to synthetics from opening new accounts, they simply come back when they can qualify. If waiting brings a higher credit line, they’ll wait. It’s important to recognize that synthetic identity isn’t a new account or a portfolio management problem - it’s both. Use analytics that are tailored to synthetic identity Many of our customers in the financial services space have been trying to solve synthetic identity fraud with credit data. There’s a false sense of security when criteria is tightened and losses go down—but the losses that are being impacted tend to not be related to credit. A better approach to synthetic ID fraud leverages a larger pool of data to assess behaviors and data linkages that are not contained in traditional credit data. You can then escalate suspicious accounts to require additional reviews, such as screening through the Social Security Administration's Electronic Consent Based SSN Verification (eCBSV) system or more stringent document verification. Find a trusted partner Experian's interconnected data and analytics platforms offer lenders turnkey identity and synthetic identity fraud solutions. In addition, lenders can take advantage of the risk management system and continuous monitoring to look for signs of SIDs and fraudulent activity, which is important for flagging accounts after opening. These tools can also help lenders identify and prevent other common forms of fraud, including account takeovers, e-commerce fraud, child identity theft fraud and elderly fraud. Learn more about our synthetic identity fraud solutions. Learn more 1Federal Reserve Bank (2021). Defining Synthetic Identity Fraud 2Aite Novarica (2022). Synthetic Identity Fraud: Solution Providers Shining Light into the Darkness 3Experian (2022). Preventing synthetic identity fraud 4The Federal Reserve (2022). Synthetic Identity Fraud: What Is it and Why You Should Care? 5Experian (2022). Preventing synthetic identity fraud

While bots have many helpful purposes, they have unfortunately become a tool for malicious actors to gain fraudulent access to financial accounts, personal information and even company-wide systems. Almost every business that has an online presence will have to face and counter bot attacks. In fact, a recent study found that across the internet on a global scale, malicious bots account for 30 percent of automated internet activity.1 And these bots are becoming more sophisticated and harder to detect. What is a bot attack and bot fraud? Bots are automated software applications that carry out repetitive instructions mimicking human behavior.2 They can be either malicious or helpful, depending on their code. For example, they might be used by companies to collect data analytics, scan websites to help you find the best discounts or chat with website visitors. These "good" bots help companies run more efficiently, freeing up employee resources. But on the flip side, if used maliciously, bots can commit attacks and fraudulent acts on an automated basis. These might even go undetected until significant damage is done. Common types of bot attacks and frauds that you might encounter include: Spam bots and malware bots: Spam bots come in all shapes and sizes. Some might scrape email addresses to entice recipients into clicking on a phishing email. Others operate on social media sites. They might create fake Facebook celebrity profiles to entice people to click on phishing links. Sometimes entire bot "farms" will even interact with each other to make a topic or page appear more legitimate. Often, these spam bots work in conjunction with malware bots that trick people into downloading malicious files so they can gain access to their systems. They may distribute viruses, ransomware, spyware or other malicious files. Content scraping bots: These bots automatically scrape content from websites. They might do so to steal contact information or product details or scrape entire articles so they can post duplicate stories on spam websites. DDoS bots and click fraud bots: Distributed denial of service (DDoS) bots interact with a target website or application in such large numbers that the target can't handle all the traffic and is overwhelmed. A similar approach involves using bots to click on ads or sponsored links thousands of times, draining advertisers' budgets. Credential stealing bots: These bots use stolen usernames and passwords to try to log into accounts and steal personal and financial information. Other bots may try brute force password cracking to find one combination that works so they can gain unauthorized access to the account. Once the bot learns consumer’s legitimate username and password combination on one website, they can oftentimes use it to perform account takeovers on other websites. In fact, 15 percent of all login attempts across industries in 2022 were account takeover attacks.1 AI-generated bots: While AI, like ChatGPT, is vastly improving the technological landscape, it's also providing a new avenue for bots.3 AI can create audio and videos that appear so real that people might think they're a celebrity seeking funds. What are the impacts of bot attacks? Bot attacks and bot fraud can have a significant negative impact, both at an individual user level and a company level. Individuals might lose money if they're tricked into sending money to a fake account, or they might click on a phishing link and unwittingly give a malicious actor access to their accounts. On a company level, the impact of a bot attack can be even more widespread. Sensitive customer data might get exposed if the company falls victim to a malware attack. This can open the door for the creation of fake accounts that drain a company's money. For example, a phishing email might lead to demand deposit account (DDA) fraud, where a scammer opens a fraudulent account in a customer's name and then links it to new accounts, like new lines of credit. Malware attacks can also cause clients to lose trust in the company and take their business elsewhere.A DDoS attack can take down an entire website or application, leading to a loss of clients and money. A bot that attacks APIs can exploit design flaws to steal sensitive data. In some cases, ransomware attacks can take over entire systems and render them unusable. How can you stop bot attacks? With so much at risk, stopping bot attacks is vital. But some of the most typical defenses have core flaws. Common methods for stopping bot attacks include: CAPTCHAs: While CAPTCHAs can protect online systems from bot incursions, they can also create friction with the user process. Firewalls: To stop DDoS attacks, companies might reduce attack points by utilizing firewalls or restricting direct traffic to sensitive infrastructures like databases.4 Blocklists: These can prevent IPs associated with attacks from accessing your system entirely. Multifactor authentication (MFA): MFA requires two forms of identification or more before granting access to an account. Password protection: Password managers can ensure employees use strong passwords that are different for each access point. While the above methods can help, many simply aren't enough, especially for larger companies with many points of potential attacks. A piecemeal approach can also lead to friction on the user's side that may turn potential clients away. Our 2024 Identity and Fraud Report revealed that up to 38 percent of U.S. adults stopped creating a new account because of the friction they encountered during the onboarding process. And often, this friction is in place to try to stop fraudulent access. Incorporating behavioral analytics to combat attacks Another effective way to enhance bot detection is through the use of behavioral analytics. This technology helps track user activity and identify patterns that may suggest malicious bot behavior. By analyzing aspects such as typing speed, mouse movement and the way users interact with websites, businesses can gain real-time insights into whether a visitor is human or a bot. Behavioral analytics in fraud uses machine learning and advanced algorithms to continuously monitor and refine user behavior patterns. This allows businesses to identify bot attacks more accurately and prevent them before they cause harm. By analyzing real-time behaviors, such as how fast someone enters information or their browsing habits, businesses can flag suspicious activity that traditional methods might miss. Why partner with Experian? What companies need is fraud and bot protection with a positive customer experience. We provide account takeover fraud prevention solutions that can help protect your company from bot attacks, fraudulent accounts and other malicious attempts to access your sensitive data. Experian's approach embodies a paradigm shift where fraud detection increases efficiency and accuracy without sacrificing customer experience. We can help protect your company from bot attacks, fraudulent accounts and other malicious attempts to access your sensitive data. Learn more This article includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information. 1"Bad bot traffic accounts for nearly 30% of APAC internet traffic," SMEhorizon, June 13, 2023. https://www.smehorizon.com/bad-bot-traffic-accounts-for-nearly-30-of-apac-internet-traffic/2"What is a bot?" AWS. https://aws.amazon.com/what-is/bot/3Nield, David. "How ChatGPT — and bots like it — can spread malware," Wired, April 19, 2023. https://www.wired.com/story/chatgpt-ai-bots-spread-malware/4"What is a DDoS attack?" AWS. https://aws.amazon.com/shield/ddos-attack-protection/

Spoiler alert: Gen AI is everywhere, including the top of Experian’s list of fraud trends 2024. “The speed and complexity of fraud attacks due to new technology and sophisticated fraudsters is leaving both businesses and consumers at risk in 2024,” said Kathleen Peters, chief innovation officer at Experian Decision Analytics in North America. “At Experian, we’re constantly innovating to deliver data-driven solutions to help our customers fight fraud and to protect the consumers they serve.” To deter fraudulent activity in 2024, businesses and consumers must get tactical for their fraud fighting strategies. And for businesses, the need for more sophisticated fraud protection solutions leveraging data and technology is greater than ever before. Experian suggests consumers and businesses watch out for these big five rounding out our fraud trends 2024. Generative AI: Generative AI accelerates DIY fraud: Experian predicts fraudsters will use generative AI to accelerate “do-it-yourself” fraud ranging from deepfake content – think emails, voice and video – as well as code creation to set up scam websites. A previous blog post of ours highlighted four types of generative AI used for fraud, including fraud automation at scale, text content generation, image and video manipulation and human voice generation. The way around it? Fight AI fraud with AI as part of a multilayered fraud prevention solution. Fraud at bank branches: Bank branches are making a comeback. A growing number of consumers prefer visiting bank branches in person to open new accounts or get financial advice with the intent to conduct safer transactions. However, face-to-face verification is not flawless and is still susceptible to human error or oversight. According to an Experian report, 85% of consumers report physical biometrics as the most trusted and secure authentication method they’ve recently encountered, but the measure is only currently used by 32% of businesses to detect and protect against fraud. Retailers, beware: Not all returns are as they appear. Experian predicts an uptick in cases where customers claim to return their purchases, only for the business to receive an empty box in return. Businesses must be vigilant with their fraud strategy in order to mitigate risk of lost goods and revenue. Synthetic identity fraud will surge: Pandemic-born synthetic identities may have been dormant, but now have a few years of history, making it easier to elude detection leading to fraudsters using those dormant accounts to “bust out” over the next year. Cause-related and investment deception: Fraudsters are employing new methods that strike an emotional response from consumers with cause-related asks to gain access to consumers’ personal information. Experian predicts that these deceptive cause-related methods will surge in 2024 and beyond. How businesses and consumers feel about fraud in 2024 According to an Experian report, over half of consumers feel they’re more of a fraud target than a year ago and nearly 70% of businesses report that fraud losses have increased in recent years. Business are facing mounting challenges – from first-party fraud and credit washing to synthetic identity and the yet-to-be-known impacts generative AI may have on fraud schemes. Synthetic identity fraud has been mentioned in multiple Experian Fraud Forecasts and the threat is ever growing. As technology continues to enhance consumers’ connectedness, it also heightens the stakes for various fraud attacks. As highlighted by this list of fraud trends 2024, the ways that fraudsters are looking to deceive is increasing from all angles. “Now more than ever, businesses need to implement a multilayered approach to their identity verification and fraud prevention strategies that leverages the latest technology available,” said Peters. Consumers are increasingly at risk from sophisticated fraud schemes. Increases in direct deposit account and check fraud, as well as advanced technologies like deepfakes and AI-generated phishing emails, put consumers in a precarious position. The call to action for consumers is to remain vigilant of seemingly authentic interactions. Experian can help with your fraud strategy To learn more about Experian’s fraud prevention solutions, please visit https://www.experian.com/business/solutions/fraud-management. Download infographic Watch Future of Fraud webinar
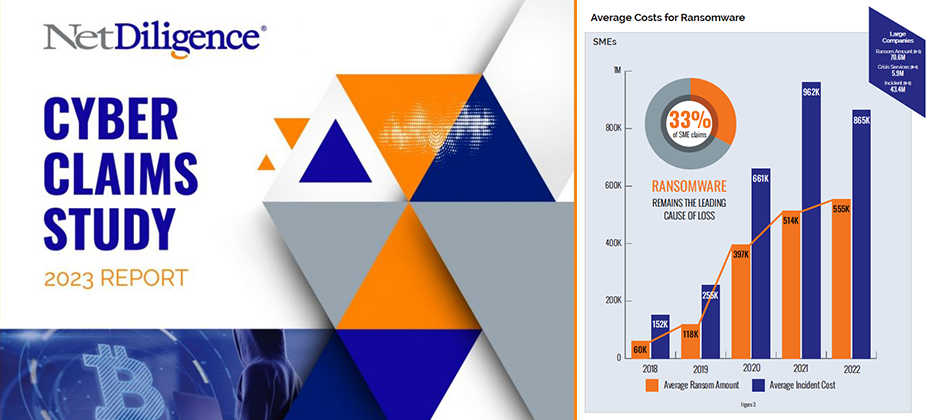
Review of Findings & Front-line Insights Panel Participants: Richard Goldberg (Moderator) – Constangy, Brooks, Smith & Prophete, LLP Michael Bruemmer – Experian Sean Renshw – RSM US, LLP Mark Greisiger – NetDiligence About NetDiligence Cyber Claims Study It is NetDiligence’s 13th year of doing this Cyber Claims Study. A total of 9,028 claims were analyzed during the past five years 2018-2022.An observation from the over 9,000 Cyber Claims (5000 of which are brand new claims this past year in 2023) analyzed is while many of the categories over the last five years have remained the same, the data has changed, sometimes dramatically. About Experian We provide call center coverage, notification coverage, as well as, identity theft protection, and all the consumer resolutions that go along with it for about 5000 data breaches every year, and I was delighted to be on the panel. Key Insights Experian has proudly sponsored the annual NetDiligence Cyber Claims Study for three years. During this time, I’ve witnessed companies adapt and transform their operations to confront the growing tide of cyber threats. The evolution of their infrastructure to anticipate and respond to these challenges has been remarkable and necessary. However, despite my front-row seat in this fast-changing landscape, the results of each study never fail to surprise and intrigue me. The insights from the latest study, conducted in 2023, continue to shape our understanding of the evolving cyber landscape. Ransomware’s Dominance Mark kicked off the discussion by shedding light on the escalating costs associated with cyber incidents. In 2022, the average incident cost for SME organizations remained stable at $169,000 (similar to the combined five-year window from 2018 to 2022 at about 175,000). However, there was a substantial increase for large companies, reaching $20.3 million in 2022 (and if you look at the five-year average, it was about 13 million). This surge raised eyebrows and set the stage for a deep dive into ransomware, a leading cause of concern. Examining Ransomware Trends The conversation swiftly shifted to ransomware, a pervasive threat in the cyber insurance landscape. As I stated, at Experian we see a correlation between the rise in ransomware and third-party breaches. Most of the industry experts on the panel participate in a Ransomware Advisory Group together. Mark brought up a good insight from our advisory group on the brazen tactics employed by threat actors lately, showcasing their intimate knowledge of the cyber insurance world. Business Sectors Under Siege Richard and Sean added to the discussion the top ten business sectors affected by ransomware, with professional services leading the pack. The impact on technology, with a payout of $830,000, stood out as well. Beyond Ransomware The conversation broadened to encompass other types of losses, such as social engineering and business email compromise. The focus on business interruption emerged as a key concern for cyber insurance claims, with the industry grappling with criminal acts versus non-criminal acts. Looking Ahead As the discussion unfolded, industry experts, including myself, expressed eagerness to anticipate the future cyber landscape. Predictions range from the industry mutating to the emergence of new players in the nation-state game. The role of artificial intelligence and innovative solutions from new vendors becomes a focal point of interest. In conclusion, the NetDiligence Cyber Claims Study 2023 Report paints a vivid picture of the challenges and transformations within the cyber insurance domain. The increasing sophistication of threat actors, coupled with evolving business strategies, sets the stage for continuous adaptation and innovation in the fight against cyber threats. As we look ahead, the resilience of businesses and the collaboration between industry stakeholders will play a pivotal role in shaping the cybersecurity landscape. I invite you to access the report and view the discussion replay for a deeper understanding of the challenges and transformations within the cyber insurance claims domain. Get NetDiligece Cyber Claims Study resources on-demand now! Download the report Watch the webinar NetDiligence’s latest Cyber Claims Study and Webinar, sponsored by Experian Data Breach, is available on-demand. This report serves as a resounding call to action, prompting businesses to ready themselves against cyber threats. Dive in to get insights and stay one step ahead of cyber adversaries.

This article was updated on February 12, 2024. The Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) space has grown massively over the last few years. But with rapid growth comes an increased risk of fraud, making "Buy Now, Pay Never" a crucial fraud threat to watch out for in 2024 and beyond. What is BNPL? BNPL, a type of short-term financing, has been around for decades in different forms. It's attractive to consumers because it offers the option to split up a specific purchase into installments rather than paying the full total upfront. The modern form of BNPL typically offers four installments, with the first payment at the time of purchase, as well as 0% APR and no hidden fees. According to an Experian survey, consumers cited managing spending (34%), convenience (31%), and avoiding interest payments (23%) as main reasons for choosing BNPL. Participating retailers generally offer BNPL at point-of-sale, making it easy for customers to opt-in and get instantly approved. The customer then makes a down payment and pays off the installments from their preferred account. BNPL is on the rise The fintech and online-payment-driven world is seeing a rise in the popularity of BNPL. According to Experian research, 3 in 4 consumers have used BNPL in 2023, with 11% using BNPL weekly to make purchases. The interest in BNPL also spans generations — 36% of Gen Z, 43% of Millennials, 32% of Gen X, and 12% of Baby Boomers have used this payment method. The risks of BNPL While BNPL is a convenient, easy way for consumers to plan for their purchases, experts warn that with lax checkout and identity verification processes it is a target for digital fraud. Experian predicts an uptick in three primary risks for BNPL providers and their customers: identity theft, first-party fraud, and synthetic identity fraud. WATCH: Fraud and Identity Challenges for Fintechs Victims of identity theft can be hit with charges from BNPL providers for products they have never purchased. First-party and synthetic identity risks will emerge as a shopper's buying power grows and the temptation to abandon repayment increases. Fraudsters may use their own or fabricated identities to make purchases with no intent to repay. This leaves the BNPL provider at the risk of unrecoverable monetary losses and can impact the business' risk tolerance, causing them to narrow their lending band and miss out on properly verified consumers. An additional risk lies with fraudsters who may leverage account takeover to gain access to a legitimate user's account and payment information to make unauthorized purchases. READ: Payment Fraud Detection and Prevention: What You Need to Know Mitigating BNPL risks Luckily, there are predictive credit, identity verification, and fraud prevention tools available to help businesses minimize the risks associated with BNPL. Paired with the right data, these tools can give businesses a comprehensive view of consumer payments, including the number of outstanding BNPL loans, total BNPL loan amounts, and BNPL payment status, as well as helping to detect and apply the relevant treatment to different types of fraud. By accurately identifying customers and assessing risk in real-time, businesses can make confident lending and fraud prevention decisions. To learn more about how Experian is enabling the protection of consumer credit scores, better risk assessments, and more inclusive lending, visit us or request a call. And keep an eye out for additional in-depth explorations of our Future of Fraud Forecast. Learn more Future of Fraud Forecast
In the fast-paced world of cybersecurity, the ability to anticipate and adapt to emerging threats is not just a competitive advantage—it’s a business imperative. As we release our 11th annual “Experian 2024 Data Breach Industry Forecast,” we invite you to embark on a journey into the future of data breaches, a journey that promises to empower data breach professionals, cyber experts, and industry leaders alike. A Glimpse into Tomorrow’s Threat Landscape Our team of experts has meticulously examined the current cybersecurity landscape to identify the trends that will shape the industry in the coming year. The “Experian 2024 Data Breach Industry Forecast” provides a roadmap for staying ahead of these challenges, arming you with the insights needed to fortify your organization’s defenses. Six Pivotal Predictions: Decoding the Future Within the report, we unveil six pivotal predictions that promise to redefine the landscape of data breaches. While we can’t reveal all the details here, we’ll offer a sneak peek to whet your appetite: Six Degrees of Separation: There’s no question that third-party data breaches this year made headlines. Delve into the intricacies of supply chain security and discover why addressing vulnerabilities in the supply chain is the next frontier in cybersecurity. Little by Little Becomes A Lot: When trying to achieve a goal, it’s said that taking small steps can lead to big results. See how hackers could apply that same rule. Not a Third Wheel: It’s widely known who the main players are globally that sponsor attacks and a new country in South Asia may join the international stage. No, not Mother Earth! Plutonium, terbium, silicon wafers — these rare earth materials present an intriguing opportunity for hackers looking to disrupt an enemy’s economy. The Scarface Effect: Like drug cartels, cybergangs are forming sophisticated organizations. Winning from the Inside: In 2024, we may see enterprising threat actors target more publicly traded companies, leveraging data extraction and their talents in plain sight as everyday investors. This is just a glimpse into the dynamic and evolving landscape detailed in our full report. Download the complete “Experian 2024 Data Breach Industry Forecast” to explore these predictions in-depth and stay ahead of the curve. Expert Analysis: Navigating Complexity with Confidence Backed by extensive research and the expertise of our seasoned analysts, the report provides more than just predictions; it offers a deep dive into the complexities of the modern cybersecurity landscape. Our experts share their insights on how these predictions will impact organizations and individuals, providing actionable intelligence that goes beyond the theoretical. Whether you’re a CISO, a Compliance Officer, or a Cyber Risk Insurer, the “Experian 2024 Data Breach Industry Forecast” equips you to navigate the challenges of tomorrow with confidence. Empowering You to Lead in Data Breach Response As you read through the report, you’ll find that our approach goes beyond merely highlighting problems; we provide solutions. Each prediction is accompanied by practical recommendations and best practices, ensuring that you not only understand the evolving landscape but also possess the tools to proactively address the challenges that lie ahead.Now, more than ever, it’s crucial to be proactive in your approach to cybersecurity. Download the full “Experian 2024 Data Breach Industry Forecast” to unlock the insights and strategies that will set you apart in the realm of data breach response. Your journey into the future starts here. The Future is Now. Are you ready to take the first step toward a more secure tomorrow? Download the report now and lead the way in data breach response. Read more

Financial institutions, merchants, and e-commerce platforms are no strangers to fraud, especially in the realm of payments. With the rise of digital currency, fraudsters are becoming more inventive, making it increasingly difficult to detect and prevent payment fraud. In this blog post, we discuss payment fraud and ways to protect your organization and your customers. What is payment fraud? Payment fraud occurs when someone uses false or stolen payment information to make a purchase or transaction. The most common types of payment fraud include: Phishing: Through emails or text messages, scammers disguise themselves as trustworthy sources to lure recipients into sharing their personal information, such as account passwords and credit card numbers. Card not present fraud: This type of fraud is one of the most challenging forms of payment fraud to detect and prevent. It occurs when a criminal uses a stolen or compromised credit card to make a purchase online, in-person, or by other means where the card is not physically present at the time of the transaction. Account takeover fraud: This type of fraud occurs when fraudsters gain unauthorized access to an individual’s account and carry out fraudulent transactions. They take over accounts by gathering and using personal or financial details to impersonate their victims. The rise of online payment fraud Online payments have become a prime destination for fraudsters as more consumers choose to store card details and make purchases digitally. As a result, consumers believe that it’s the responsibility of businesses to protect them online. If there’s a lack of trust and safety, consumers will have no problem switching providers, leading to declines in customer loyalty and monetary losses for organizations. No matter the type of payment fraud, it can result in devastating consequences for your organization and your customers. According to Experian’s 2024 U.S. Identity and Fraud Report, fraud scams and bank fraud schemes resulted in more than $458 billion in losses globally. On the consumer side, 52 million Americans had fraudulent charges on their credit or debit cards, with unauthorized purchases exceeding $5 billion. Given these findings, it’s more important than ever to implement robust online payment fraud detection and prevention measures. How can payment fraud be detected and prevented? Approaches to payment fraud detection and prevention have evolved over time. Some of the current and emerging trends include: Additional layers of security: Security measures like two-factor authentication, a CVV code, and a billing zip code can help verify a customer’s identity and make it more difficult for fraudsters to complete a transaction. Enhanced identity verification: A credit card owner verification solution, like Experian LinkTM, matches the customer identity with the credit card being presented for payment, allowing businesses to make better decisions, reduce false declines, and protect legitimate customers. Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning: AI-powered models and machine learning algorithms can identify patterns consistent with fraudulent activity in real time, resulting in proactive fraud prevention and reduced financial losses. Behavioral analytics: Using behavioral analytics to monitor user behavior, such as how they navigate a website or interact with the payment process, can help identify inconsistencies and potential fraud. Token-based authentication: Tokenization protects card information by replacing sensitive data with a unique identifier (token), which makes data breaches less damaging. How Experian can help As the payments landscape continues to evolve, so do fraudsters. Experian offers a wide range of payment fraud analytics, account takeover fraud prevention and fraud management solutions that allow you to better detect and prevent payment fraud. Your organization’s reputation and your customers’ trust shouldn’t be compromised. To learn more, visit us today. Learn more This article includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information.

It is a New Year and a new start. How about a new job? That is what thousands of employees will consider over the next month. It is also a time for employers to attract new talents, but they must be aware of different types of employment fraud. The rise of remote work has significantly increased the prevalence of remote hiring practices, from the initial job application to the onboarding process and beyond. Unfortunately, this shift has also opened the door to a surge in imposter employees, also known as ‘candidate fraud,’ posing a significant concern for organizations. How does employment identity theft happen? Instances of potential job candidates utilizing real-time deepfake video and deepfake audio, along with personally identifiable information (PII), during remote interviews to secure positions within American companies have been on the rise. The Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI) reports that fraudulent individuals often acquire PII through fake job opening posts, which enable them to gather candidate information and resumes. Surprisingly, the tools necessary for impersonation on live video calls do not require sophisticated or expensive hardware or software. Employment identity theft can occur in several ways. Here are a few examples: Inaccurate credentials: Employers may inadvertently hire someone with false or stolen credentials if they fail to conduct comprehensive background checks. When the employer discovers the deception, it can be challenging to trace the true identity of the person they unknowingly hired. Limited-term job offers: Some industries offer temporary job opportunities in distant locations. Individuals with criminal backgrounds may steal victims' identities to apply for these jobs, hoping that their crimes will go unnoticed until after the job is complete. Perpetrated by colleagues: In rare instances, jealous colleagues or coworkers can commit employment identity theft. They may steal a coworker's information during a data breach and sell it on the dark web or use the victim's credentials to frame them for fraudulent workplace actions. Preventing employment identity theft In addition to the reported cases of imposter employee fraud, it is crucial to acknowledge the potential for other scams that exploit new technologies and the prevalence of remote work. Malicious cyber attackers could secure employment using stolen credentials, enabling them to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or company systems. A proficient hacker possessing the necessary IT skills may find it relatively easy to leverage social engineering techniques during the hiring process. Consequently, the reliability of traditional methods for employee verification, such as face-to-face interactions and personal recognition, is diminishing in the face of remote work and the technological advancements that enable individuals to manipulate their appearance, voice, and identity. To mitigate risks associated with hiring imposters, it is imperative to incorporate robust measures into the recruitment process. Here are some key considerations: Establish clear policies and employment contracts: Clearly communicate your organization's policies regarding moonlighting in employment contracts, employee handbooks, or other official documents. Confidentiality and non-compete agreements: Implement confidentiality and non-compete agreements to protect your company's sensitive information and intellectual property. Monitoring: Automate employment and income verification of your employees. Provide training on cybersecurity best practices: Educate employees about cyber-attacks and identity scams, such as phishing scams, through seminars and workplace training sessions. Implement robust security measures: Use firewalls, encrypt sensitive employee information, and limit access to personal data. Minimize the number of employees who have access to this information. Thoroughly screen new employees: Verify the accuracy of Social Security numbers and other information during the hiring process. Conduct comprehensive background checks, including checking bank account information and credit reports and fight against synthetic identities. Offer identity theft protection as a benefit: Consider providing identity theft protection services to your employees as part of their benefits package. These services can detect and alert victims of potential identity theft, facilitating a fast response. The new era of remote work necessitates a fresh perspective on the hiring process. It is crucial to reevaluate HR practices and leverage AI fraud detection technologies to ensure that the individuals you hire, and employ are who they claim to be, guarding against the infiltration of imposters. Navigating employment fraud with effective solutions Employment fraud presents significant risks and challenges for employers, including conflicts of interest, reputation damage, and breaches of confidentiality. By taking the right preventative measures, you can safeguard your organization and employees. Streamlining the hiring process is essential to remain competitive. But how do you balance the need for speed and ease of use with essential ID checks? By combining the best data with our automated ID verification processes, Experian helps you protect your business and onboard new talents efficiently. Our best-in-class solutions employ device recognition, behavioral biometrics, machine learning and global fraud databases to spot and block suspicious activity before it becomes a problem. Learn more about preventing employement fraud *This article includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information.

The threat of data breach is constant in our modern, digital world. And as technology advances, so do the strategies and tactics of malicious actors seeking ways to monetize the vulnerabilities of organizations. It’s not a matter of if, but when, a data breach could impact your organization, and it is important for businesses to understand how to operate in it. What is a Data Breach? For many organizations, a data breach is arguably one of the greatest threats to prevent. What is a data breach? Imagine your organization as a fortress, safeguarding a treasure trove of sensitive information—customer data, financial records, proprietary algorithms. A data breach is the unwelcome intrusion into this fortress, where unauthorized individuals gain access to confidential information, often with malicious intent. This can encompass many types of data, including personal identification information (PII), financial data, and intellectual property. Classifications of breaches can vary from intentional cyberattacks to inadvertent exposure due to system vulnerabilities or human error. To grasp the gravity of data breaches, Businesses face tangible consequences when their defenses are breached, and there are no signs of it slowing down. The frequency and severity of data breaches are alarming. According to recent studies¹, the healthcare sector experienced a 55% increase in data breaches in 2022. No business is immune to the evolving threat landscape especially companies that capture customer data and are also inherently the stewards of this data. Understanding the landscape of data breaches will help you better fortify your business against a breach. In the next sections, we’ll explore the causes, impacts, post-breach response strategies, and preventative tactics businesses can employ to safeguard their data. Causes of Data Breaches Human error Even the most well-intentioned employees can become the weak link in an organization’s security chain. According to the “2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report,” 74% of data breaches involve a human element². Investing in comprehensive training programs is essential to foster a culture of cybersecurity awareness and mitigate the risk of employee-related mistakes. Cybersecurity vulnerabilities The digital landscape is rife with potential vulnerabilities, and cybercriminals are adept at exploiting them. Regular cybersecurity assessments, prompt system updates, and the implementation of robust security protocols are recommended proactive measures to fortify against breaches that capitalize on system vulnerabilities. Insider threats Data breaches can originate from within, whether through disgruntled employees with malicious intent or well-meaning staff who inadvertently compromise security. Gurucul’s “2023 Insider Threat Report” highlights that 60% of organizations experienced insider-related incidents in the past year³. Establishing stringent access controls, closely monitoring user activities, and implementing employee education programs are vital steps to mitigate the risks associated with insider threats. Weak and Stolen Passwords Weak and stolen passwords stand as one of the most common gateways for data breaches. Cybercriminals exploit individuals who use easily guessable passwords or recycle them across multiple platforms. This creates a vulnerability that can be easily exploited through automated attacks. Ensuring robust password policies, employing multi-factor authentication, and regularly updating credentials are necessary measures to thwart these breaches and safeguard sensitive information. Malware The insidious world of malware is a persistent threat to data security. Malicious software, often disguised as innocuous files or links, infiltrates systems, and wreak havoc by compromising data integrity and confidentiality. Malware can then swiftly spread, leading to unauthorized access and data exfiltration. Regularly updating antivirus software, conducting thorough system scans, and educating employees about the dangers of clicking on suspicious links are pivotal defenses against malware-driven breaches. Social Engineering Social engineering has emerged as a cunning and effective tactic in data breaches, such as manipulating individuals to divulge confidential information willingly. Whether through phishing emails, deceptive phone calls, or impersonation, cybercriminals exploit human trust to gain unauthorized access. Raising awareness among employees about the dangers of social engineering, implementing rigorous verification processes, and fostering a culture of skepticism can fortify an organization’s defenses against these subtle yet potent attacks. Physical Attacks While the digital realm often takes center stage, physical attacks on data infrastructure remain a tangible and underestimated risk. Breaches can occur through unauthorized access to servers, theft of physical storage devices, or tampering with network equipment. Implementing stringent access controls, employing surveillance systems, and securing physical infrastructure are crucial steps to mitigate the threat of data breaches stemming from physical incursions. Building digital and physical protective measures can help with your defense against the multifaceted landscape of data breaches. Impacts on Businesses Financial repercussions Data breaches are costly to businesses with immediate and enduring consequences. The “Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023” by IBM reported that the average cost of a data breach was $4.45 million per organization⁴. Long-term financial implications include loss of customers, diminished revenue streams, and increased cybersecurity investments to rebuild trust and fortify defenses against future breaches. Reputational damage The fallout from a data breach extends beyond the balance sheet, leaving an indelible mark on a business’s reputation. According to a 2023 survey by Vercara, 66% of U.S. consumers would not trust a company that falls victim to a data breach with their data. Rebuilding trust with transparent communication, swift remediation, and proactive measures to prevent future breaches is essential, demonstrating a commitment to safeguarding sensitive information. Operational disruptions Data breaches causes disruptions in the operations of daily business activities. It takes an average of 73 days to contain a cyber-attack according to the Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 from IBM⁴. Swift recovery requires a meticulous balance between addressing the breach’s immediate impact and resuming normal operations to minimize further operational strain. Legal and regulatory implications The legal aftermath of a data breach involves navigating a complex landscape of regulations and compliance standards. In the United States, data breaches may trigger legal consequences under various state laws. For instance, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) allows for fines ranging from $100 to $750 per consumer per incident⁵. Ensuring adherence to data protection laws, promptly reporting breaches to regulatory authorities, and implementing robust security measures become top priorities in avoiding the legal quagmire that often follows a data breach. Notable data breaches Yahoo! (2014): The personal information of 3 billion people was exposed, including names, birth dates, passwords, and phone numbers. Cause: It is believed that the hack originated through a phishing email sent to a Yahoo! employee. Through this phishing email, it’s believed the hackers were able to access user databases and tools.⁶ Cost: $117.5 million in settlements and $350 million off its sale price to Verizon⁷ Marriott International (2018): Information of approximately 500 million guests was compromised, including names, contact details, passport numbers, and travel details. Cause: A cyber-espionage campaign linked to a state-sponsored actor. Attackers gained access to Marriott’s Starwood guest reservation database due to vulnerabilities in the system.⁸ Cost: Over $100 million for remediation efforts and regulatory fines.⁹ Capital One (2019): 106 million customers’ personal information, including credit card applications and Social Security numbers, was exposed. Cause: A misconfigured web application firewall that allowed a hacker to exploit a server-side request forgery vulnerability, leading to unauthorized access and the theft of sensitive customer data.¹⁰ Cost: Estimated between $100 million and $150 million in 2019 alone.¹¹ SolarWinds (2020): Hackers compromised the software supply chain, affecting numerous government agencies and major corporations globally. Cause: The SolarWinds breach was a sophisticated supply chain attack where malicious actors compromised the software update process, injecting malware into software updates distributed by SolarWinds, allowing them access to numerous government and corporate networks.¹² Cost: At least $18 million¹³ JBS USA (2021): The ransomware attack on the world’s largest meat processor disrupted operations and impacted the company’s IT systems. Cause: A ransomware attack, where cybercriminals exploited vulnerabilities in the company’s IT systems to encrypt data and demand a ransom for its release, causing significant disruptions to operations.¹⁴ Cost: $11 million ransom paid to hackers from JBS to restore their IT systems. Post-breach response Assessment and Damage Control Immediate Action Steps In the event of a data breach, the immediacy of response becomes one factor in determining the outcome. Swift and decisive actions during the initial moments can be instrumental in preventing the situation from escalating. The primary focus at this stage is isolating the affected systems, swiftly disconnecting compromised servers and devices from the network. This can help stop unauthorized access and establishes the foundation for a more concentrated and effective response. Alerting the incident response team, IT personnel, and relevant stakeholders promptly is also worth considering to help gain control over the situation. Forensic Analysis Understanding the who, what, and how of an incident is also an important step following a breach. In this context, involving forensic experts in a meticulous analysis is prudent. These professionals specialize in unraveling the intricacies of the breach, identifying entry points, and tracing the movements of attackers within your systems. The significance of forensic analysis extends beyond mere identification; it serves as the groundwork for prevention. Through a comprehensive study of the employed attack vectors and techniques, organizations can enhance their cybersecurity infrastructure. This process of gathering critical information about the breach contributes to the ability to preempt similar incidents, fostering a more resilient stance against evolving cyber threats. Communication Strategy Internal Communication Effective internal communication plays a pivotal role in building a resilient response framework. In the early stages of a crisis, employees emerge as the initial line of defense. Clearly conveying the severity of the situation provides them with a comprehensive understanding of the impact and the organization’s devised response plan. This also empowers the workforce, fostering a sense of unity within the organization and help the organization navigate challenges ahead cohesively, reinforcing its resilience in the face of adversity. External Communication External communication holds equal importance, reaching beyond the organization to customers, partners, and stakeholders. It’s essential to recognize the significance of constructing messages with transparency, honesty, and a proactive stance. Silence or ambiguity can intensify the repercussions, so prioritizing openness becomes foundational for rebuilding trust. Being timely and forthright in sharing information about the breach and the steps taken to rectify the situation is generally a good strategy when engaging with partners and stakeholders. This approach not only informs but can also mold the perception of the organization’s dedication to security and integrity following the aftermath of a breach with a strategic and forward-thinking mindset. Legal and Regulatory Compliance Notification Requirements Within the regulatory framework, a prompt response is an important post-breach step for organizations. It may first involve comprehensively detailing the legal obligations surrounding breach notifications to both regulatory authorities and affected individuals. It’s essential to recognize the variability in requirements across different regions and industries, underscoring the importance of remaining well-informed about these specific nuances. Timeliness of notifications is also factor for organizations to consider. Numerous jurisdictions impose substantial fines for delays in reporting, making it essential for organizations to adhere to strict timelines. Transparency holds equal weight, necessitating clear communication about the extent of the breach, the nature of compromised information, and the specific measures being implemented to address the situation. This approach can help in being compliant with legal standards and plays a vital role in fostering trust among those directly impacted by the breach. Legal Counsel Engagement Organizations generally seek the support of legal counsel to help navigate the intricate legal aftermath of a data breach. Legal experts can help an organization through potential lawsuits and regulatory fines. Engaging legal experts early allows their insights to guide the overall strategy, shaping everything from the communication plan to the recovery efforts. With early legal counsel support, the organization can be proactive in addressing legal challenges, potentially mitigating the severity of consequences that may arise. Recovery and Remediation IT System Restoration The intricacies of IT system restoration mirror the reconstruction of a fortress following an intrusion. Restoring affected IT systems to normal functionality involves comprehensive measures such as thorough system checks, vulnerability assessments, and the eradication of any residual traces left by a breach. Additionally, organizations generally look to enhance security measures during the recovery phase. Simply reverting to the pre-breach state is not enough; instead, the recovery process serves as an opportunity to accept vulnerabilities in old systems and bolster defenses. This entails updating and patching systems, reassessing access controls, and contemplating the incorporation of advanced threat detection tools. Such measures collectively work to minimize the risk of a recurrence and contribute to an overall fortified cybersecurity posture. Prevention Strategies Best practices for securing sensitive data Securing sensitive data is important in the age of relentless cyber threats. Employing encryption protocols, conducting regular security audits, and limiting access privileges are foundational best practices. These proactive measures help create a robust defense, forming an intricate web that shields critical information from potential breaches. Employee training programs to mitigate human error Human error remains a significant contributor to data breaches. Implementing comprehensive employee training programs can be helpful in cultivating a security-conscious workforce and mitigating human error-caused vulnerabilities. From recognizing phishing attempts to practicing proper password hygiene, a well-informed staff acts as the first line of defense and can significantly reduce the likelihood of unintentional security lapses. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures The cornerstone of any data breach prevention strategy is the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures. This includes advanced intrusion detection systems, firewalls, and regular software updates. Proactively addressing vulnerabilities and staying abreast of the latest cybersecurity advancements help fortify an organization’s digital perimeter, creating an environment that is inherently resistant to malicious infiltrations. Staying abreast of emerging trends Staying ahead of data breach threats requires a keen awareness of emerging trends. From sophisticated phishing techniques to novel forms of malware, businesses should continuously adapt their cybersecurity strategies against evolving tactics employed by cybercriminals. The dynamic nature of the cybersecurity landscape demands constant innovation. Adopting cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence for threat detection and investing in predictive analytics allows businesses to stay one step ahead, proactively identifying and neutralizing potential threats before they escalate. Collaboration and information-sharing within industries In the face of evolving cyber threats, collaboration is a powerful defense. Establishing networks for information-sharing within industries enables businesses to benefit from collective intelligence. By sharing best practices and threat intelligence, organizations can collectively strengthen their defenses against the ever-changing data breach landscape. Takeaway Data breaches are a persistent threat for all businesses capturing and storing personal identifiable information. Such businesses are inherently the stewards of this data and must protect that data to avoid bad actors gaining access for malicious intent. Knowing what a data breach is just the first step of protecting that data, and it is key to take action. From securing sensitive data to fostering a cybersecurity-aware workforce, businesses must not merely react to the escalating threat of data breaches but proactively strive to create an impenetrable shield around their valuable information. Visit our website for more information about our offerings and how Experian can help you prepare and respond to data breaches. ¹Hippa Journal, 55% of Healthcare Organizations Suffered a Third-Party Data Breach in the Past Year [2022]²Verizon, 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report³Gurucul, 2023 Insider Threat Report⁴IBM, Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023⁵Office of the Attorney General, California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)⁶CSO, INside the Russian hack of Yahoo: How they did it⁷BPB Online, Yahoo Data Breach: What Actually Happened?⁸CSO, Marriott data breach FAQ: How did it happen and what was the impact?⁹Cybersecurity Dive, Marriott finds financial reprieve in reduced GDPR penalty¹⁰Investopedia, Capital One Data Breach Impacts 106 Million Customers¹¹CNET, Capital One $190 Million Data Breach Settlement: Today Is the Last Day to Claim Money¹²Tech Target, SolarWinds hack explained: Everything you need to know¹³Reuters, SolarWinds says dealing with hack fallout cost at least $18 million¹⁴BBC, Meat giant JBS pays $11m in ransom to resolve cyber-attack

The online gaming industry has experienced tremendous growth in recent years, with millions of players engaging in immersive virtual worlds and competitive gameplay. Unfortunately, this surge in popularity has also sparked an increase in online gaming fraud. Unscrupulous individuals have sought to exploit the industry through fraudulent activities, leading to financial losses and reputational damage for gaming vendors.According to a recent study conducted by Lloyds Bank, children are spending more time playing online games than ever before – over five million children between the ages of three and 15 are now regularly playing games online, up from approximately 4.6 million in 2019.Fraudsters, always ready to take advantage of opportunities presented by new trends, are now increasingly targeting this rising demographic. Gaming vendors have a responsibility to shield minors from fraud in online gaming by implementing robust safety measures, educating young players and their parents, and actively monitoring and addressing fraudulent activities. A vulnerable target That same study from Lloyds revealed that over a third (36%) of parents are concerned about the possibility of their children falling victim to gaming fraud and losing money. In today's tech-savvy world, the ease of payment authorization has only exacerbated these concerns. All it takes for a child to make a payment is to key in their parents' online store username and password. It is a practice fraught with danger. Parents can only do so much to safeguard their children while gaming, and despite their best efforts, there will always remain a lingering possibility of encountering scammers. Gaming vendors should establish robust age verification processes during account creation to ensure that minors are not exposed to age-inappropriate content. Additionally, they should incorporate comprehensive parental controls that allow parents to regulate their children's online activities, including chat limitations, spending controls, and access to certain features.But contrary to common assumptions, the gaming population is not restricted to teenagers or young adults. With an average age of 35, gamers have significant purchasing power and actively participate in the gaming ecosystem. They spend an average of over six hours per week gaming, dedicating nearly an hour each day to their preferred gaming experiences. This engagement is spread across all age groups and financial profiles, making the gaming community a vast market to attract cybercrime. Types of fraud in online gaming In 2022, the revenue from the worldwide gaming market was estimated at almost 347 billion U.S. dollars, with the mobile gaming market generating an estimated 248 billion U.S. dollars of the total. The gaming market is constantly evolving, and technological advancements are opening new possibilities for game developers to create more immersive and engaging experiences.But alarming reports indicate that scammers have honed in on the younger demographic of gamers, leveraging their innocence to exploit their finances and identities. Identity theft (67%) and hacking (61%) rank as the two most prevalent forms of fraud experienced by young gamers, according to the Lloyds Bank study. Here are some different types of online gaming fraud: Account hacking: Hackers employ various techniques like phishing, keylogging, and credential stuffing to gain unauthorized access to players' accounts. Once compromised, accounts could be used for fraudulent activities, including unauthorized in-game transactions or selling virtual assets for real money. Chargeback fraud: This occurs when players make legitimate purchases within a game using real money and then issue chargebacks, falsely claiming that the transaction was unauthorized or fraudulent. This results in financial losses for gaming vendors as they lose the revenue and virtual goods/services provided to the player. Virtual asset fraud: Virtual assets, such as in-game currency, items, or characters, hold economic value. Fraudsters engage in scams involving fake virtual asset transactions or market manipulation, exploiting players' desires to acquire rare or high-value items. Match-fixing and cheating: Competitive gaming is at the heart of many online games. Fraudsters seek to manipulate matches, exploit glitches, or use cheat software to gain an unfair advantage over others. This undermines the integrity of the gaming experience and discourages fair competition. The game changer for online platforms: fraud prevention strategies Given the anticipated growth of these threats in the foreseeable future, it is imperative that online platforms prioritize the protection of young gamers and their parents. In line with the enhanced safeguards and anti-fraud initiatives observed in banks and financial institutions, it is high time for game companies to elevate their security and consumer protection measures by adopting the following guidelines: Implement strong account security measures: Encourage players to create unique, complex passwords, and consider implementing multifactor authentication solutions. Regularly educate players about common hacking techniques and promote safe browsing habits to prevent phishing attempts. Utilize fraud detection systems: Invest in advanced fraud detection tools that employ machine learning algorithms and biometrics templates to identify suspicious activities and patterns. These systems can flag potentially fraudulent transactions, allowing you to take appropriate measures promptly. Monitor and analyze user behavior: Keep an eye on players' activities and digital identity, such as unusual login patterns, high-value transactions, or frequent chargebacks. Analyze gameplay data, interactions, and purchasing behavior to identify patterns indicative of fraud or cheating. Secure payment processing systems: Choose reputable payment gateways that prioritize security measures. Employ tokenization and encryption technologies to safeguard players' payment information during transactions. Regularly test and update your payment system's security infrastructure. Raise player awareness: Educate your player community about common fraud techniques and the importance of securing their accounts with identity authentication. Share security tips through newsletters, blog posts, and in-game messaging. Foster a culture of vigilance and encourage players to report any suspicious activities. Foster fair gameplay and zero tolerance policy: Implement robust anti-cheat measures and regularly update your game to address vulnerabilities and exploits. Promote fair competition and enforce a zero-tolerance policy against cheating, match-fixing, and other forms of unfair gameplay. Leveling-up Ultimately, the ability to protect players online could be the ultimate gamechanger for gaming platforms. By embracing identity verification mechanisms that rely on secure and privacy-centric facial recognition, online fraud and identity theft can be significantly curtailed. Moreover, the verification and onboarding processes can be streamlined, simplifying the user experience further. Just as bringing top-tier games on board is crucial, game platforms must ensure their customers engage in a secure gaming environment. Streamlining the onboarding and sign-in process is essential to remain competitive. But how do you balance the need for speed and ease of use with essential ID checks? By combining the best data with our automated ID verification checks, Experian helps you safeguard your business and onboard customers efficiently. Using passive, invisible checks when customers sign into their accounts helps to keep fraudsters at bay and protects legitimate players without the need for irritating security challenges. Experian’s best-in-class solutions employ device recognition, behavioral biometrics, machine learning and global fraud databases to spot and block suspicious activity before it becomes a problem. Learn more *This article leverages/includes content created by an AI language model and is intended to provide general information.

Financial institutions are under increasing pressure to grow deposits and onboard more demand deposit accounts (DDA). But as demand increases, so do fraud attempts from scammers. While a robust mitigation effort is needed to stop fraud, this same effort can also drive away potential clients. In fact, 37 percent of U.S. adults said that they abandoned opening an account online due to experiencing friction. This leaves institutions in a unique quandary: how do they stop DDA fraud without scaring away potential clients? The answer lies in utilizing robust, machine learning tools that can help you navigate fraud attempts without increasing onboarding friction. Chris Ryan, Go to Market Lead for Experian Identity and Fraud, shares his thoughts on demand deposit account fraud and which decisioning tools can best combat it. Q: What is a demand deposit account and how is it used? "Demand deposit is just your basic checking account," Ryan explains." The funds are deposited and held by an institution, which enables you to spend those assets or resources, whether it be through checks, debit cards, person-to-person, Automated Clearing House (ACH) — all the things we do every day as consumers to manage our operating budget." Q: What is demand deposit account fraud? "There are two different ways that demand deposit account fraud works," Ryan says. "One is with existing account holders, and the other is with the account opening process.” When fraud affects existing account holders, it typically involves tricking an account holder into sending money to a scammer or using fraudulent actions, like phishing emails or credit card skimmers, to gain access to their accounts. There is also a resurgence in fraud involving duplication, theft and forgery of paper checks, Ryan explains. Fraud impacting the account opening process occurs when scammers originate new DDAs. This can work in a variety of ways, such as these three examples: A scammer steals your identity and opens an account at the same bank where you have a home equity loan. They link their DDA to your line of credit, transferring your money into their new account and withdrawing the funds. A scammer uses a synthetic identity (SID) to open a fraudulent DDA. They will then use this new DDA to open more lucrative accounts that the institution cross-sells to them. A scammer uses a stolen or SID to open “mule” accounts to receive funds they dupe consumers into sending through fake relationship schemes, bogus merchandise sales and dozens of similar scams. While both types of fraud need to be dealt with, account opening fraud can have especially large repercussions for lenders or financial institutions. Q: What are the consequences of DDA fraud for organizations? "Fraud hurts in a number of ways," Ryan explains. "There are direct losses, which is the money that criminals take from our financial system. Under most circumstances, the financial institution replaces the money, so the consumer doesn’t absorb the loss, but the money is still gone. That takes money away from lending, community engagement and other investments we want banks to make. The direct losses are what most people focus on." But there are even more repercussions for institutions beyond losing money, and this can include the attempts that institutions put into place to stop the fraud. "Preventing fraud requires some friction for the end consumer," Ryan says. "The volume of fraudulent attempts is overwhelmingly large in the DDA space. This forces institutions to apply more friction. The friction is costly, and it often drives would-be-customers away. The results include high costs for the institutions and low booking rates. At the same time, institutions are hungry for deposit money right now. So, it's kind of a perfect storm." Q: What is the impact of DDA fraud on customer experience? Experian’s 2023 Identity and Fraud Report revealed that up to 37 percent of U.S. adults in the survey had abandoned a new account entirely in the previous six months because of the friction they encountered during onboarding. And 51 percent reported considering abandoning the process because of problems they encountered. Unfortunately, fraud mitigation and deposit fraud detection efforts can end up driving customers away. "People can be impatient," Ryan says, "and in the online world, a competing product is a mouse-click away. So, while it is tempting to ask new applicants for more information, or further proof of identity, that conflicts with their need for convenience and can impact their experience.” Companies looking for cheap and fast mitigation can end up impeding customers trying to onboard to sweep out the bad actors, Ryan explains. "How do you get the bad people without interrupting the good people?" Ryan asks. "That's the million-dollar question." Q: What are some other problems with how organizations traditionally combat DDA fraud? Unfortunately, traditional attempts to combat DDA fraud are inefficient due to the fragmentation of technology. Ryan says this was revealed by Liminal, an industry analyst think tank. "Nearly half of institutions use four-or-more-point solutions to manage identity and fraud-related risk," Ryan explains. "But all of those point solutions were meant to work on their own. They weren't developed to work together. So, there's a lot of overlap. And in the case of fraud, there's a high likelihood that the multiple solutions are going to find the same fraud. So, you create a huge inefficiency." To solve this challenge, institutions need to shift to integrated identity platforms, such as Experian CrossCore®. Q: How is Experian trying to change the way organizations approach DDA fraud? Experian is pushing a paradigm shift for institutions that will increase fraud detection efficiency and accuracy, without sacrificing customer experience. "Organizations need to start thinking of identity through a different lens," Ryan says. Experian has developed an identity graph that aggregates consumer information in a manner that reaches far beyond what an institution can create on its own. "Experian is able to bring the entire breadth of every identity presentation we see into an identity graph," Ryan says. "It's a cross-industry view of identity behavior." This is important because people who commit fraud manipulate data, and those manipulations can get lost in a busy marketplace. For example, Ryan explains, if you're newly married, you may have recently presented your identity using two different surnames: one under your maiden name and one under your married name. Traditional data sources may show that your identity was presented twice, but they won’t accurately reflect the underlying details; like the fact that different surnames were used. The same holds true for thousands of other details seen at each presentation but not captured in a way that enables changes over time to be visible, such as information related to IP addresses, email accounts, online devices, or phone numbers. "Our identity graph is unlocking the details behind those identity presentations," Ryan says. "This way, when a customer comes to us with a DDA application, we can say, 'That's Chris's identity, and he's consistently presenting the same information, and all that underlying data remains very stable.'" This identity graph, part of Experian's suite of fraud management solutions — also connects unique identity details to known instances of fraud, helping catch fraudulent attempts much faster than traditional methods. "Let's say you and your spouse share an address, phone numbers, all the identity details that married couples typically share," Ryan explains. "If an identity thief steals your identity and uses it along with a brand-new email and IP address not associated with your spouse, that might be concerning. However, perhaps you started a new job, and the email/IP data is legitimate. Or maybe it’s a personal email using a risky internet service provider that shares a format commonly used by a known ring of identity thieves. Traditional data might flag the email and IP information as new, but our identity graph would go several layers deeper to confirm the possible risks that the new information brings. Q: Why is this approach superior to traditional methods of fraud detection? "Historically, organizations were interested in whether an identity was real,” Ryan says. "The next question was if the provided data (I.e., addresses, date of birth, Social Security numbers, etc.) have been historically associated with the identity. Last, the question would be whether there’s known risk associated with any of the identity components.” The identity graph turns that approach upside down. "The identity graph allows us to pull in insights from past identity presentations, " Ryan says. "Maybe the current presentation doesn’t include a phone number. Our identity graph should still recognize previously provided phone numbers and the risks associated with them. Instead of looking at identity as a small handful of pieces of data that were given at the time of the presentation, we use the data given to us to get to the identity graph and see the whole picture." Q: How are businesses applying this new paradigm? The identity graph is part of Experian's Ascend Fraud Platform™ and a full suite of fraud management solutions. Experian's approach allows companies to clean out fraud that already occurred and stop new fraudulent actors before they're onboarded. "Ideally, you want to start with cleaning up the house, and then figure out how to protect the front door," Ryan says. In other words, institutions can start by applying this view to recently opened accounts to identify problematic identities that they missed. The next step would be to bring these insights into the new account onboarding process. Q: Is this new fraud platform accessible to both small and large businesses? The Ascend Fraud Platform will support several use cases that will bring value to a broad range of businesses, Ryan explains. It can not only enable Experian experts to build and deliver better tools but can enable self-serve analytical development too. "Larger organizations that have robust, internal data science capabilities will find that it’s an ideal environment for them to work in," Ryan says. "They can add their own internal data assets to ours, and then have a better place to develop analytics. Today, organizations spend months assembling data to develop analytics internally. Our Ascend Fraud Platform will reduce the timeline of the data assembly and analytical development process to weeks, and speed to market is critical when confronting continually changing fraud threats. "But for customers who have less robust analytical teams, we're able to do that on their behalf and bring solutions out to the marketplace for them," Ryan explains. Q: What type of return on investment (ROI) are businesses experiencing? "Some customers recover their investment in days," Ryan says. "Part of this is from mitigating fraud risks among recently opened accounts that slipped through existing defenses.” "In addition to reducing losses, institutions we're working with are also seeing potentially millions of dollars a month in additional bookings, as well as significant cost savings in their account opening processes," Ryan says. "We're able to help clients go back and audit the people who had fallen out of their process, to figure out how to fine-tune their tools to keep those people in," Ryan says. “By reducing risks among existing accounts, better protecting the front door against future fraud, and growing more efficiently, we’re helping clients Q: What are Experian's plans for this service? "We're working with top-tier financial institutions on the do-it-yourself techniques," Ryan says. "In parallel, we're launching our first offerings that are created for the broader marketplace. That will start with the portfolio review capability, along with making the most predictive attributes available through our integrated identity resolution platform. And while the Ascend Fraud Platform has a strong use case for DDA fraud, its uses extend beyond that to small business lending and other products. In fact, Experian offers an entire suite of fraud management solutions to help keep your DDA accounts secure and your customers happy. Experian can help optimize your DDA fraud detection Experian is revolutionizing the approach to combating DDA fraud, helping institutions create a faster onboarding process that retains more customers, while also stopping more bad actors from gaining access. It's a win-win for everyone. Experian's full suite of fraud management solutions can optimize your business's DDA fraud detection, from scrubbing your current portfolio to gatekeeping bad actors before they're onboarded. Learn more Speak with a specialist About our expert: Chris Ryan has over 20 years of experience in fraud prevention and uses this knowledge to identify the most critical fraud issues facing individuals and businesses in North America, and he guides Experian’s application of technology to mitigate fraud risk.