Tag: credit scores

Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming industries worldwide, and financial services are no exception. One of the most impactful applications is AI credit scoring, a modern approach that uses advanced algorithms to assess consumer creditworthiness with precision, fairness and efficiency.AI credit scoring addresses traditional limitations by introducing more advanced, data-driven techniques. Instead of relying solely on static, historical data points, AI models can process vast amounts of diverse information in real time, spotting patterns and predicting behaviors more accurately. How AI is being used in credit scoring Traditional credit scoring has long relied on structured data such as payment history, credit utilization, and length of credit history. While effective, these models can be limited in capturing a holistic view of an individual’s financial behavior. AI credit scoring expands this view by: Leveraging alternative data: AI models can analyze non-traditional data sources such as rental payments, utility bills, and even digital transaction histories, providing a broader perspective for those with limited credit history. Real-time analysis: Machine learning enables lenders to evaluate applicants faster by instantly processing large amounts of data. Pattern recognition: AI systems identify subtle behavioral and financial patterns that may indicate creditworthiness beyond what traditional models can detect. Continuous learning: Unlike static scoring systems, AI-based models may improve over time as they ingest more data and refine their predictions. Using these methods, AI credit score systems create a richer, more nuanced picture of a borrower’s financial health, making lending more inclusive and predictive. The benefits of AI credit scoring The adoption of AI in credit scoring has created significant benefits for lenders, regulators, and consumers alike: Improved accuracy: AI models draw on a broader range of data, reducing reliance on limited or outdated metrics. Financial inclusion: Millions of consumers globally remain outside the traditional credit system. AI credit scoring allows lenders to evaluate previously overlooked applicants, such as young adults, recent immigrants, or gig economy workers. By factoring in alternative data, lenders can serve historically underserved individuals. Faster and more efficient processes: AI can automate large portions of the decision-making workflow, significantly reducing the time it takes to approve applications. This means faster access to credit for consumers and reduced operational costs for lenders. Fraud detection and risk mitigation: Advanced machine learning models can detect anomalies in borrower behavior that may indicate fraud or identity theft. By flagging these risks earlier, lenders protect both themselves and their customers. Enhanced customer experience: AI-driven insights help lenders design more personalized products and repayment plans. Institutions can better understand customer needs and financial behaviors by offering tailored solutions that improve loyalty and trust. Challenges of AI in credit scoring While the promise of AI is transformative, it also brings new challenges that financial institutions must navigate carefully. Bias and fairness: AI models may inadvertently replicate biases in training data, raising concerns about fairness and equity. Transparency: Complex algorithms can be challenging to explain to regulators, lenders, and consumers, creating a "black box" perception. Data privacy: Using alternative data for credit scoring requires strict compliance with privacy regulations and consumer consent. Regulatory alignment: As AI evolves, credit scoring must comply with evolving financial and consumer protection laws. Why partner with us At Experian®, we understand that trust, accuracy, and transparency are essential in the financial ecosystem. By combining decades of expertise in credit data with AI solutions, we deliver AI credit score solutions that empower lenders to make smarter, fairer, and faster decisions. With us as your trusted partner, you can embrace AI-powered credit solutions confidently and responsibly. Global data expertise: We leverage one of the world’s most comprehensive credit databases, ensuring high-quality insights. Responsible AI: Our solutions are built with fairness, transparency, and regulatory compliance at the forefront. Proven results: We partner with financial institutions worldwide to unlock opportunities for lenders and consumers through AI-driven insights. Commitment to inclusion: Our AI credit scoring tools are designed to expand financial access for underserved communities. The rise of AI credit scoring marks a new era in financial services, where accuracy, speed, and inclusivity converge to benefit lenders and consumers alike. While challenges remain, responsible use of AI ensures that credit scoring becomes more transparent, fair, and effective. Learn more

Conventional credit scoring systems are based on models developed over six decades. As consumer behavior evolves, it's important to seek newer, fresher sources of data to assess creditworthiness. Because the data used by conventional credit scoring models does not provide the full picture of a consumer's financial health, a large population segment of the United States is excluded from accessing credit.With changing times and new technology, forward-thinking financial institutions are using alternative data1 to gain a more holistic consumer view. A move toward inclusive finance, including incorporating alternative data in credit scoring models, is a crucial step towards promoting financial inclusion and helping millions of consumers achieve their financial and personal goals. More importantly, it provides the insight needed for lender confidence, which can help fuel business growth. Understanding limitations of the conventional scoring system Credit scores can be obtained from any one of the major credit bureaus based on information found in a consumer's credit report and are incorporated into a lender's credit-decisioning process. While there are various credit scoring models based on lender preference that could yield slightly different scores, all traditional scores are comprised of credit characteristics within these categories: payment history, credit mix, credit history length, amounts owed and new credit account inquires. Lenders use past credit performance to predict whether extending credit is a risk, posing a major challenge for credit invisible and thin-file consumers and leaving millions at a disadvantage. This dilemma also limits business growth for lenders. Consumers who are unable to access mainstream credit often turn to the alternative financial services (AFS) industry, a $140 billion market that continues to grow by 7-10 percent each year.2 The AFS industry offers consumers additional products, like payday loans, cash advances, short-term installment loans, and rent-to-own loans, none of which are included in a traditional credit file. With alternative credit data, lenders can obtain a more holistic view of creditworthiness and risk, helping to enhance inclusive lending by broadening their pool of potential loan candidates. Why conventional scoring models simply aren't enough Because of the criteria used to assess creditworthiness, conventional credit scoring models do not accurately capture an individual's financial behavior or health. Indeed, many people demonstrate financial responsibility in other legitimate ways that are not reported to the major credit bureaus.In contrast, non-traditional data considers a consumer's everyday financial behavior to provide a more accurate score for lenders. It can include a range of indicators, such as: Bill payments: Consistent payment history on typical household bills (which may have been paid from a debit account). Bank account data: Shows average balance and withdrawal activity and recurring payroll deposits (indicating that a consumer is employed and receives a regular income). Rental data: Indicates a consumer's long-term stability in making regular, on-time monthly rent payments. Registered licenses: Registered licenses or membership with a skilled trade or profession can indicate the likelihood to generate income. Including this type of data can benefit both lenders and applicants. According to an Experian report, by adding alternative credit data to a near-prime population, lenders could see an increase in approvals for consumers historically being left behind. When Clear Early Risk Score™ is paired with the VantageScore® credit score, approvals climb to 16 percent of the population inside the same risk criteria, representing a 60 percent lift in credit approvals for near-prime consumers.2 The pool of people from whom this type of alternative data can reliably be collected is growing, with 70 percent of consumers willing to provide additional financial information to a lender if it increases their chance for approval or improves their interest rate for a mortgage or car loan.3 Plenty of available yet untapped data exists that can add value to a consumer's profile and lead to greater inclusive lending. For example, 95 percent of Americans own a cell phone and about two-thirds of households headed by young adults are being rented. Reporting on this data could potentially "thicken" a credit file and provide deeper insight into a consumer's credit behavior.3Indeed, turning to non-traditional data can expand the credit universe and lead to more inclusive credit scoring models, especially by leveraging existing technology and financial inclusion solutions. Research shows that with Lift Premium™, virtually all of the 21 million conventionally unscorable consumers would become scoreable, and over 1 million of them would have scores in the near-prime range or better. Of these, 1.7 million would be Black American and Hispanic/Latino people.3 For lenders, these numbers reveal potential opportunities to grow their businesses. Of the 255 million adults in the U.S., 19 percent of credit eligible adults are left out of mainstream scoring systems. 28 million are considered credit invisible – meaning they have no credit history (11%). 21 million are considered unscorable – have partial credit history but not enough to generate a score using conventional models (8%). Of the remaining credit eligible adults, 57 million were considered subprime (22%). 106 million U.S. adults can't get mainstream credit rates (42%). Adopting inclusive finance lending practices is not only the right thing to do but also provides financial institutions with the chance to reach untapped markets, grow their business and promote a healthier economy. Financial inclusion is not a destination, but an ever-evolving journey. Don't miss out on this critical opportunity to join the movement. Learn more about our financial inclusion tools to help enhance your inclusive lending approach. 1"Alternative Credit Data,” refers to the use of alternative data and its appropriate use in consumer credit lending decisions, as regulated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act. Hence, the term “Expanded FCRA Data” may also apply in this instance and both can be used interchangeably.2Experian: 2020 State of Alternative Credit Data.3Oliver Wyman white paper, “Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit," January 12, 2022.

These days, the call for financial inclusion is being answered by a disruptive force of new financial products and services. From fintech to storied institutional players, we're seeing a variety of offerings that are increasingly accessible and affordable for consumers. It's a step in the right direction. And beyond the moral imperative, companies that meet the call are finding that financial inclusion can be a source of business growth and a necessity for staying relevant in a competitive marketplace. A diaspora of credit-invisible consumers To start, let's put the problem in context. A 2022 Oliver Wyman report found about 19 percent of the adult population is either credit invisible (has no credit file) or unscoreable (not enough credit information to be scoreable by conventional credit scoring models). But some communities are disproportionately impacted by this reality. Specifically, the report found: Black Americans are 1.8 times more likely to be credit invisible or unscoreable than white Americans. Recent immigrants may have trouble accessing credit in the U.S., even if they're creditworthy in their home country. About 40 percent of credit invisibles are under 25 years old. In low-income neighborhoods, nearly 30 percent of adults are credit invisible and an additional 16 percent are unscoreable. Younger and older Americans alike may shy away from credit products because of negative experiences and distrust of creditors. Similarly, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC) reports that an estimated 5.4 percent (approximately 7.1 million) households, were unbanked in 2019 — often because they can't meet minimum balance requirements or don't trust banks. Credit invisibles and unscoreables may prefer to deal in a cash economy and turn to alternative credit and banking products, such as payday loans, prepaid cards, and check-cashing services. But these products can perpetuate negative spirals. High fees and interest can create a vicious cycle of spending money to access money, and the products don't help the consumers build credit. In turn, the lack of credit keeps the consumers from utilizing less expensive, mainstream financial products. The emergence of new players Recently, we've seen explosive growth in fintech — technology that aims to improve and automate the delivery and use of financial services. According to market research firm IDC, fintech is expected to achieve a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 25 percent through 2022, reaching a market value of $309 billion. It's reaching mass adoption by consumers: Plaid® reports that 88 percent of U.S. consumers use fintech apps or services (up from 58 percent in 2020), and 76 percent of consumers consider the ability to connect bank accounts to apps and services a top priority. Some of these new products and services are aimed at helping consumers get easier and less expensive access to traditional forms of credit. Others are creating alternative options for consumers. Free credit-building tools. Experian Go™ lets credit invisibles quickly and easily establish their credit history. Likewise, consumers can use Experian Boost™ to build their credit with non-traditional payments, including their existing phone, utility and streaming services bills. Alternative credit-building products. Chime® and Varo® , two neobanks, offer credit builder cards that are secured by a bank account that customers can easily add or withdraw money from. Mission Asset Fund, a nonprofit focused on helping immigrants, offers a fee- and interest-free credit builder loan through its lending circle program. Cash-flow underwriting. Credit card issuers and lenders, including Petal and Upstart, are using cash-flow underwriting for their consumer products. Buy now, pay later. Several Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) providers make it easy for consumers to pay off a purchase over time without a credit check. Behind the scenes, it's easier than ever to access alternative credit data1 — or expanded Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA)-regulated data — which includes rental payments, small-dollar loans and consumer-permissioned data. And there are new services that can help turn the raw data into a valuable resource. For example, Lift PremiumTM uses multiple sources of expanded FCRA-regulated data to score 96 percent of American adults — compared to the 81 percent that conventional scoring models can score with traditional credit data. While we dig deeper to help credit invisibles, we're also finding that the insights from previously unreported transactions and behavior can offer a performance lift when applied to near-prime and prime consumers. It truly can be a win-win for consumers and creditors alike. Final word There's still a lot of work to be done to close wealth gaps and create a more inclusive financial system. But it's clear that consumers want to participate in a credit economy and are looking for opportunities to demonstrate their creditworthiness. Businesses that fail to respond to the call for more inclusive tools and practices may find themselves falling behind. Many companies are already using or planning to use alternative data, advanced analytics, machine learning, and AI in their credit-decisioning. Consider how you can similarly use these advancements to help others break out of negative cycles. 1When we refer to “Alternative Credit Data," this refers to the use of alternative data and its appropriate use in consumer credit lending decisions, as regulated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act. Hence, the term “Expanded FCRA Data" may also apply in this instance and both can be used interchangeably.

Credit scores hold the key to many aspects of our financial lives. Whether qualifying for a mortgage, insurance, or a smartphone plan, financial institutions rely on credit reports — a document detailing how responsibly a person has used credit accounts in the past — to decide if they should approve your financing application. However, here's the problem: because today's scoring system leans heavily on a person’s credit history to generate a credit score, it leaves out large segments of the United States population from accessing credit. According to a recent Oliver Wyman report, an estimated 28 million U.S. consumers are considered ”credit invisible," while another 21 million are deemed "unscorable," meaning they don’t have the types of accounts that have been traditionally used to generate a credit score. Using the traditional credit-scoring formula, certain populations, such as communities of color and low-income consumers, are left behind. Now, times are changing. A modern approach to credit scoring can significantly improve the financial inclusion of millions of U.S. consumers and correct past and present inequities. Tapping into advanced technologies that leverage expanded data assets can produce powerful results. A cycle of exclusion: The limitations of conventional credit scoring A big part of the problem lies with how credit scores are calculated. Between payment history and length of accounts held, a consumer’s credit history accounts for 50 percent of a FICO credit score — the credit score used by 90 percent of top lenders for credit decisions. In other words, the credit system rewards people who already have (or can get) credit and penalizes those that cannot or don't yet have credit. For those who do not have credit, their financial behaviors — such as timely rental and utility payments, bank account data and payday loan installment payments — may not get reported to credit bureaus. As a result, consumers without a credit history may appear as credit invisible or unscorable because they don't have enough tradelines to generate a score. But they also can’t get credit to improve their score. It creates a cycle of exclusion that’s hard to break. Who gets left behind? According to the latest research, the limitations on the traditional credit scoring system disproportionately impact certain communities: Low-income: 30 percent of those in low-income neighborhoods are credit invisible, and 16 percent are considered unscorable, compared with just 4 percent and 5 percent, respectively, in upper-income neighborhoods.1 Communities of color: 27 percent of Black and 26 percent of Hispanic consumers are either credit invisible or unscorable, while only 16 percent of white consumers are.1 Immigrants: People who have recently arrived in the United States can lack a credit history here, even if they may have had one in their home country. Meanwhile, undocumented immigrants, who don’t have a Social Security number, can find it difficult to get a credit card or use other financial services. Young adults: 40 percent of credit invisibles in the U.S. are under the age of 25,1 with 65 percent of 18- to 19-year-olds lacking a credit score. Being labeled unscorable or credit invisible can hinder participation in the financial system and prevent populations from accessing the socioeconomic opportunities that go with it. Why are certain individuals and communities excluded? There are often complex — and valid — reasons for why many consumers are deemed unscorable or credit invisible. For example, newcomers may appear to be credit invisible because haven’t yet generated a credit history in the U.S., although they may have a solid score in their home country. Young consumers are also a common category of unscorable or credit invisible people, largely because they haven't acquired credit yet. Only 35 percent of 18- to 19-year-olds have a credit score, while 91 percent of 25- to 29-year-olds do. However, those who can quickly get a credit history typically come from wealthier households, where they can rely on a creditworthy guarantor to help them establish credit. Finally, some consumers have had negative experiences with the financial system. For instance, a prior default can make it difficult to access credit in the future, which can result in an extended period without credit, eventually leading to being labelled unscorable. Others may distrust the mainstream financial system and choose not to participate. Underpinning all this are racial disparities, with Black and Hispanic consumers being classified as unscorable and credit invisible at significantly higher rates than white and Asian consumers. According to the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), Black and Hispanic people, as well as low-income consumers, are more likely to have “scant or non-existent” credit histories. Financial inclusion is an equity issue Traditional credit scoring places big barriers on certain communities. Without access to credit, marginalized communities will continue to face challenges. They will lack the ability to purchase property, secure business and/or personal loans and deal with financial emergencies, further widening the wealth gap. Since credit scores are used to decide loan eligibility and what interest rate to offer, those with low or no credit rating tend to pay higher interest rates or are denied desired loans, which compounds financial difficulty. The impact is profound: a significant percentage of the population struggles to access basic financial services as well as life opportunities, such as financing an education or buying a home. Without the ability to generate a credit score, unscorable or credit invisible consumers often turn to less-regulated financial products (such as payday loans or buy now pay later agreements) and pay more for these, often locking them in a vicious cycle. Consumers who are credit invisible or unscorable often end up paying more for everyday transactions. They may be required to put up hefty deposits for housings and utilities. Auto and homeowners insurance, which use credit score as a factor in setting rates, may be more expensive too. Consider how much this could impede someone’s ability to save and build generational wealth. Financial inclusion seeks to bring more consumers into the financial system and enable access to safe, affordable financial services and products. With the right technology on your side, there are solutions that make it easier to do so. Tap into technology Banks, credit unions and other lending institutions are well positioned to move the needle on financial inclusion by embracing expanded definitions of creditworthiness. By seeking out expanded FCRA-regulated data with wider sources of financial information, financial institutions can find a vast untapped pool of creditworthy consumers to bring into the fold. Technology makes achieving this goal easier than ever. New credit scoring tools, like Lift Premium™, can give lenders a more complete view of the consumer to use for credit decisioning. It combines traditional credit data with expanded FCRA-regulated data sources, helping lenders uncover more creditworthy consumers. Lift Premium can score 96 percent of U.S. consumers, compared to just 81 percent that conventional scoring systems do now. By applying machine learning to expanded data sets, Lift Premium can build a fuller and more accurate view of consumer behaviors. Moreover, the 6 million consumers whose scores are now considered subprime could be upgraded to prime or near-prime by analyzing the expanded data that Lift Premium uses. The opportunity presented by financial inclusion is significant. Imagine being able to expand your portfolio of creditworthy borrowers by almost 20 percent. The last word With a renewed focus on social justice, it’s no surprise that regulators and activists alike are turning their attention to financial inclusion. A credit-scoring system that allows lenders to better evaluate more consumers can give more people access to transparent, cheaper and safer financial products and the socioeconomic benefits that go along with them. New models and data assets offer additional data points into the credit scoring system and make it possible for lenders to expand credit to a greater number of consumers, in the process creating a fairer system than exists today. Early adopter lenders who embrace financial inclusion now can gain a first-mover advantage and build a loyal customer base in a competitive market. Learn more Download white paper 1Oliver Wyman white paper, “Financial Inclusion and Access to Credit,” January 12, 2022.
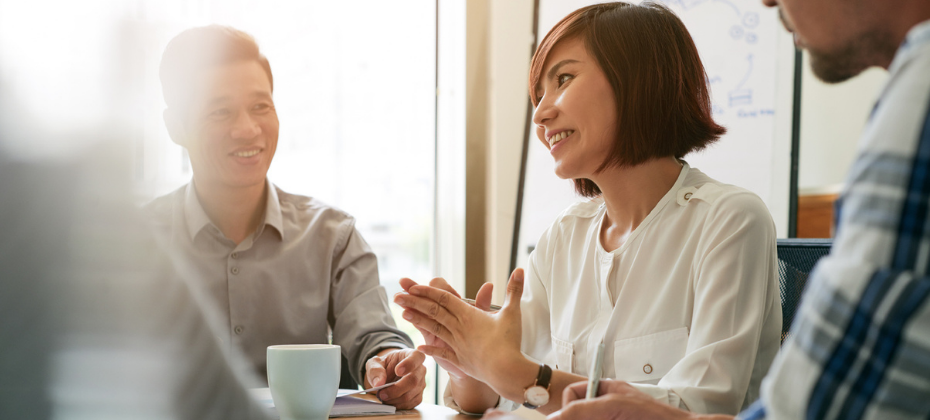

No two customers are the same. That’s why it’s important to go beyond the traditional credit score for a closer look at each consumer’s individual circumstance and create personalized response plans. Learn more about some of the many different customers you’ll encounter and download our guide to get recommendations for every stage of the lifecycle. Get the Guide

This is the third in a series of blog posts highlighting optimization, artificial intelligence, predictive analytics, and decisioning for lending operations in times of extreme uncertainty. The first post dealt with optimization under uncertainty and the second with predicting consumer payment behavior. In this post I will discuss how well credit scores will work for consumer lenders during and after the COVID-19 crisis and offer some recommendations for what lenders can be doing to measure and manage that model risk in a time like this. Perhaps no analytics innovation has created opportunity for more individuals than the credit score has. The first commercially available credit score was developed by MDS (now part of Experian) in 1987. Soon afterwards FICO® popularized the use of scores that evaluate the risk that a consumer would default on a loan. Prior to that, lending decisions were made by loan officers largely on the basis on their personal familiarity with credit applicants. Using data and analytics to assess risk not only created economic opportunity for millions of borrowers, but it also greatly improved the financial soundness of lending institutions worldwide. Predictive models such as credit scores have become the most critical tools for consumer lending businesses. They determine, among other things, who gets a loan and at what price and how an account such as a credit line is managed through its life cycle. Predictive models are in many cases critical for calculating loan and loss reserves, for stress testing, and for complying with accounting standards. Nearly all lenders rely on generic scores such as the FICO® score and VantageScore® credit score. Most larger companies also have a portfolio of custom scorecards that better predict particular aspects of payment behavior for the customers of interest. So how well are these scorecards likely to perform during and after the current pandemic? The models need to predict consumer credit risk even as: Nearly all consumers change their behaviors in response to the health crisis, Millions of people—in America and internationally—find their income suddenly reduced, and Consumers receive large numbers of accommodations from creditors, who have in turn temporarily changed some of their credit reporting practices in response to guidelines in the federal CARES Act. In an earlier post, I pointed out that there is good reason to believe that credit scores will tend to continue to rank order consumers from most likely to least likely to repay their debts even as we move from the longest economic expansion in history to a period of unforeseen and unexpected challenges. But the interpretation of the score (for example, the log odds or the bad rate) may need to be adjusted. Furthermore, that assumes that the model was working well on a lender’s population before this crisis started. If it has been a long time since a scorecard was validated, that assumption needs to be questioned. Because experts are considering several different scenarios regarding both the immediate and long-term economic impacts of COVID-19, it’s important to have a plan for ongoing monitoring as long as necessary. Some lenders have strong Model Risk Management (MRM) teams complying with requirements from the Federal Reserve, Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC), the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC). Those resources are now stretched thin. Other institutions, with fewer resources for MRM, are now discovering gaps in their model inventories as they implement operational changes. In either case, now’s the time to reassess how well scorecards are working. Good model validation practices are especially critical now if lenders are to continue to make the sound data-driven decisions that promote fairness for consumers and financial soundness for the institution. If you’re a credit risk manager responsible for the generic or custom models driving your lending, servicing, or capital allocation policies, there are several things you can do--starting now--to be sure that your organization can continue to make fair and sound lending decisions throughout this volatile period: Assess your model inventory. Do you have good documentation showing when each of the models in your organization was built? When was it last validated? Assign a level of criticality to each model in use. Starting with your most critical models, perform a baseline validation to determine how the model was performing prior to the global health crisis. It may be prudent to conduct not only your routine validation (verifying that the model was continuing to perform at the beginning of the period) but also a baseline validation with a shortened performance window (such as 6-12 months). That baseline validation will be useful if the downturn becomes a protracted one—in which case your scorecard models should be validated more frequently than usual. A shorter outcome window will allow a timelier assessment of the relationship between the score and the bad rate—which will help you update your lending and servicing policies to prevent losses. Determine if any of your scorecards had deteriorated even before the global pandemic. Consider recalibrating or rebuilding those scorecards. (Use metrics such as the Population Stability Index, the K-S statistic and the Gini Coefficient to help with that decision.) Many lenders chose not to prioritize rebuilding their behavioral scorecards for account management or collections during the longest period of economic growth in memory. Those models may soon be among the most critical models in your organization as you work to maintain the trust of your accountholders while also maintaining your institution’s financial soundness. Once the CARES accommodation period has expired, it will be important to revalidate your models more frequently than in the past—for as long as it takes until consumer behavior normalizes and the economy finds its footing. When you find it appropriate to rebuild a scorecard model, consider whether now is the time to implement ethical and explainable AI. Some of our clients are finding that Machine Learned models are more predictive than traditional scorecards. Early Experian research using data from the last recession indicates this will continue to be true for the foreseeable future. Furthermore, Experian has invested in Research and Development to help these clients deliver FCRA-compliant Adverse Action reasons to their consumers and to make the models explainable and transparent for model risk governance and compliance purposes. The sudden economic volatility that has resulted from this global health crisis has been a shock to all organizations. It is important for lenders to take the pulse of their predictive models now and throughout the downturn. They are especially critical tools for making sound data-driven business decisions until the economy is less volatile. Experian is committed to helping your organization during times of uncertainty. For more resources, visit our Look Ahead 2020 Hub. Learn more

Last week, the unemployment rate soared past 20%, with over 30 million job losses attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic. As a result, many consumers are facing financial stress, which has raised many questions and discussions around how credit history and reporting should be treated at this time. Since the initial start of the pandemic, credit reporting companies and data furnishers have been put under the spotlight to ensure that consumers are able to get the assistance that they need. Numerous questions and concerns have also been raised around the extent of which consumers have access to fair and affordable credit. On March 27th, 2020, Congress signed the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act into law, which was a bill created to provide support and relief for American workers, families, and small businesses. This newly proposed Act also provides guidelines on how creditors and data furnishers should report information to credit bureaus, to ensure that lenders remain flexible as consumers navigate the current pandemic. The Act requires that creditors must provide “accommodations” to consumers affected by COVID-19 during “covered periods.” According to the National Credit Union Administration, “The CARES Act requires credit reporting agency data providers, including credit unions, to report loan modifications resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic as ‘current’ or as the status reported before the accommodation unless the consumer becomes current,” as stated in Section 4021. Section 4021 of the CARES Act also provides other guidelines for accurate data reporting. During this time, lenders can use attributes to determine risk during COVID-19. Attributes within custom scores can also capture consumer behavior and help lenders determine the best treatments. Payment attributes, debt burden attributes, inquiry attributes, credit extensions and originations are all key indicators to keep an eye on at this time as lenders monitor risk in their portfolios. Listen in as our panel of experts explore the areas related to data reporting that impact you the most. In addition to a regulatory update and discussions around programs to help support consumers and businesses, we’ll also review what other lenders are doing and early indicators of credit trends. You’ll also be able to walk away with key strategies around what your organization can do right now. Discover the latest information on: Data reporting and CDIA regulations Regulatory updates, including the CARES Act, a breakdown of Section 4021, and guidelines to remember Credit attribute trends and highlights, treatment of scores and attributes, as well as recommended attributes Watch the webinar

There are more than 100 million people in the United States who don’t have a fair chance at access to credit. These people are forced to rely on high-interest credit cards and loans for things most of us take for granted, like financing a family car or getting an apartment. At Experian, we have a fundamental mission to be a champion for the consumer. Our commitment to increasing financial inclusion and helping consumers gain access to the financial services they need is one of the reasons we have been selected as a Fintech Breakthrough Award winner for the third consecutive year. The Fintech Breakthrough Awards is the premier awards program founded to recognize the fintech innovators, leaders and visionaries from around the world. The 2020 Fintech Breakthrough Award program attracted more than 3,750 nominations from across the globe. Last year, Experian took home the award for Best Overall Analytics Platform for our Ascend Analytical Sandbox™, a first-to-market analytics environment that promised to move companies beyond just business intelligence and data visualization to data insights and answers they could use. The year prior, Experian won the Consumer Lending Innovation Award for our Text for Credit™ solution, a powerful tool for providing consumers the convenience to securely bypass the standard-length ‘pen & paper’ or keystroke intensive credit application process while helping lenders make smart, fraud protected lending decisions. This year, we are excited to announce that Experian has been selected once again as a winner in the Consumer Lending Innovation category for Experian Boost™. Experian Boost – with direct, active consumer consent – scans eligible accounts for ‘boostable’ positive payment data (e.g., utility and telecom payments) and provides the means for consumers to add that data to their Experian credit reports. Now, for the very first time, millions of consumers benefit from payments they’ve been making for years but were never reflected on their credit reports. Since launching in March 2019, cumulatively, more than 18 million points have been added to FICO® Scores via Experian Boost. Two-thirds of consumers who completed the Experian Boost process increased their FICO Score and among these, the average score increase has been more than 13 points, and 12% have moved up in credit score category. “Like many fintechs, our goal is to help more consumers gain access to the financial services they need,” said Alex Lintner, Group President of Experian Consumer Information Services. “Experian Boost is an example of our mission brought to life. It is the first and only service to truly put consumers in control of their credit. We’re proud of this recognition from Fintech Breakthrough and the momentum we’ve seen with Experian Boost to date.” Contributing consumer payment history to an Experian credit file allows fintech lenders to make more informed decisions when examining prospective borrowers. Only positive payment histories are aggregated through the platform and consumers can remove the new data at any time. There is no limit to how many times one can use Experian Boost to contribute new data. For more information, visit Experian.com/Boost.

Retailers are already starting to display their Christmas decorations in stores and it’s only early November. Some might think they are putting the cart ahead of the horse, but as I see this happening, I’m reminded of the quote by the New York Yankee’s Yogi Berra who famously said, “It gets late early out there.” It may never be too early to get ready for the next big thing, especially when what’s coming might set the course for years to come. As 2019 comes to an end and we prepare for the excitement and challenges of a new decade, the same can be true for all of us working in the lending and credit space, especially when it comes to how we will approach the use of alternative data in the next decade. Over the last year, alternative data has been a hot topic of discussion. If you typed “alternative data and credit” into a Google search today, you would get more than 200 million results. That’s a lot of conversations, but while nearly everyone seems to be talking about alternative data, we may not have a clear view of how alternative data will be used in the credit economy. How we approach the use of alternative data in the coming decade is going to be one of the most important decisions the lending industry makes. Inaction is not an option, and the time for testing new approaches is starting to run out – as Yogi said, it’s getting late early. And here’s why: millennials. We already know that millennials tend to make up a significant percentage of consumers with so-called “thin-file” credit reports. They “grew up” during the Great Recession and that has had a profound impact on their financial behavior. Unlike their parents, they tend to have only one or two credit cards, they keep a majority of their savings in cash and, in general, they distrust financial institutions. However, they currently account for more than 21 percent of discretionary spend in the U.S. economy, and that percentage is going to expand exponentially in the coming decade. The recession fundamentally changed how lending happens, resulting in more regulation and a snowball effect of other economic challenges. As a result, millennials must work harder to catch up financially and are putting off major life milestones that past generations have historically done earlier in life, such as homeownership. They more often choose to rent and, while they pay their bills, rent and other factors such as utility and phone bill payments are traditionally not calculated in credit scores, ultimately leaving this generation thin-filed or worse, credit invisible. This is not a sustainable scenario as we enter the next decade. One of the biggest market dynamics we can expect to see over the next decade is consumer control. Consumers, especially millennials, want to be in the driver’s seat of their “credit journey” and play an active role in improving their financial situations. We are seeing a greater openness to providing data, which in turn enables lenders to make more informed decisions. This change is disrupting the status quo and bringing new, innovative solutions to the table. At Experian, we have been testing how advanced analytics and machine learning can help accelerate the use of alternative data in credit and lending decisions. And we continue to work to make the process of analyzing this data as simple as possible, making it available to all lenders in all verticals. To help credit invisible and thin-file consumers gain access to fair and affordable credit, we’ve recently announced Experian Lift, a new suite of credit score products that combines exclusive traditional credit, alternative credit and trended data assets to create a more holistic picture of consumer creditworthiness that will be available to lenders in early 2020. This new Experian credit score may improve access to credit for more than 40 million credit invisibles. There are more than 100 million consumers who are restricted by the traditional scoring methods used today. Experian Lift is another step in our commitment to helping improve financial health of consumers everywhere and empowers lenders to identify consumers who may otherwise be excluded from the traditional credit ecosystem. This isn’t just a trend in the United States. Brazil is using positive data to help drive financial inclusion, as are others around the world. As I said, it’s getting late early. Things are moving fast. Already we are seeing technology companies playing a bigger role in the push for alternative data – often powered by fintech startups. At the same time, there also has been a strong uptick in tech companies entering the banking space. Have you signed up for your Apple credit card yet? It will take all of 15 seconds to apply, and that’s expected to continue over the next decade. All of this is changing how the lending and credit industry must approach decision making, while also creating real-time frictionless experiences that empower the consumer. We saw this with the launch of Experian Boost earlier this year. The results speak for themselves: hundreds of thousands of previously thin-file consumers have seen their credit scores instantly increase. We have also empowered millions of consumers to get more control of their credit by using Experian Boost to contribute new, positive phone, cable and utility payment histories. Through Experian Boost, we’re empowering consumers to play an active role in building their credit histories. And, with Experian Lift, we’re empowering lenders to identify consumers who may otherwise be excluded from the traditional credit ecosystem. That’s game-changing. Disruptions like Experian Boost and newly announced Experian Lift are going to define the coming decade in credit and lending. Our industry needs to be ready because while it may seem early, it’s getting late.

Alex Lintner, Group President at Experian, recently had the chance to sit down with Peter Renton, creator of the Lend Academy Podcast, to discuss alternative credit data,1 UltraFICO, Experian Boost and expanding the credit universe. Lintner spoke about why Experian is determined to be the leader in bringing alternative credit data to the forefront of the lending marketplace to drive greater access to credit for consumers. “To move the tens of millions of “invisible” or “thin file” consumers into the financial mainstream will take innovation, and alternative data is one of the ways which we can do that,” said Lintner. Many U.S. consumers do not have a credit history or enough record of borrowing to establish a credit score, making it difficult for them to obtain credit from mainstream financial institutions. To ease access to credit for these consumers, financial institutions have sought ways to both extend and improve the methods by which they evaluate borrowers’ risk. By leveraging machine learning and alternative data products, like Experian BoostTM, lenders can get a more complete view into a consumer’s creditworthiness, allowing them to make better decisions and consumers to more easily access financial opportunities. Highlights include: The impact of Experian Boost on consumers’ credit scores Experian’s take on the state of the American consumer today Leveraging machine learning in the development of credit scores Expanding the marketable universe Listen now Learn more about alternative credit data 1When we refer to "Alternative Credit Data," this refers to the use of alternative data and its appropriate use in consumer credit lending decisions, as regulated by the Fair Credit Reporting Act. Hence, the term "Expanded FCRA Data" may also apply in this instance and both can be used interchangeably.

Analyzing credit scores and card balances According to a study by VantageScore® Solutions LLC, consumers with credit scores between 601 and 650 carry the largest credit card bills, at more than $10,000 — nearly 2x that of the average consumer. Other key findings include: Those with the highest scores have the largest total credit limit ($46,735), compared with just $2,816 for those with the lowest scores. The average credit card holder has $29,197 in credit lines, with an average balance of $5,720. Those with scores between 701 and 750 use an average of 27% of their available credit versus 47% for those with scores between 651 and 700. The study reinforces the importance of staying current on the latest credit trends to best identify areas of opportunity and adjust lending strategies accordingly. Make better decisions >
Credit reports provide a wealth of information. But did you know credit attributes are the key to extracting critical intelligence from each credit report? Adding attributes into your decisioning enables you to: Improve acquisition strategies and implement policy rules with precision. Segment your scored population for more refined risk assessment. Design more enticing offers and increase book rates. Attributes can help you make more informed decisions by providing a more granular picture of the consumer. And that can make all the difference when it comes to smart lending decisions. Video: Making better decisions with credit attributes

Knowing a consumer’s credit information at a single point in time tells only part of the story. For the whole story, lenders need to assess a consumer’s credit behavior over time. Understanding how a consumer uses credit or pays back debt over several months can better position you to: Offer the right products and terms to increase response rates. Identify profitable customers. Avoid consumers with payment stress. Trended data adds needed color to the consumer’s credit story. And with the right analytics and systems, you can derive valuable insights on consumers. Trended data>

Looking to score more consumers, but worried about increased risk? A recent VantageScore® LLC study found that consumers rendered “unscoreable” by commonly used credit scoring models are nearly identical in their financial and credit behavior to scoreable consumers. To get a more detailed financial portrait of the “expanded” population, credit files were supplemented with demographic and economic data. The study found: Consumers who scored above 620 using the VantageScore® credit score exhibited profiles of sufficient quality to justify mortgage loans on par with those of conventionally scoreable consumers. 3 to 2.5 million – a majority of the 3.4 million consumers categorized as potentially eligible for mortgages – demonstrated sufficient income to support a mortgage in their geographic areas. The findings demonstrate that the VantageScore® credit score is a scalable solution to expanding mortgage credit without relaxing credit standards should the FHFA and GSEs accept VantageScore® credit scores. Want to know more?

According to a national survey by Experian, one in five college grads give their school an “F” in credit education. Additional survey highlights: 69% will have student loan debt after graduation 71% did not learn about credit and debt management in college 55% feel like they are “going it alone” when it comes to their finances 72% express concern about paying off their debt Credit is a skill — one that can be developed through the right education. The Experian Credit Education blog has useful information to help college grads learn the basics of credit and how they can improve their credit score. College Graduate Survey Report