Latest Posts

Your password is weak, whether you use 40 random characters or your dog’s name. With so many large data breaches leading to hundreds of millions of compromised credentials and payment cards in the past two years, it’s no surprise that e-commerce account takeover attempts have grown dramatically in recent months – to a degree we have never seen before. Previously, account takeover was primarily a banking issue, not something merchants had to deal with. Account takeover is an alarming trend that spans global airline loyalty programs, e-commerce transactions, social networking logins and virtually any web site leveraging username and password authentication. News of the latest cybersecurity concern should serve as yet another reminder that we live in a heightened state of risk where establishing online trust based solely on username and password or identity data is not sufficient. There are a number of factors that are contributing to the evolving fraud landscape namely that the Internet was not designed for security. This places pressure on organizations to continually adopt new approaches to managing fraud like this growing account takeover threat. In this case, multiple layered controls including device intelligence are essential. As merchants extend more services online and allow customers to store payment information or get more convenient checkout via logged in vs. guest access, we’ll continue to see fraud migrating deeper into the e-commerce ecosystem. The account takeover problem will continue as consumers share usernames and passwords across dozens of online profiles and e-commerce logins, opening the door for attackers to access multiple accounts through a single compromised credential. Most of the account portals used by e-commerce merchants and loyalty programs were not built with the same level of security that their online transaction and fraud management systems have in place. So it’s a bit of a new risk, but fraudsters are aggressively exploiting the security gaps around things like simple username/password authentication. What can consumers and organizations do to protect themselves? Our recommendation for consumers is that they have unique username and password combinations for every online profile. This protects against attackers compromising one site and leveraging the same credentials to access all of the victim’s accounts and online profiles across the web. For businesses, we recommend implementing technology solutions that increase visibility to and recognition of devices for every online interaction so the organization can differentiate attackers from legitimate consumers. Some businesses believe that their products, services and loyalty offerings do not require the same level of protection as online bank accounts, so they leave them exposed to cyber criminals via simple authentication controls. As we’ve seen fraudsters will migrate to the path of least resistance and exploit the fact that most consumers re-use credentials out of convenience. In the digital age where consumers are increasingly represented by their devices the ability to know when there are authentication discrepancies between the data presented by the user and the device presenting those credentials is absolutely important to effectively controlling the threat. The authentication process will shift from a single view to a layered, risk-based authentication approach that will include comprehensive and real-time updates of consumer information. Conversations around the fact that the password is dead or dying have been circulating in the industry recently. What we don’t want is consumers getting tired of constantly changing passwords and giving up trying to protect themselves online. That is the worst case scenario that is becoming more of a reality as the days pass. Educated and aware consumers are still the best way to identify fraudulent attacks, and to keep identity data safe from hackers and devices free of malware. Increased adoption of biometrics, device intelligence and the sharing of authenticated and credentialed identities across industries will become commonplace to help combat account takeovers as they increase. Until then we need to find a password replacement. Learn more about 41st Parameter fraud detection and prevention solutions here.

While automotive loan originations grew 15 percent year over year in Q1 2014, a recent Experian Automotive study found that more consumers are continuing to drive older-model vehicles.

In our most recent webinar, I had the pleasure of moderating a panel session with four fraud experts spanning across many diverse backgrounds. The consistent theme throughout was that cyber criminals have become quite proficient at stealing data or account credentials. Once a cyber criminal has valid account data, they have incredible access to a broad range of possibilities. How an account is used; a real-time view of deposit and withdrawal patterns and what types of alerts and notification settings are in place. A determined fraudster may observe accounts for long periods to ensure they are able to make their move at the optimal time. One of the biggest issues is being able to tell “friend from foe”, particularly in light of the endless supply of perfect, disposable data. I posed this scenario to our panel and asked what organizations can do now to protect themselves: SCENARIO – Telling friend from foe Credit card companies encourage travellers to alert them in advance of unusual travel to avoid red flags or declines while out of town. This can be a double-edged sword. A fraudster with appropriate credentials can contact a credit card company a few weeks before a “trip” to alert them of planned travel. At the start of the “trip” the distraught fraudster can then contact the credit card company to report a stolen card and request a replacement be expedited to them at their “destination.” The result is a fraudster armed with a completely legitimate card they can use at their leisure and with little risk of detection. There were three key take-aways the expert panel recommended: Enhance your visibility. Without this important tactic, you won’t know what hit you. Fraudsters are armed with pristine identity data so they will look and act more like your best customers. Employee multiple security layers. You may be focused on ensuring that you know your customer, but does the transaction pattern fit normal behavior for the user? Malware could be embedded on the device. Are items such as language and other settings consistent with what you’d expect for your legitimate customers? Protect profile setups / online enrolment and reward programs the way you protect transactions. While the financial risk to your business may be limited, the potential regulatory exposure and brand reputation hit can be significant. It takes years to build your reputation with your best customers – but only seconds to destroy it. Undermining their trust in online or mobile interactions with your business has an immediate and destructive impact on loyalty. What do you think? Let us know.
Residential real estate lending was the leading component of the Great Recession of 2007-2009. Could it happen again? Let’s analyze our Intelliview data to see where U.S. lending trends are headed with HELOCs. A large portion of Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) were originated from 2004 to 2007. The term structure of these HELOCs will soon result in larger monthly payments, which could potentially promote consumer debt burden troubles. Additionally, with as much as 13% of all first mortgage customers having balances greater than the value of homes, many HELOCs wallow underwater. HELOCs typically have a ten year draw followed by a twenty-year repayment period. However, there are variations in the term structures. HELOCs can have as little as a five year draw, while others have a fifteen year repayment period. During the draw period, customers only pay interest on the balance. In the repayment period, the account functions like a loan, customers pay principal and interest. In 2012, the Office of Comptroller of the Currency (OCC, the primary banking regulator) reported that 58% of all bank HELOC balances would enter the repayment period and begin to amortize between 2014 and 2017 (OCC, Semiannual Risk Perspective, Spring 2012). This report renewed fears that the increase in payments would lead to higher delinquencies and foreclosures, limit consumer spend and provide a drag on the U.S. economy. Paradoxically, the OCC estimates of the HELOC balances entering the repayment period may be low. The OCC has accounted only for $392 billion of HELOC balances among banks. Experian’s review of all HELOC trades shows a significantly higher level of balances. Additionally, American Banker estimates the top 200 banks and thrifts had more than $477 billion in HELOC outstanding as of the end of 2013, with the top three lenders (Bank of America, Wells Fargo and JP Morgan Chase) comprising nearly $300 billion. Experian examined HELOCs in the four states with the greatest surges in home values and lending prior to the Great Recession. California comprises nearly 19% of all HELOC balances and lines. With averaging HELOC balances of 53% above the national mean, Arizona, Florida and Nevada are the three highest utilization rates by state. Nevada has the highest 30+ day delinquency rate in the country at 2.92%, while the national average is 1.64%. According to CoreLogic’s most recent home price index report, Nevada, Florida and Arizona home prices remain 30-39% below their peak real estate values. California’s prices are down 17%, and the national average home value is still 14% below its highest value. Refinancing HELOCs may be difficult due to the significant number of second liens still underwater. Compounding this difficulty, lending standards also have tightened, with regard to loan-to-value, debt ratios and credit quality. The average HELOC was examined at a 4.5% interest rate and a 20 year repayment period. The average monthly payment increases almost 69% when the account leaves the draw period and requires paying principal balance as well as interest. This payment increase accounts for approximately 2.6% of the median U.S. household gross annual income. It is estimated that the increase in HELOC payments will comprise $1 billion in additional annual payments during 2014, and an additional $9 billion between 2015 through 2017. However, it is important to remember that not all HELOCs will reach repayment. HELOCs are priced based on the prime rate. That rate has been 3.25% for more than five years, a historical low. When prime rate reached this level in December 2008, the rate was at its lowest in 53 years. Only 18 months prior to reaching 3.25%, the prime rate had been 8%. If the prime rate increases by 1% to 4.25%, the average payment of accounts in the draw period would increase 22%, affecting just about every HELOC, with a national increase in annual payments of about $5 billion. The volume of HELOCs that are beginning to enter the repayment period may eventually increase delinquency rates. However, no such increase is yet evident. As shown below, delinquency rates are steady after a long decline. In the past three years, 90+ days delinquency has declined 41%. The Majority of HELOCs are second mortgages. Successful completion of a foreclosure would involve making the customer’s monthly first mortgage payment in addition to all other expenses incurred in foreclosure and the sale of the property. Very often foreclosing from a second lien does not make financial sense unless the financial institution also holds the first mortgage on the property. As a large portion of HELOCs enter the repayment period in the next four years, the payments that customers must make will increase considerably. With interest rates as low as they are, the prime rate will eventually rise, and increase debt service ratios. These payment increases will have implications on consumers, lenders and the economy. Having grown 10.5% in the last year, home values continue to recover from the recession. It is yet to be determined whether this payment increase will have a broader or more isolated impact. In the meantime, HELOCs will continue to see their resurgence. For more insight like this from Experian Decision Analytics, watch our 2014 Q1 Experian–Oliver Wyman Market Intelligence Report presentation.
Are you sure you are making the best consumer credit decisions? Given the constantly evolving market conditions, it is a challenge to keep informed. In order to confidently grow and manage the bottom line, organizations need to avoid these four basic risks of making credit decisions with limited trend visibility. Competitive Risk - With limited visibility to industry trends, organizations cannot understand their position relative to peers. Product Risk - Organizations without access to the latest consumer behaviors cannot identify and capitalize on emerging trends. Market Risk - Decisions suffer when made without considering market trends in the context of the economy. Resource Risk - Extracting useful insights from vast market data requires abundant resources and comprehensive expertise. Get more information on the business risks of navigating credit decisions with limited trend visibility.

A recent study conducted by the Ponemon Institute found that a data breach is among the top three occurrences that affect brand reputation, along with poor customer service and an environmental incident.

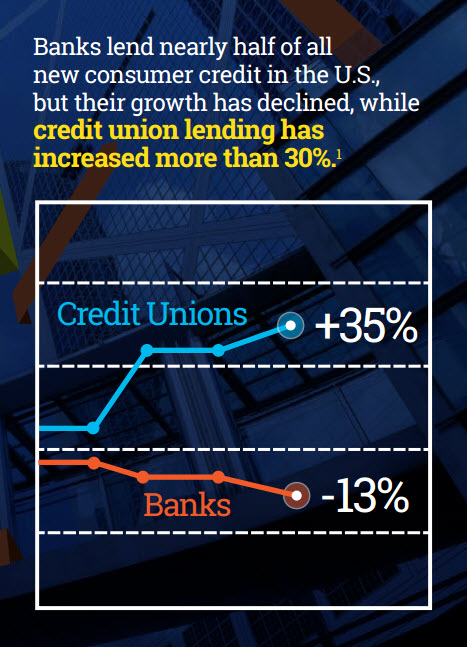
Universe expansion is key to any lender's growth strategy. Sophisticated, advanced risk models, such as the VantageScore®3.0 model, allow lenders to score up to 35 million more consumers than other risk models.

According to Experian Marketing Services’ Q1 2014 Email Benchmark Report, personalized abandoned cart emails that dynamically show the actual customer cart had 25 percent higher transaction rates than reminder emails that just linked back to the brand’s Website.

Data breach notification letters serve multiple purposes. They ensure a breached company is compliant with data breach notification laws, they alert consumers to the breach and their involvement in it, they can warn customers of potential identity theft risks and educate them on how to cope with those risks. The one thing no company wants its notification letter to do, however, is make the recipients any more upset than they already are. Yet that’s the reaction many consumers reported upon having received data breach notification letters, according to the study “The Aftermath of a Mega Data Breach: Consumer Sentiment.” Conducted by the Ponemon Institute on behalf of Experian Data Breach Resolution, the study provides some eye-opening insights into how consumers feel and what they do after receiving a breach notification letter. To put consumer sentiment in perspective, consider these revelations from the study: Among those polled, 63% said they felt the breached company should offer consumers identity theft protection by way of compensation, yet just 25% of people who had received a notification letter said were offered identity theft protection in that letter. The financial impact of the data breach was less significant for consumers than the emotional aspects. 81% of data breach victims said they had not out-of-pocket costs because of the breach. Conversely, 76% said they experienced stress as a result of the breach. Consumers ranked a data breach as the third-most damaging event for a company’s reputation. Only poor customer service and an environmental incident (e.g. an oil spill or pollution) were seen as more damaging. Other than getting stressed, what, then, do consumers do after they’ve received a data breach notification letter? Most do little or nothing at all, which should be just as concerning to companies as the customers who end their business relationship with a company in the wake of a data breach. More than half (55%) said they did nothing to protect their identities after receiving a notification letter, and 32% ignored the notifications and did nothing at all. This may seem counter-intuitive considering that the majority (77%) were at least somewhat to very concerned about becoming an identity theft victim because of the breach. Perhaps if these customers had been offered free identity theft protection in the notification letter, they would have accepted the offer. These survey results underscore the need for companies to send strong, informative and compassionate data breach notification letters – and to offer consumers identity theft protection as part of the company’s data breach response. Learn more about our Data Breach solutions

Today I co-hosted a TweetChat with Experian on mobile fraud trends. To be honest, it was the first Twitter Chat I took part in. It was fun, informative and a great way to connect with folks in our industry – from our customer base, partners and more. The discussion was fast paced and the 140-character limit for tweets means I wasn’t able to elaborate on many of the points I made. Thus, thought I would share my insight through a blog post. What are the most common types of mobile fraud? Malware. According to Forbes, 97 percent of mobile malware is on Android devices. That’s not to say that Apple isn’t seeing it, too. They are, but at a much reduced scale due to their validation processes. Forbes also states that android malware rose from 238 threats in 2012 to 804 new threats in 2013 and continues to rise. Mobile malware has a couple of varieties that everyone should be aware of. They’re increasingly common and you’ve likely seen the first one making media headlines like rapid fire in recent months: Ransomware: locks a user’s phone and fraudsters demand payment to unlock it. Credential stealing malware: attempts to capture the credentials of the victim as they access a service. Premium dialing/texting malware that uses victim phones to increase traffic and charges to rogue accounts. Mobile fraud, as a category, also needs to include the use of the mobile device by fraudsters as the attacking instrument. Fraudsters exploit the fact that organizations may not have applied the same security measures to their mobile access points that they have in their traditional online access. Big mistake. All organizations should make sure that they are not exposed to fraud originating from the mobile channel (either mobile app or mobile web based.) Companies need to ensure they can identify the device regardless of platform. Am I more at risk on my mobile device than I am on my computer? As a consumer, industry data has illustrated that there is no significant difference between the risk of the PC and a mobile device. The PC is still a much more valuable target to fraudsters, considering its wide use. But as the mobile platform continues to grow, mobile exploits are also growing, forcing the industry to build in more robust strategies around mobile access. This includes the platform providers, app developers and businesses that want to increase their mobile offerings. The bigger point here is that the Apple platform has much less malware activity than the Android platform does today. Apple has stringent developer policies and scrutiny. For businesses, as a relative percentage of device activity, we are beginning to see that there is more fraud in the mobile channel than in the traditional channel. Bear in mind that mobile volumes today are still much smaller than the traditional PC. Mobile can also be a fraud staging area, where fraudsters can see balances and activity and then takeover your account… But this is not a vulnerability with the consumer using their device, rather it’s with the fraudsters using the mobile channel since it’s a separate channel where the banks may not have effective cross-channel visibility. How do I know if you have a legitimate app vs a fake / fraudulent app? There are a few simple steps to verify the legitimacy of apps – check for typos, grainy logos and images and check user reviews on the app store. Moreover, this is an issue of where users are getting their apps. Make sure you are only downloading apps from the platforms’ authorized app environments. And keep in mind that the prevalence of malware on the Google Play platform is much higher than that on the AppStore. What other risks do mobile devices pose to personal identity? The phone doesn’t necessarily present greater risks than PCs, but people do tend to use them more frequently, and with less of a thought toward security. My advice: make a habit of locking your phone and don’t buy apps from sketchy platforms. What are the methods that banks and retailers are choosing to secure mobile payments? It’s a device access versus personal access issue. Need for business is to recognize devices regardless of payment type. In the NFC space, there’s also a question of liability… who is on the hook when happens? Is it the merchant? The card issuer? There are still some gray areas when it comes to mobile wallet (NFC) transactions being used for physical purchases. For NFC (in person) payments, the POS makers use industry standards – but they can still be vulnerable to attack based on malware distributed via POS terminals, as we have seen lately. For mobile bank payments – some banks use device recognition and device behavior– but all banks really should use it – best way to detect rogue activity from the device. Most retail mobile payments are tied to a wallet – so wallet providers must also secure access to the wallet ensure that it doesn’t become the weakest link. Will passwords ever die? What other forms of identification might be used? For businesses, passwords are already dead, since most have been stolen over the years. Businesses should be using device recognition – it’s one of the strongest tools to differentiate between good and bad users. Any final tips on how people can protect themselves from mobile fraud? Don’t buy apps from sketchy third party platforms. Don’t click on links from untrusted parties, lock your device, make sure your device is backed up and don’t pay ransomware demands. If you have any other questions that weren’t answered in the #TweetChat, please leave a comment here or tweet to me at @DBritton41st.

A recent Experian Consumer Services survey focusing on the most important attributes in a prospective spouse found that married adults value financial responsibility more than physical attractiveness.

It’s no secret that e-commerce merchants, retailers, and financial institutions are prime targets for these digital ghosts as they look to quickly monetize their recent data heist. Unfortunately, many organizations are still scrambling to deploy proper defenses. So how do you defend against an unregulated, networked enemy intent on inciting chaos and filling their bank accounts? Following any data breach, it is essential that organizations gain complete visibility of their customers and transactions across channels. Once a breach has occurred, it is critical for organizations to perform a forensic review of the attack to identify and understand all of the potential points of vulnerability, what data was stolen and how that data was transmitted back to the attackers. What can be more concerning is that the initial scope may quickly expand into something much larger. This makes it essential that retailers and financial institutions rapidly gain complete visibility of their customer data and transactions across channels and keep drilling-down until the root cause can be identified and protected against a repeat attack. Unfortunately, that type of consolidated view does not exist in most companies. Organizations need to ask themselves some serious questions. Do you really know who is logging into your customers’ accounts? Without realizing their data has been compromised, consumers can fall prey to personalized phishing attacks and “give away the keys” to their accounts. How can you be certain a VIP customer is really behind a high-dollar transaction being rushed to an overseas address? No one wants to decline legitimate orders from loyal customers; but with revenue, reputation and brand equity at stake, no one can afford to ignore the potential risk. What controls are in-place to ensure that a fraudster in Malaysia isn’t using legitimate identity data and an anonymous proxy to submit credit card applications that are a perfect match to credit bureau data? Or to alert when a long-standing offline banking relationship suddenly enrolls online? Once access is established, address and other data can be updated and sold to the highest bidder in underground forums. All of these questions can be addressed through the combination of complex device intelligence, a powerful risk engine and support from industry-leading experts in fraud and risk management. Even after a breach has occurred, the risk can be managed. First, consumers need to be informed on how to protect themselves from sophisticated use of their data. Second, arm your organization with a layered security strategy that includes device intelligence. This will prepare you for the onslaught of compromised card usage, fraudulent enrollments, phishing attacks and attempted account takeovers that follow in the wake of a data breach.

The World Cup of Fraud By David Britton The World Cup “kicks” off this week in Brazil and is a tremendous business opportunity for merchants around the world to sell merchandise, apps, tickets and even the caxirola - this year’s version of the Vuvuzela. This opens the doors for cross-border business transactions and as the doors open for more business, they also open for fraudsters to take advantage of cracks in the system or unsuspecting shoppers. Businesses should remember that the Internet was never designed with security in mind, and that it also affords great anonymity, regardless of the locale of the buyer. International ecommerce studies have shown that ecommerce cross-border fraud can be 7 times higher than fraud within your own country. The anonymity of the Internet allows fraudsters to extend their reach to do damage – and to do so with greater confidence than they might in their own country. Here are some fraud tips for businesses to consider with cross-border ecommerce: Marketing budgets are typically 15% of total costs and require time to plan – don’t let those efforts get hurt by your fraud system. The marketing team needs to work closely with the fraud team. Share those marketing goals with your fraud team so they are aware of marketing projects. Are campaigns on mobile, is there a special sale, package, promotions, gift card, etc. The fraud team needs to know what is out there. Know your target international market to help recognize fraud outliers. Know ahead of time what the measured attack rate is against your business. Have appropriate countermeasures and business rules in place when attacks surface. High risk products require a different strategy than low risk products. Have good data from within your business to understand the threat and to be ready to change course rapidly based on that data. There is also a major shift occurring in the mobile environment where users are rapidly adopting the practice of both perusing and shopping from their pocket-based devices. This shift includes fraud. More credit cards available on the underground than ever before. Estimates put the total number of compromised identities at over 1 billion records over the past 2 years, many of which include credit card information. Combine this information with the fact that the card issuers, for cost reasons do not proactively re-issue new cards – it is up to the merchants to be extra diligent when it comes to looking for fraud. Because the data breaches do not just divulge card data, but also the personal identity data elements of the victims, the fraudsters are able to create transactions that look very legitimate. Merchants must employ technologies that allow them to see beyond the data presented by the user, to the data about the device that is transmitting that data, in order to have real visibility into the transaction. The data may be completely legitimate; it just may not belong to the person using it. Conversely, this same insight and capability can allow merchants to safely expand into new geographic markets, by allowing legitimate international transactions, without disruption, and without requiring an army of personnel to do the investigative work. Companies like 41st Parameter, a part of Experian, have spent a decade perfecting the art of how to detect the fraudster in the online anonymous environment. See how we can help bolster your business defenses, while allowing your business to grow safely into new regions – and take advantage of the millions of customers that might have a hankering for your products. After Heartbleed: are you vulnerable?

With the cost of new vehicles continuing to increase, consumers are opting for longer loan terms.

Apple held its annual developers conference last week to showcase its new features within iOS8. One area that still needs clarification is Apple’s intent for mobile payments. Cherian Abraham, Experian Decision Analytics mobile payments analyst, shares what he thinks Apple might look to do in the mobile payment space going forward. In my first post, I touched upon Apple’s program for third party hardware attachment market as being significant and likely to be a key aspect of its payments approach. In this post I discuss these three things: 1. How Apple’s new security paves the way for mobile payments 2. Bluetooth being secured enough where Payments is a use-case 3. Why the iPhone 6 will not have NFC Last week, 9to5mac reported that Apple has introduced a new specification for manufacturers in its MFi program (Made for iPad, iPhone and iPod) that allows them to create headphones that connect to iOS devices using a lightning connector instead of relying on the 3.5mm audio jack. Why is it important? Because as Apple looks to rid itself of any such remaining legacy vestiges, it’s also shedding any ambiguity around who is in control of the iOS hardware ecosystem and what it means to be a third party accessory maker – once reliant on open standards supported by all devices and now serving at Apple’s pleasure. It is a strategy that fits against the backdrop of an iOS ecosystem that is made up of software that is increasingly becoming more open, and hardware that is slowly being walled off – primarily in the name of security. The former is evident in how Apple has opened up third-party access to core authentication services like TouchID. What about the latter? Apple’s new security blanket Well, first let’s look at what Apple has publicly acknowledged about the MFi program. Every iOS device will initiate communication with a third-party accessory by asking it to prove sufficient authorization by Apple — to respond with an Apple-provided certificate, which iOS subsequently verifies. Further, the iOS device then issues a challenge, which is then answered by the third-party accessory by a signed response. These two steps require that a third-party accessory must have: • An Apple certificate • Requisite cryptographic capabilities — preferably in hardware to comply. That is precisely what Apple does by encapsulating all this in an Integrated Circuit that it controls – where the entire handshake is transparent to the accessory. With this – Apple’s role in the third-party accessory market becomes non-negotiable. You think you have a cool accessory that requires a trusted connection and intends to share data with an iOS device? Unless you inherit Apple’s controls you are relegated to speaking analog and conducting a limited set of user-driven operations — Start, Pause, Rewind (standard Serial UART audio playback controls) — usable only to headphones using the audio jack. Now, how about them apples? It’s important to note that these steps to validate whether an accessory is authorized to communicate with an iOS device can happen over the lightning connector, Bluetooth or WiFi. The advantage here is that this repels man-in-the-middle attacks because a malicious interceptor will not have the Apple IC to pass authorization, and subsequently will not have the negotiated key that encrypts all subsequent communication. The whole key negotiation occurs over Bluetooth. It is important because this approach can solve man-in-the-middle attacks for Bluetooth in scenarios including payments. A cynical view of the MFi program would be to consider it a toll that Apple is eager to extract from the third-party accessory makers building accessories authorized to communicate with an iOS device. A more pragmatic view would be to recognize Apple’s efforts as an ecosystem owner, whose primary intent is authenticating any and all devices within and in the periphery of the iOS ecosystem and secure all inbound and outbound data transfers. With more iOS device types, and a heterogeneous accessory market Apple is entirely justified in its role as the ecosystem owner to be at the front of the curve, to ensure security is not an afterthought - and instead to – mandate that data in transit or at rest is fully secured at all end-points. In fact, interest in Wearables, Home automation, Healthcare and Telematics are completely rewiring the rules of what it means to be an accessory anymore I believe this approach to security will be the mainstay of how Apple visualizes its role in enabling payments — regardless of channel. Anything it does to reduce payments friction will be counterbalanced by serious cryptographic measures that secure devices that have a need to communicate in payments — to authenticate, to encrypt and to subsequently transfer a payment token. With TouchID today it does so by verifying the fingerprint before authorizing the transmission of an authentication token from the Secure Enclave to an Apple server in the cloud. I don’t doubt that the authentication token being sent to the Apple server in the cloud is itself signed by the device’s unique ID – which is verified, before the server completes the purchase with a card on file. Thus, crypto pervades everything the iPhone does, touches or trusts. So how do the MFi program, Bluetooth, iOS Security fit in within Apple’s plan to tackle retail payments? For that, let’s start with NFC. With NFC anointed as the only way forward by networks and other stakeholders — every other approach was regarded as being less secure without much thought given to that classification by way of actual risk of fraud. You could build the best payments “whatchamacallit” and throw everything and the kitchen sink at it — and be still branded as ‘Card Not Present’ and inherit a higher cost. Understandably — merchants passed on it as they couldn’t scale with the costs that it confronted. No self-respecting merchant could afford to scale — unless they owned all of the risk (via decoupled debit, ACH or private label). All they could do was reject contactless and prevent themselves from being burdened by the network’s definition of a payments future. Thus the current NFC impasse was born. Now with merchants rolling out EMV-compliant terminals, many of which have contactless built in, they are desperately looking to Apple for clarity. If Apple does NFC then they have the entirety of a terminal refresh cycle (approximately 10 years) within which they hope that common sense may prevail (for example, debit as an acceptable payments choice via contactless) and correspondingly toggle the switch to begin accepting contactless payments. If Apple goes in a different direction, a merchant who has chosen an EMV-compliant terminal with or without contactless is locked out until the end of the current refresh cycle. But what if Apple went with Bluetooth? Two factors stand in the way: Bluetooth is not secure enough for payments today and terminal makers need to comply. Yet, with EMVCo publishing draft standards around tokenization one can argue that non-NFC modalities now are being given fair share, where proximity is not the only guarantee for security and other options such as Bluetooth can begin to address the challenge creatively. Where is the opportunity among all this for Bluetooth? Let’s tackle Bluetooth Range and Device Pairing that limit its utility in payments today. Range is as much a curse as it is a blessing for Bluetooth. If security via proximity was NFC’s raison d’être, then in contrast Bluetooth had to worry about man-in-the-middle attacks due to its range. Though Bluetooth communication is invariably always encrypted, the method in which two devices arrive at the encryption key is suboptimal. Since much of the early key negotiation between devices happens in the clear, brute forcing the shared secret that is key to encryption is a fairly easy and quick attack — and the range makes man-in-the-middle attacks easy to implement and harder to detect. The approach to device pairing also differs from Bluetooth to BLE. Needless to say, it is even less secure for BLE. Pairing in a payments context brings up further challenges, as it has to be silent, customer initiated and simple to execute. I am not going to pair my iPhone with a point-of-sale by punching in “000000” or another unique code each time I must pay Can NFC be of use here? It can. In fact, Bluetooth pairing is the only use case where I believe that Apple may feel there is utility for NFC so that an out-of-band key exchange can be possible (versus an in-band key exchange wholly over Bluetooth). This is far more secure than using Bluetooth alone and derives a much stronger encryption key. An out-of-band key exchange thus enables both devices to agree on a strong encryption key that can prevent malicious third parties from splicing themselves in the middle. BLE however does not allow for out-of-band key exchange and therefore is limited in its utility. This is another reason why if you are a BLE accessory maker Apple excludes you from having to participate in the MFi program. How can Apple secure Bluetooth and make it the standard of choice for a retail payment use case? The answer to that lies inside Apple’s specification for MFi participants — manifested in the form of the Integrated Circuit Apple provides to them so that these iOS accessories may authorize themselves to an iOS device and secure the communication that follows. This IC which encapsulates the initial setup including the certificate, mutual key negotiation and deriving the encryption key — can support Bluetooth. So if all that ails Bluetooth can be cured by including an IC – will point-of-sale manufacturers like Verifone and Ingenico line up to join Apple’s MFi program? The message is clear. You must curry favor with Apple if you want to be able to securely communicate with the iOS ecosystem. That is no tall barrier for terminal makers who would willingly sacrifice far more to be able to speak to 800M iOS devices and prevent being made irrelevant in an ever-changing retail environment. So why not include a single IC and instantaneously be able to authorize to that broad ecosystem of devices, and be capable of trusted communication? And if they do — or when they do — how will merchants, networks and issuers react? Today a point of sale is where everything comes together — payments, loyalty, couponing — and it’s also where everything falls apart. Will this be considered Card Present? Even with all the serious crypto that would become the underpinnings of such a system, unfairly or not the decision is entirely that of a few. Networks and issuers To answer how they may respond, we must ask how they may be impacted by what Apple builds. Is Apple really upending their role in the value chain? I believe Apple cares little about the funding source. Apple would instead defer to – the merchants who believe it should be debit, and the issuers who believe the customer should choose – and secretly hope that it is credit. I don’t think that Apple would want to get between those two factions. It wants to build simply the most secure, easy way to bring retail payments to iOS devices — and allow all within the transaction flow to benefit. The rails do not change, but the end-points are now much more secured than they ever were, and they form a trusted bond and a far bigger pipe. A customer who authenticates via TouchID, a phone that announces to the point of sale that it’s ready to talk, a smart circuit that negotiates the strongest encryption possible while being invisible to all and a token that stands in for your payment credential that is understood by the point of sale. It is business as usual, and yet not. Will the iPhone6 have NFC? The presence of NFC in iPhone6 — if it’s announced — will not mean that NFC will be utilized in the same manner as it is today (for example, Isis). The radio will exist, but there will be no global platform secure element. Today the role of the radio is instrumental (in both secure element or HCE cases) in transmitting the PAN to the point of sale. When there are coupons that need to be presented and reconciled at the point of sale — things begin to get complex. Since the radio becomes the bottleneck, it requires longer than a quick tap for more data to be transmitted. Proximity is a good guarantee for device presence as well as the customer, but it’s a poor vehicle for information. So why wouldn’t one try to relegate it to the initial handshake to enable authentification of the device and therefore the customer with the point of sale? As I mentioned above, if Apple uses NFC, its role will be to facilitate an out-of-band key exchange to secure the subsequent Bluetooth communication so that an iOS device can trust the point of sale and securely transmit payment data. This data may include any and all tokenized payment credential along with loyalty, couponing and everything else. By using NFC for out-of-band authentication in conjunction with the authentication IC (provided by Apple) in the point of sale, Apple can run circles around the limitations imposed by a pure NFC approach — exceeding it on usability, security, adaptability and merchant utility. Yet, if NFC’s role is limited to the initial key negotiation, then the case can be made that NFC has very limited utility, it exists only to serve Apple’s security narrative, and utilizing NFC for the initial pairing strengthens the encryption and makes it harder to snoop. If it has only derived incremental value, would Apple care to put it on iPhone6 — and split its utility among customers using iPhone6 versus all others? With more than 400M iPhones out there that can support Bluetooth LE and iOS8, why ignore that advantage and create a self-induced dependency on a radio that has no subscribers today? So where do I fall within this debate? I believe iPhone6 will not have NFC. Learn more about our Global Consulting Practice.