Time heals countless things, including credit scores. Many of the seven million people who saw their VantageScore® credit scores drop to sub-prime levels after suffering a foreclosure or short sale during the Great Recession have recovered and are back in the housing market.
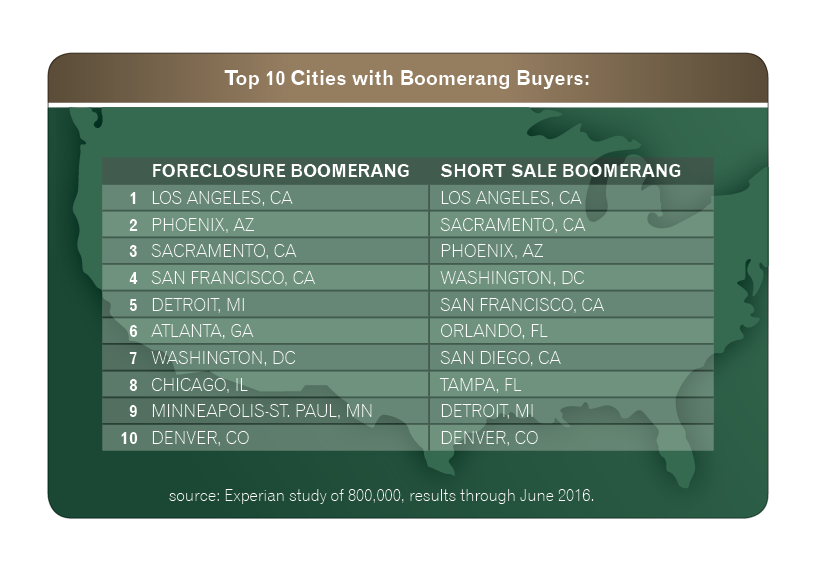
These Boomerang Buyers — people who foreclosed or short sold between 2007 and 2014 and have opened a new mortgage — will be an important segment of the real estate market in the coming years. According to Experian data, through June 2016 roughly 800,000 people had boomeranged, with Los Angeles, Phoenix, and Sacramento housing the most buyers.
Some analysts believe more than three million Americans will become eligible for a home over the next three years.
Are potential Boomerang Buyers a great opportunity to boost market share or a high risk for a portfolio?
Early trends are positive. The majority of Boomerang Buyers who opened mortgages between 2011 and June 2016 are current on their debts.
An Experian study revealed more than 29 percent of those who short sold have boomeranged, and just 1.5 percent are delinquent on their mortgage —falling below the national average of 2.8 percent. This group is also ahead of or even with the national average for delinquency on auto loans (1.2 percent vs. the national average of 2.2 percent), bankcards (3 percent vs. 4.3 percent) and retail (even at 2.7 percent).
For those Boomerang Buyers who had foreclosed, the numbers are also strong. More than 12 percent have boomeranged, with just 3 percent delinquent on their mortgage. They also match or are below national average delinquency rates on auto loans (1.9 percent) and bankcards (4.1 percent), and have a slightly higher delinquency rate for retail (3.5 percent).
Due to their positive credit behaviors, Boomerang Buyers also have higher VantageScore® credit scores than before.
On average, the overall non-boomerang group’s credit score sunk during a foreclosure but went up 10 percent higher than before the foreclosure, and Boomerang Buyers rose by nearly 14 percent. For people who previously had a prime credit score, their number dropped by nearly 5 percent, while those who boomeranged returned to the score they had prior to the foreclosure.
By comparison, the overall non-boomerang and boomerang group saw their credit score drop during a short sale and increase more than 11 percent from before the short sale. For people who previously had prime credit, they dropped 2 percent while those who boomeranged were almost flat to where they were before the short sale.
Another part of the equation is the stabilized housing market and relatively low loan-to-value (LTV) limits that lenders have maintained.
In the past, borrowers most often strategically defaulted on their mortgages when their LTV ratios were well over 100 percent.
So as long as lenders maintain relatively low LTV limits and the housing market remains strong, strategic default is unlikely to re-emerge as a risk.