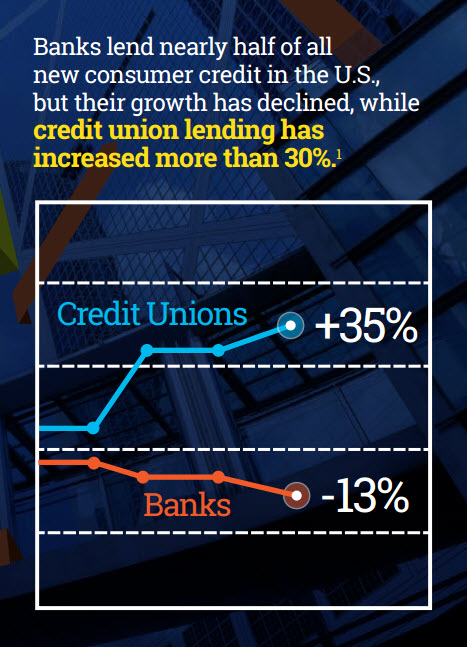
Credit Lending

By: Maria Moynihan At a time when people are accessing information when, where and how they want to, why aren’t voter rolls more up to date? Too often, voter lists aren’t scrubbed for use in mailing, and information included is inaccurate at the time of outreach. Though addresses and other contact information becomes outdated, new address identification and verification has not typically been a resource focus. Costs associated with mandated election-related communications between government and citizens can add up, especially if messages never get to their intended recipients and, in turn, Registrar Offices never get a response. To date, the most common pitfalls with poorly maintained lists have been: Deceased records — where contact information for deceased voters has not been removed or flagged for mailing Email and address errors — where those who have moved or recently changed information failed to update their records, or where errors in the information on file make it unlikely for the United States Postal Service® to reach individuals effectively Duplicate records — where repeat records exist due to update errors or lack of information standardization With resources being tighter than ever, Registrar Offices now are placing emphasis on mailing accuracy and reach. Through third-party-verified data and advanced approaches to managing contact information, Registrar Offices can benefit from truly connecting with their citizens while saving on communication outreach efforts. Experian Public Sector recently helped the Orange County Registrar of Voters increase the quality of its voter registration process. Click here to view the write-up, or stay tuned as I share more on progress being made in this area across states.

One of the challenges that we hear from many of our clients is managing multiple collection agencies in order to recover bad debts. Collection managers who use multiple collection agencies recognize the potential upside to utilizing multiple agencies. Assigning allocate accounts to different agencies based on geography, type of account, status of account (such as a skip), first, second or third placement, and other factors may lead to greater recoveries than just using a single agency. Also, collection managers recognize the advantage of pitting agencies against each other in a positive manner to achieve significantly better results. However this can present a challenge in that the more agencies collection managers use, the greater the risk of losing operational control. Here are some questions to ask before engaging in a multiple collection agency strategy: Do you know which agency has which accounts? Were some accounts accidently assigned to more than one agency? Is it easy to locate an account with an agency if it needs to be withdrawn from it? Is information flowing from one agency to another if agencies are used for second and third placements? Managing multiple agencies can get complex pretty quickly, but rather than just using one agency to avoid these complexities, there is an alternative to consider: Loss of control can be overcome with effective systems that allocate and manage accounts assigned to multiple agencies. These systems allow for the allocation, recall, activity tracking, performance reporting, and commission calculations or vendor audits. No more spreadsheets or other time consuming, error prone manual processes. Experian can help with its agency allocation and management solutions through Tallyman Agency Allocation. Learn more about our Tallyman Agency Allocation software.

by John P. Robertson, Senior Business Process Specialist As a Senior Business Process Specialist for the Experian Decision Analytics, John provides guidance to clients in the areas of profitability strategies for risk based pricing and relationship profitability. He assists banks in developing and implementing successful transitions for commercial lending that improve both the financial efficiency of the lending process and the productivity of the lending officers. John has 26 years of experience in the banking industry, with prior background in cash, treasury, and asset /liability management. For quite some time now, the banking industry has experienced a flat funding curve. Very small spreads have existed between the short and long term rates. Slowly, we have begun to see the onset of a normalized curve. At this writing, the five year FHLB Advance rate is about 2.00%. A simplistic view of loan pricing looks something like this: + Interest Income + Non-Interest Income - Cost of Funds - Non-Interest Expense - Risk Expense = Income before Tax The example is pretty simple and straight forward, “back of the napkin” kind of stuff. We back into a spread needed to reach breakeven on a five year fixed rate loan by using the UBPR (Uniform Bank Performance Report) national peer average for Non-Interest Expense of approximately 3.00%. You would need a pre-tax rate requirement of 5.00% before you consider the risk and before you make any money. If you tack on 1.00% for risk and some kind of return expectation, the rate requirement would put you around a 6.00% offering level. From a lender’s perspective, a 6.00% rate on a minimal risk five year fixed rate loan doesn’t exist. They might as well go home. CFO’s have been asking themselves, “What do we do with this excess cash? We get such a paltry spread. How can we put higher yielding loans on our books at today’s competitive rates? We’ve got plenty of capital even with the new regulation requirements so can we repo the securities and use the net spread for our cost of funds?” Leveraging the excess cash and securities in order to meet the pressing rate demands may be a way banks have been funding selective loans at such low rates on highly competitive, quality loan originations of size. But you have to wonder, what about that old adage, “You don’t short fund long term loans.” Won’t you eventually have to deal with compression and “margin squeeze”? Oh and by the way, aren’t you creating a mismatch in the balance sheet which requires explanation. Are they buying a swap to extend the maturity? If so, are they really making their targeted return? If this is what they are doing, why not just accept a lower return but one that is better than the securities? Share your thoughts with me.

Every prospecting list needs to be filtered by your organizations specific credit risk threshold. Whether you’re developing a campaign targeting super-prime, sub-prime, or consumers who fall somewhere in between, an effective credit risk model needs to do two things: 1) accurately represent a consumer’s risk level and 2) expand the scoreable population. The newly redeveloped VantageScore® credit score does both. With the VantageScore® credit score, you get a scoring model that’s calibrated to post-recession consumer behavior, as well the ability to score nearly 35 million additional consumers - consumers who are typically excluded from most marketing lists because they are invisible to older legacy models. Nearly a third of those newly-scoreable consumers are near-prime and prime. However, if your market is emerging to sub-prime consumers - you’ve found the mother-load! Delinquency isn’t the only risk to contend with. Bankruptcies can mean high losses for your organization at any risk level. Traditional credit risk models are not calibrated to specifically look for behavior that predicts future bankruptcies. Experian's Bankruptcy PLUS filters out high bankruptcy risk from your list. Using Bankruptcy PLUS you’re able to bring down your overall risk while removing as few people as possible. My next post looks into ways to identify profitable consumers in your list. For more see: Four steps to creating the ideal prospecting list.

Companies are facing incredible difficulties identifying fraud risks at the point of origination. Setting up accurate fraud detection processes has become more and more challenging as mobile and online channels have become widely used by consumers. At the same time, fraudsters’ techniques are becoming increasingly sophisticated. To compensate, organizations have had the choice of either: a) Implementing very tough identity-proofing standards — risking turning away legitimate customers. b) Lessening their criteria and opening themselves to increased risk. Any business that functions in a web connected environment that has a need to recognize new or returning consumers must look beyond the simple credentials that have been provided by the user such as usernames, passwords, email addresses, phone numbers, handles, secret questions or secret answers. To increase assurance businesses need to start need to start looking at authenticating users through their devices that are being used to present those credentials. The underground is awash in legitimate but stolen credentials and should be treated with a great deal of skepticism by the businesses attempting to authenticate their customers. There will always be a pendulum swaying in the echoes of this kind of news – with businesses locking down access with more stringent policies and in doing so they begin to undo all the work that has been done to create a frictionless consumer experience. The industry may now begin to realize the ultimate dream of the consumer: completely effortless access. Rather than requiring consumers to type in credentials that may have been compromised why not leverage the various technologies that exist to simply recognize the consumer when they access the site in question? Digital consumers interact with businesses via their digital proxies – their devices – which must come in digital contact with the web servers in order to gain access. The industry should require the machines to do heavy lifting (rather than consumers) when it comes to “recognizing” them when they return. The right technology offers a more robust, privacy-compliant and transparent way for businesses to recognize their digital consumers. As we’ve discussed previously the authentication process will shift from a single view to a layered, risk-based authentication approach that will include comprehensive and real-time updates of consumer information. This is done through technology that has been tested over the years and protects millions of customer accounts today with incredible results in terms of both fraud detection and frictionless consumer experience. The time has come to embrace the realities and the possibilities of the new digital environment in which we operate. Learn more about how your business can authenticate consumers confidently.
By: Mike Horrocks As summer comes to end, so does the summer reading list but if you are still trying to get one in, I just finished reading “Isaac's Storm: A Man, a Time, and the Deadliest Hurricane in History”, which is about Isaac Cline the resident meteorologist for U.S. Weather Bureau and the 1900 Hurricane that devastated Galveston, Texas. It is a great read, using actual telegraphs, letters, and reports to show the flaws of an outdated system and how not looking to new sources of information and not seeing the values of nontraditional views, etc., lead to unfathomable destruction for the people of Galveston. As I read the book, I was challenged to think of what is right in front of me that I am not seeing for what it is, just like Mr. Cline ignored reports that would have clearly saved lives and helped predict the storm. So, how can this historical storm teach us a thing or two in the financial industry? Clearly one of the most rapidly changing aspects in banking today is the mobile channel. Many institutions have already adjusted to using it as a service channel, with remote deposit capture, balance, inquiry etc., but what are they doing to take it to the next step? On August 7, 2014, Experian is hosting a webinar by American Banker titled, “What is next for mobile banking?” The webinar will have a powerful panel with thought leaders such as Dominic Venturo, the Chief Innovation Officer at U.S. Bank, Gordon Baird, the Chief Executive Officer at Independence Bancshares, and Cherian Abraham, Senior Business Consultant with Experian’s Global Consulting Practice. If you are already using mobile or maybe trying to look at what you could change, this is a great session to attend. Over the next couple of weeks, we are going to go into some of the key topics from this webinar and explore them some more. Hope to see you at this American Banker webinar.

At Experian, we frequently get asked by clients how they can get bigger mailing list that open new markets and reach more people. But bigger isn’t necessarily better, and it doesn’t always translate to a higher return on your marketing investment. Instead of just increasing volume, let’s consider a different, more focused approach - using the latest in analytic tools and scores. This approach relies on effective pre-screening to create the ideal prospecting lists based on your business objective. We’ve identified four key steps to building a prescreen list of your ideal prospects: Optimize risk selection Find the most profitable consumers Target customers who need or want your products Design the right offer In the next post, Optimal Risk Selection, I’ll dig deeper into each step and present some tools and scores that can help meet the objective of each.

By: Teri Tassara “Do more with less” is a pervasive and familiar mantra nowadays as lenders seek to make smarter and more precise lending decisions while expertly balancing growth objectives and tightened budgets. And lest we forget, banks must also consider the latest regulations and increased regulatory scrutiny from the industry’s governing bodies - such as OCC and CFPB. Nowadays, with the extensive application of predictive analytics in everyday lending practices, it makes sense to look to analytics to fine tune decision-making and achieve a greater return on investment in three common growth objectives for bankcard acquisitions: Profitable growth - How do I find the most profitable acquisition targets? How do I know the borrowing characteristic of each consumer? Are they high spend or high income? Do they carry a balance but always make timely payments? Universe expansion - How many more consumers are there that meet my lending criteria? How can I effectively reach them? Customer experience - How do I offer the right product to the right customer? How do I communicate to my customers that I understand their lending needs? To that end, growth objectives vary by lender; as such, so should their bankcard acquisitions analytical toolkit. The analytical toolkit arsenal should enable lenders to develop refined bankcard campaign strategies based on their specific objectives. Look for upcoming posts on the essential components of the bankcard acquisitions analytical toolkit.
Residential real estate lending was the leading component of the Great Recession of 2007-2009. Could it happen again? Let’s analyze our Intelliview data to see where U.S. lending trends are headed with HELOCs. A large portion of Home Equity Lines of Credit (HELOCs) were originated from 2004 to 2007. The term structure of these HELOCs will soon result in larger monthly payments, which could potentially promote consumer debt burden troubles. Additionally, with as much as 13% of all first mortgage customers having balances greater than the value of homes, many HELOCs wallow underwater. HELOCs typically have a ten year draw followed by a twenty-year repayment period. However, there are variations in the term structures. HELOCs can have as little as a five year draw, while others have a fifteen year repayment period. During the draw period, customers only pay interest on the balance. In the repayment period, the account functions like a loan, customers pay principal and interest. In 2012, the Office of Comptroller of the Currency (OCC, the primary banking regulator) reported that 58% of all bank HELOC balances would enter the repayment period and begin to amortize between 2014 and 2017 (OCC, Semiannual Risk Perspective, Spring 2012). This report renewed fears that the increase in payments would lead to higher delinquencies and foreclosures, limit consumer spend and provide a drag on the U.S. economy. Paradoxically, the OCC estimates of the HELOC balances entering the repayment period may be low. The OCC has accounted only for $392 billion of HELOC balances among banks. Experian’s review of all HELOC trades shows a significantly higher level of balances. Additionally, American Banker estimates the top 200 banks and thrifts had more than $477 billion in HELOC outstanding as of the end of 2013, with the top three lenders (Bank of America, Wells Fargo and JP Morgan Chase) comprising nearly $300 billion. Experian examined HELOCs in the four states with the greatest surges in home values and lending prior to the Great Recession. California comprises nearly 19% of all HELOC balances and lines. With averaging HELOC balances of 53% above the national mean, Arizona, Florida and Nevada are the three highest utilization rates by state. Nevada has the highest 30+ day delinquency rate in the country at 2.92%, while the national average is 1.64%. According to CoreLogic’s most recent home price index report, Nevada, Florida and Arizona home prices remain 30-39% below their peak real estate values. California’s prices are down 17%, and the national average home value is still 14% below its highest value. Refinancing HELOCs may be difficult due to the significant number of second liens still underwater. Compounding this difficulty, lending standards also have tightened, with regard to loan-to-value, debt ratios and credit quality. The average HELOC was examined at a 4.5% interest rate and a 20 year repayment period. The average monthly payment increases almost 69% when the account leaves the draw period and requires paying principal balance as well as interest. This payment increase accounts for approximately 2.6% of the median U.S. household gross annual income. It is estimated that the increase in HELOC payments will comprise $1 billion in additional annual payments during 2014, and an additional $9 billion between 2015 through 2017. However, it is important to remember that not all HELOCs will reach repayment. HELOCs are priced based on the prime rate. That rate has been 3.25% for more than five years, a historical low. When prime rate reached this level in December 2008, the rate was at its lowest in 53 years. Only 18 months prior to reaching 3.25%, the prime rate had been 8%. If the prime rate increases by 1% to 4.25%, the average payment of accounts in the draw period would increase 22%, affecting just about every HELOC, with a national increase in annual payments of about $5 billion. The volume of HELOCs that are beginning to enter the repayment period may eventually increase delinquency rates. However, no such increase is yet evident. As shown below, delinquency rates are steady after a long decline. In the past three years, 90+ days delinquency has declined 41%. The Majority of HELOCs are second mortgages. Successful completion of a foreclosure would involve making the customer’s monthly first mortgage payment in addition to all other expenses incurred in foreclosure and the sale of the property. Very often foreclosing from a second lien does not make financial sense unless the financial institution also holds the first mortgage on the property. As a large portion of HELOCs enter the repayment period in the next four years, the payments that customers must make will increase considerably. With interest rates as low as they are, the prime rate will eventually rise, and increase debt service ratios. These payment increases will have implications on consumers, lenders and the economy. Having grown 10.5% in the last year, home values continue to recover from the recession. It is yet to be determined whether this payment increase will have a broader or more isolated impact. In the meantime, HELOCs will continue to see their resurgence. For more insight like this from Experian Decision Analytics, watch our 2014 Q1 Experian–Oliver Wyman Market Intelligence Report presentation.
Are you sure you are making the best consumer credit decisions? Given the constantly evolving market conditions, it is a challenge to keep informed. In order to confidently grow and manage the bottom line, organizations need to avoid these four basic risks of making credit decisions with limited trend visibility. Competitive Risk - With limited visibility to industry trends, organizations cannot understand their position relative to peers. Product Risk - Organizations without access to the latest consumer behaviors cannot identify and capitalize on emerging trends. Market Risk - Decisions suffer when made without considering market trends in the context of the economy. Resource Risk - Extracting useful insights from vast market data requires abundant resources and comprehensive expertise. Get more information on the business risks of navigating credit decisions with limited trend visibility.

By: Mike Horrocks Living just outside of Indianapolis, I can tell you that the month of May is all about "The Greatest Spectacle in Racing", the Indy 500. The four horsemen of the apocalypse could be in town, but if those horses are not sponsored by Andretti Racing or Pennzoil – forget about it. This year the race was a close one, with three-time Indy 500 winner, Helio Castroneves, losing by .06 of a second. It doesn’t get much closer. So looking back, there are some great lessons from Helio that I want to share with auto lenders: You have to come out strong and with a well-oiled machine. Castroneves lead the race with no contest for 38 laps. You cannot do that without a great car and team. So ask yourself - are you handling your auto lending with the solution that has the ability to lead the market or are you having to go to the pits often, just to keep pace? You need to stay ahead of the pack until the end. Castroneves will be the first to admit that his car was not giving him all the power he wanted in the 196th lap. Now remember there are only 200 laps in the race, so with only four laps to go, that is not a good time to have a hiccup. If your lending strategy hasn't changed "since the first lap", you could have the same problem getting across the the finish line? Take time to make sure your automated scoring approach is valid, question your existing processes, and consider getting an outside look from leaders in the industry to make sure your are still firing on all cylinders. Time kills. Castroneves lost by .06 seconds. That .06 of a second means he was denied access into a very select club of four time winners. That .06 of a second means he does not get to drink that coveted glass of milk. If your solution is not providing your customers with the fastest and best credit offers, how many deals are you losing? What exclusive club of top auto lenders are you being denied access to? Second place is no fun. If you're Castroneves, there's no substitute for finishing first at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway. Likewise, in today’s market, there is more need than ever to be the Winner’s Circle. Take a pit stop and check out your lending process and see how you're performing against your competitors and in the spirit of the race – “Ladies and gentlemen, start your engines!”
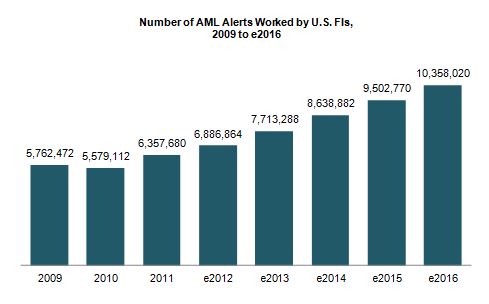
Julie Conroy - Research Director, Aite Group Finding patterns indicative of money laundering and other financial crimes is akin to searching for a needle in a haystack. With the increasing pressure on banks’ anti-money laundering (AML) and fraud teams, many with this responsibility increasingly feel like they’re searching for those needles while a combine is bearing down on them at full speed. These pressures include: Regulatory scrutiny: The high-profile—and expensive—U.S. enforcement actions that took place during the last couple of years underscore the extent to which regulators are scrutinizing FIs and penalizing those who don’t pass muster. Payment volumes and types increasing: As the U.S. economy is gradually easing its way into a recovery, payment volumes are increasing. Not only are volumes rebounding to pre-recession levels, but there have also been a number of new financial products and payment formats introduced over the last few years, which further increases the workload for the teams who have to screen these payments for money-laundering, sanctions, and global anti-corruption-related exceptions. Constrained budgets: All of this is taking place during a time in which top line revenue growth is constrained and financial institutions are under pressure to reduce expenses and optimize efficiency. Illicit activity on the rise: Criminal activity continues to increase at a rapid pace. The array of activity that financial institutions’ AML units are responsible for detecting has also experienced a significant increase in scope over the last decade, when the USA PATRIOT Act expanded the mandate from pure money laundering to also encompass terrorist financing. financial institutions have had to transition from activity primarily focused on account-level monitoring to item-level monitoring, increasing by orders of magnitude the volumes of alerts they must work (Figure 1) Figure 1: U.S. FIs Are Swimming in Alerts Source: Aite Group interviews with eight of the top 30 FIs by asset size, March to April 2013 There are technologies in market that can help. AML vendors continue to refine their analytic and matching capabilities in an effort to help financial insitutions reduce false positives while not adversely affecting detection rates. Hosted solutions are increasingly available, reducing total cost of ownership and making software upgrades easier. And many institutions are working on internal efficiency efforts, reducing vendors, streamlining processes, and eliminating the number of redundant efforts. How are institutions handling the increasing pressure cooker that is AML compliance? Aite Group wants to know your thoughts. We are conducting a survey of financial insitution executives to understand your pain points and proposed solutions. Please take 20 minutes to share your thoughts, and in return, we’ll share a complimentary copy of the resulting report. This data can be used to compare your efforts to those of your peers as well as to glean new ideas and best practices. All responses will be kept confidential and no institutions names will be mentioned anywhere in the report. You can access the survey here: SURVEY

As we discussed in our earlier Heartbleed post, there are several new vulnerabilities online and in the mobile space increasing the challenges that security professionals face. Fraud education is a necessity for companies to help mitigate future fraud occurrences and another critical component when assessing online and mobile fraud is device intelligence. In order to be fraud-ready, there are three areas within device intelligence that companies must understand and address: device recognition, device configuration and device behavior. Device recognition Online situational awareness starts with device recognition. In fraudulent activity there are no human users on online sites, only devices claiming to represent them. Companies need to be able to detect high-risk fraud events. A number of analytical capabilities are built on top of device recognition: Tracking the device’s history with the user and evaluating its trust level. Tracking the device across multiple users and evaluating whether the device is impersonating them. Maintaining a list of devices previously associated with confirmed fraud. Correlation of seemingly unrelated frauds to a common fraud ring and profiling its method of operation. Device configuration The next level of situational awareness is built around the ability to evaluate a device’s configuration in order to identify fraudulent access attempts. This analysis should include the following capabilities: Make sure the configuration is compatible with the user it claims to represent. Check out internal inconsistencies suggesting an attempt to deceive. Review whether there any indications of malware present. Device behavior Finally, online situational awareness should include robust capabilities for profiling a device’s behavior both within individual accounts and across multiple users: Validate that the device focus is not on activity types often associated with fraud staging. Confirm that the timing of the activities do not seem designed to avoid detection rules. By proactively managing online channel risk and combining device recognition with a powerful risk engine, organizations can uncover and prevent future fraud trends and potential attacks. Learn more about Experian fraud intelligence products and services from 41st Parameter, a part of Experian.
The discovery of Heartbleed earlier this year uncovered a large-scale threat that exploits security vulnerability in OpenSSL posing a serious security concern. This liability gave hackers access to servers for many Websites and put consumers’ credentials and private information at risk. Since the discovery, most organizations with an online presence have been trying to determine whether their servers incorporate the affected versions of OpenSSL. However, the impact will be felt even by organizations that do not use OpenSSL, as some consumers could reuse the same password across sites and their password may have been compromised elsewhere. The new vulnerabilities online and in the mobile space increase the challenges that security professionals face, as fraud education is a necessity for companies. Our internal fraud experts share their recommendation in the wake of the Heartbleed bug and what companies can do to help mitigate future occurrences. Here are two suggestions on how to prevent compromised credentials from turning into compromised accounts: Authentication Adopting layered security strategy Authentication The importance of multidimensional and risk-based authentication cannot be overstated. Experian Decision Analytics and 41st Parameter® recommend a layered approach when it comes to responding to future threats like the recent Heartbleed bug. Such methods include combining comprehensive authentication processes at customer acquisition with proportionate measures to monitor user activities throughout the life cycle. "Risk-based authentication is best defined and implemented in striking a balance between fraud risk mitigation and positive customer experience," said Keir Breitenfeld, Vice President of Fraud Product Management for Experian Decision Analytics. "Attacks such as the recent Heartbleed bug further highlight the foundational requirement of any online business or agency applications to adopt multifactor identity and device authentication and monitoring processes throughout their Customer Life Cycle." Some new authentication technologies that do not rely on usernames and passwords could be part of the broader solution. This strategic change involves the incorporation of broader layered-security strategy. Using only authentication puts security strategists in a difficult position since they must balance: Market pressure for convenience (Note that some mobile banking applications now provide access to balances and recent transactions without requiring a formal login.) New automated scripts for large-scale account surveillance. The rapidly growing availability of compromised personal information. Layered security "Layered security through a continuously refined set of ‘locks’ that immediately identify fraudulent access attempts helps organizations to protect their invaluable customer relationships," said Mike Gross, Global Risk Strategy Director for 41st Parameter. "Top global sites should be extra vigilant for an expected rush of fraud-related activities and social engineering attempts through call centers as fraudsters try to take advantage of an elevated volume of password resets." By layering security consistently through a continuously refined set of controls, organizations can identify fraudulent access attempts, unapproved contact information changes and suspicious transactions. Learn more about fraud intelligence products and services from 41st Parameter, a part of Experian.
Both Visa and MasterCard announced their support for Host Card Emulation (HCE) and their intent to release HCE specifications soon. I have been talking about HCE from late 2012 (partly due to my involvement with SimplyTapp) and you could read as to why HCE matter and what Android KitKat-HCE announcement meant for payments. But in light of the network certification announcements yesterday, this post is an attempt to provide some perspective on what the Visa/MasterCard moves mean, how do their approaches differ in certifying payments using cloud hosted credentials, what should issuers expect from a device and terminal support perspective, why retailers should take note of the debate around HCE and ultimately – the role I expect Google to continue to play around HCE. All good stuff. First, what do the Visa/MasterCard announcements mean? It means that it’s time for banks and other issuers to stop looking for directions. The network announcements around HCE specifications provide the clarity required by issuers to meaningfully invest in mobile contactless provisioning and payment. Further, it removes some of the unfavorable economics inherited from a secure element-centric model, who were forced to default to credit cards with higher interchange in the wallet. Renting space on the secure element cost a pretty penny and that is without taking operational costs in to consideration, and as an issuer if you are starting in the red out of the gate, you were not about to put a Durbin controlled debit card in the wallet. But those compulsions go with the wind now, as you are no longer weighed down by these costs and complexities on day one. And further, the door is open for retailers with private label programs or gift cards to also look at this route with a lot more interest. And they are. MasterCard mentioned bank pilots around HCE in its press release, but MCX is hardly the only retailer payment initiative in town. Let me leave it at that. How do the Visa/MasterCard specs differ? From the press releases, some of those differences are evident – but I believe they will coalesce at some point in the future. MasterCard’s approach speaks to mobile contact-less as the only payment modality, whereas Visa refers to augmenting the PayWave standard with QR and in-app payments in the future. Both approaches refer to payment tokens (single or multi-use) and one can expect them to work together with cloud provisioned card profiles, to secure the payment transaction and verify transactional integrity. To MasterCard’s benefit – it has given much thought to ensuring that these steps – provisioning the card profile, issuing payment tokens et al – are invisible to the consumer and therefore refrains from adding undue friction. I am a purist at heart – and I go back to the first iteration of Google Wallet – where all I had to do to pay was turn on the screen and place the device on the till. That is the simplicity to beat for any issuer or retailer payment experiences when using contactless. Otherwise, they are better off ripping out the point-of-sale altogether. MasterCard’s details also makes a reference to a PIN. The PIN will not be verified offline as it would have been if a Secure Element would have been present in the device, rather – it would be verified online which tells me that an incorrect PIN if input would be used to create an “incorrect cryptogram” which would be rejected upstream. Now I am conflicted using a PIN at the point of sale for anything – to me it is but a Band-Aid, it reflects the inability to reduce fraud without introducing friction. Visa so far seems to be intentionally light on details around mandating a PIN, and I believe not forcing one would be the correct approach – as you wouldn’t want to constrain issuers to entering a PIN as means to do authentication, and instead should have laid down the requirements but left it to the market to decide what would suffice – PIN, biometrics et al. Again – I hope these specs will continue to evolve and move towards a more amenable view towards customer authentication. Where do we stand with device and terminal support? All of this is mute if there are not enough devices that support NFC and specifically – Android KitKat. But if you consider Samsung devices by themselves (which is all one should consider for Android) they control over 30% of the NA market – 44.1 million devices sold in 2013 alone. Lion share of those devices support NFC out of the box – including Galaxy Note II and 3, Galaxy S3 and S4 – and their variants mini, Active, Xoom et al. And still, the disparity in their approach to secure elements, continuing lack of availability in standards and Android support – Tap and Pay was largely a dream. What was also worrisome is that 3 months after the launch of Android KitKat – it still struggles under 2% in device distribution. That being said, things are expected to get markedly better for Samsung devices at least. Samsung has noted that 14 of its newer devices will receive KitKat. These devices include all the NFC phones I have listed above. Carriers must follow through quickly (tongue firmly in cheek) to deliver on this promise before customers with old S3 devices see their contracts expire and move to a competitor (iPhone 6?). Though there was always speculation as to whether an MNO will reject HCE as part of the Android distribution, I see that as highly unlikely. Even carriers know a dead horse when they see one, and Isis’s current model is anything but one. Maybe Isis will move to embrace HCE. And then there is the issue of merchant terminals. When a large block of merchants are invested in upending the role of networks in the payment value chain – that intent ripples far and wide in the payments ecosystem. Though it’s a given that merchants of all sizes can expect to re-terminalize in the next couple of years to chip & pin (with contactless under the hood) – it is still the prerogative of the merchant as to whether the contactless capability is left turned on or off. And if merchants toe Best Buy’s strategy in how it opted to turn it off store-wide, then that limits the utility of an NFC wallet. And why wouldn’t they? Merchants have always viewed “Accept all cards” to also mean “Accept all cards despite the form factor” and believes that contactless could come to occupy a higher interchange tier in the future – as questions around fraud risk are sufficiently answered by the device in real-time. This fear is though largely unsubstantiated, as networks have not indicated that they could come to view mobile contact-less as being a “Card Present Plus” category that charges more. But in the absence of any real assurances, fear, uncertainty and doubt runs rampant. But what could a retailer do with HCE? If re-terminalization is certain, then retailers could do much to explore how to leverage it to close the gap with their customer. Private label credit, closed loop are viable alternatives that can be now carried over contactless – and if previously retailers were cut out of the equation due to heavy costs and complexity for provisioning cards to phones, they have none of those limitations now. A merchant could now fold in a closed loop product (like a gift card) in to their mobile app – and accept those payments over contact-less without resorting to clunky QR or barcode schemes. There is a lot of potential in the closed loop space with HCE, that Retailers are ignoring due to a “scorched earth” approach towards contactless. But smarter merchants are asking ‘how’. Finally, what about Google? Google deserves much praise for finally including HCE in Android and paving the way for brands to recognize the opportunity and certify the approach. That being said, Google has no unequal advantage with HCE. In fact, Google has little to do with HCE going forward, despite GoogleWallet utilization of HCE in the future. I would say – HCE has as much to do with Google going forward, as Amazon’s Kindle Fire has to do with Android. Banks and Retailers have to now decide what this means for them – and view HCE as separate to Google – and embrace it if they believe it has potential to incent their brands to remain top of wallet, and top of mind for the consumer. It is a level playing field, finally. Where do you go next? Indeed – there is a lot to take in – starting with HCE’s role, where it fit in to your payment strategy, impact and differences in Visa/MasterCard approaches, weaving all of these in to your mobile assets while not compromising on customer experience. Clarity and context is key and we can help with both. Reach out to us for a conversation. HCE is a means to an end – freeing you from the costs and complexities of leveraging contactless infrastructure to deliver an end-to-end mobile experience, but there is still the question of how your business should evolve to cater to the needs of your customers in the mobile channel. Payment is after all, just one piece of the puzzle.