Financial Services

By: Mike Horrocks The other day in the American Banker, there was an article titled “Is Loan Growth a Bad Idea Right Now?”, which brings up some great questions on how banks should be looking at their C&I portfolios (or frankly any section of the overall portfolio). I have to admit I was a little down on the industry, for thinking the only way we can grow is by cutting rates or maybe making bad loans. This downer moment required that I hit my playlist shuffle and like an oracle from the past, The Clash and their hit song “Should I stay or should I go”, gave me Sage-like insights that need to be shared. First, who are you listening to for advice? While I would not recommend having all the members of The Clash on your board of directors, could you have maybe one. Ask yourself are your boards, executive management teams, loan committees, etc., all composed of the same people, with maybe the only difference being iPhone versus Android?? Get some alternative thinking in the mix. There is tons of research to show this works. Second, set you standards and stick to them. In the song, there is a part where we have a bit of a discussion that goes like this. “This indecision's buggin' me, If you don't want me, set me free. Exactly whom I'm supposed to be, Don't you know which clothes even fit me?” Set your standards and just go after them. There should be no doubt if you are going to do a certain kind of loan or not based on the pricing. Know your pricing, know your limits, and dominate that market. Lastly, remember business cycles. I am hopeful and optimistic that we will have some good growth here for a while, but there is always a down turn…always. Again from the lyrics – “If I go there will be trouble, An' if I stay it will be double” In the American Banker article, M&T Bank CFO Rene Jones called out that an unnamed competitor made a 10-year fixed $30 million dollar loan at a rate that they (M&T) just could not match. So congrats to M&T for recognizing the pricing limits and maybe congrats to the unnamed bank for maybe having some competitive advantage that allowed them to make the loan. However if there is not something like that supporting the other bank…the short term pain of explaining slower growth today may seem like nothing compared to the questioning they will get if that portfolio goes south. So in the end, I say grow – soundly. Shake things up so you open new markets or create advantages in your current market and rock the Casbah!
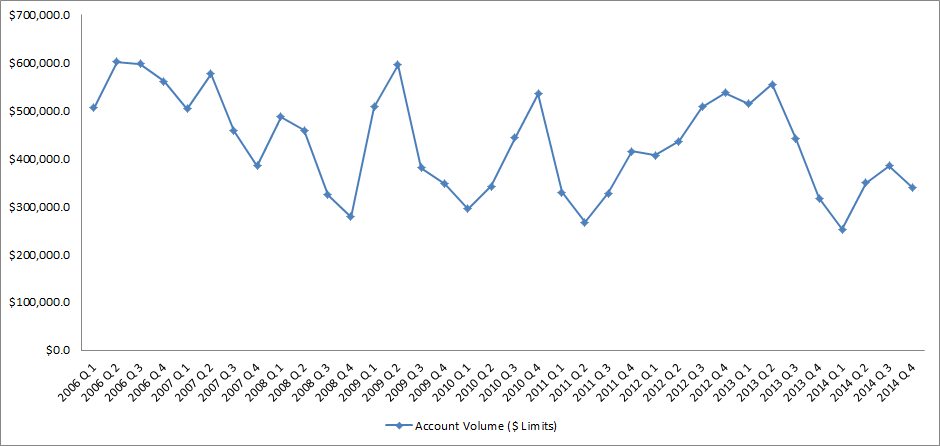
Source: IntelliViewsm powered by Experian Sales of existing homes dropped 50% from the peak in August 2005 to the low point in July 2010. The spike in home sales in late 2009 and early 2010 was due to the large number of foreclosure sales as well as very low prices. Since 2010, sales have increased to almost to the level they were in 2000, before the financial crisis. However, the homeownership rate has steadily gone down. How could sales have picked up while the homeownership rate declined? Investors have entered the market snapping up single family homes and renting them. Therefore, the recent good news in the existing home market has been driven by investors, not homeowners. But as I point out below, this is changing. Looking at the homeownership rate by age, shown in the table below, it is clear that since the crisis the rate has declined most for people under 45. The potential for marketing is greatest in this cohort as the numbers indicate a likely demand for housing. Homeownership Rate by Age Source: U.S. Census Bureau and Haver Analytics as reported on the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Fred database The factors that have impeded growth, described above, are beginning to reverse which, along with pent-up demand, will present an opportunity for mortgage originators in 2015. Home prices have risen in 246 of the 277 cities tracked by Clear Capital.With prices going up, investors have begun to back away from the market, resulting in prices increasing at a slower rate in some cities but they are still increasing.Therefore the perception that homeownership is risky will likely change.In fact, in some areas, such as California’s coastal cities, sales are strong and prices are going up rapidly. Lenders and regulators are recognizing that the stringent guidelines put in place in reaction to the crisis have overly constrained the market.Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac are reducing down payment requirements to as low as 3%.FHA is lowering their guarantee fee, reducing the amount of cash buyers need to close transactions.Private securitizations, which dried up completely, are beginning to reappear, especially in the jumbo market. As unemployment continues to go down, consumer confidence will rise and household formation will return to more normal levels which result in more sales to first time homebuyers, who drive the market.According to Lawrence Yun, chief economist for the National Association of Realtors, “…it’s all about consistent job growth for a prolonged period, and we’re entering that stage.” The number of houses in foreclosure, according to RealtyTrac, has fallen to pre-crisis levels.This drag on the market has, for the most part, cleared and as prices continue to inflate, potential buyers will be motivated to buy before homes become unaffordable.Despite the recent increases, home prices are still, on average, 23% lower than they were at the peak. Focusing marketing dollars on those people with the highest propensity to buy has always been a challenge but in this market there are identifiable targets. “Boomerangs” are people who owned real estate in the past but are currently renting and likely to come back into the market.Marketing to qualified former homeowners would provide a solid return on investment. People renting single family houses are indicating a lifestyle preference that can be marketed to. Newly-formed households are also profitable targets. The housing market, at long last, appears to be finally turning the corner and normalizing. Experian’s expertise in identifying the right consumers can help lenders to pinpoint the right people on whom marketing dollars should be invested to realize the highest level of return. Click here to learn more.

End-of-Draw approaching for many HELOCs Home equity lines of credit (HELOCs) originated during the U.S. housing boom period of 2006 – 2008 will soon approach their scheduled maturity or repayment phases, also known as “end-of-draw”. These 10 year interest only loans will convert to an amortization schedule to cover both principle and interest. The substantial increase in monthly payment amount will potentially shock many borrowers causing them to face liquidity issues. Many lenders are aware that the HELOC end-of-draw issue is drawing near and have been trying to get ahead of and restructure this debt. RealtyTrac, the leading provider of comprehensive housing data and analytics for the real estate and financial services industries, foresees this reset risk issue becoming a much bigger crisis than what lenders are expecting. There are a large percentage of outstanding HELOCs where the properties are still underwater. That number was at 40% in 2014 and is expected to peak at 62% in 2016, corresponding to the 10 year period after the peak of the U.S. housing bubble. RealtyTrac executives are concerned that the number of properties with a 125% plus loan-to-value ratio has become higher than predicted. The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC), the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, and the National Credit Union Administration (collectively, the agencies), in collaboration with the Conference of State Bank Supervisors, have jointly issued regulatory guidance on risk management practices for HELOCs nearing end-of-draw. The agencies expect lenders to manage risks in a disciplined manner, recognizing risk and working with those distressed borrowers to avoid unnecessary defaults. A comprehensive strategic plan is vital in order to proactively manage the outstanding HELOCs on their portfolio nearing end-of-draw. Lenders who do not get ahead of the end-of-draw issue now may have negative impact to their bottom line, brand perception in the market, and realize an increase in regulatory scrutiny. It is important for lenders to highlight an awareness of each consumer’s needs and tailor an appropriate and unique solution. Below is Experian’s recommended best practice for restructuring HELOCs nearing end-of-draw: Qualify Qualify consumers who have a HELOC that was opened between 2006 and 2008 Assess Viability Assess which HELOCs are idea candidates for restructuring based on a consumer’s Overall debt-to-income ratio Combined loan-to-value ratio Refine Offer Refine the offer to tailor towards each consumer’s needs Monthly payment they can afford Opportunity to restructure the debt into a first mortgage Target Target those consumers most likely to accept the offer Consumers with recent mortgage inquiries Consumers who are in the market for a HELOC loan Lenders should consider partnering with companies who possess the right toolkit in order to give them the greatest decisioning power when restructuring HELOC end-of-draw debt. It is essential that lenders restructure this debt in the most effective and efficient way in order to provide the best overall solution for each individual consumer. Revamp your mortgage and home equity acquisitions strategies with advanced analytics End-of-draw articles

By: Kyle Enger, Executive Vice President of Finagraph Small business remains one of the largest and most profitable client segments for banks. They provide low cost deposits, high-quality loans and offer numerous cross-selling opportunities. However, recent reports indicate that a majority of business owners are dissatisfied with their banking relationship. In fact, more than 33 percent are actively shopping for a new relationship. With limited access to credit after the worst of the financial crisis, plus a lack of service and attention, many business owners have lost confidence in banks and their bankers. Before the financial crisis, business owners ranked their banker number three on the list of top trusted advisors. Today bankers have fallen to number seven – below the medical system, the president and religious organizations, as reported in a recent Gallup poll, “Confidence in Institutions.” In order to gain a foothold with existing clients and prospects, here is a roadmap banks can use to build trust and effectively meet the needs to today’s small business client. Put feet on the street. To rebuild trust, banks need to get in front of their clients face to face and begin engaging with them on a deeper level. Even in the digital age, business customers still want to have face-to-face contact with their bank. The only way to effectively do that is to put feet on the street and begin having conversations with clients. Whether it be via Skype, phone calls, text, e-mail or Twitter – having knowledgeable bankers accessible is the first step in creating a trusting relationship. Develop business acumen. Business owners need someone who is aware of their pain points, can offer the correct products according to their financial need, and can provide a long-term plan for growth. In order to do so, banks need to invest in developing the business and relationship acumen of their sales forces to empower them to be trusted advisors. One of the best ways to launch a new class of relationship bankers is to start investing in educational events for both the bankers and the borrowers. This creates an environment of learning, transparency and growth. Leverage technology to enhance client relationships. Commercial and industrial lending is an expensive delivery strategy because it means bankers are constantly working with business owners on a regular basis. This approach can be time-consuming and costly as bankers must monitor inventory, understand financials, and make recommendations to improve the financial health of a business. However, if banks leverage technology to provide bankers with the tools needed to be more effective in their interactions with clients, they can create a winning combination. Some examples of this include providing online chat, an educational forum, and a financial intelligence tool to quickly review financials, provide recommendations and make loan decisions. Authenticate your value proposition. Business owners have choices when it comes to selecting a financial service provider, which is why it is important that every banker has a clearly defined value proposition. A value proposition is more than a generic list of attributes developed from a routine sales training program. It is a way of interacting, responding and collaborating that validates those words and makes a value proposition come to life. Simply claiming to provide the best service means nothing if it takes 48 hours to return phone calls. Words are meaningless without action, and business owners are particularly jaded when it comes to false elevator speeches delivered by bankers. Never stop reaching out. Throughout the lifecycle of a business, its owner uses between 12 and 15 bank products and services, yet the national product per customer ratio averages around 2.5. Simply put, companies are spreading their banking needs across multiple organizations. The primary cause? The banker likely never asked them if they had any additional businesses or needs. As a relationship banker to small businesses, it is your duty to bring the power of the bank to the individual client. By focusing on adding value through superior customer experience and technology, financial institutions will be better positioned to attract new small business banking clients and expand wallet share with existing clients. By implementing these five strategies, you will create closer relationships, stronger loan portfolios and a new generation of relationship bankers. To view the original blog posting, click here. To read more about the collaboration between Experian and Finagraph, click here.

By: Linda Haran Complying with complex and evolving capital adequacy regulatory requirements is the new reality for financial service organizations, and it doesn’t seem to be getting any easier to comply in the years since CCAR was introduced under the Dodd Frank Act. Many banks that have submitted capital plans to the Fed have seen them approved in one year and then rejected in the following year’s review, making compliance with the regulation feel very much like a moving target. As a result, several banks have recently pulled together a think tank of sorts to collaborate on what the Fed is looking for in capital plan submissions. Complying with CCAR is a very complex, data intensive exercise which requires specialized staffing. An approach or methodology to preparing these annual submissions has not been formally outlined by the regulators and banks are on their own to interpret the complex requirements into a comprehensive plan that will ensure their capital plans are accepted by the Fed. As banks work to perfect the methodology used in this exercise, the Fed continues to fine tune the requirements by changing submission dates, Tier 1 capital definitions, etc. As the regulation continues to evolve, banks will need to keep pace with the changing nature of the requirements and continually evaluate current processes to assess where they can be enhanced. The capital planning exercise remains complex and employing various methodologies to produce the most complete view of loss projections prior to submitting a final plan to the Fed is a crucial component in having the plan approved. Banks should utilize all available resources and consider partnering with third party organizations who are experienced in both loss forecasting model development and regulatory consulting in order to stay ahead of the regulations and avoid a scenario where capital plan submissions may not be accepted. Learn how Experian can help you meet the latest regulatory requirements with our Loss Forecasting Model Services.

Do you really know where your commercial and small business clients stand financially? I bet if you ask your commercial lending relationship managers they will say they do - but do they really? The bigger question is how you could be more tied into to your business clients so that you could give them real advice that may save their businesses. More questions?? Nope, just one answer. Finagraph with Experian’s Advisor for relationship lending is a perfect setup to gather data that you currently are using within your financial institution that can then be matched that up with real financial spreads from the accounting systems that your business client use in their everyday process. By comparing the two sources of records you can get a true perspective on where your business clients stands and empower your relationship managers like ever before.

Apple Pay fraud solution Apple Pay is here and so are increased fraud exposures, confirmed losses, and customer experience challenges among card issuers. The exposure associated with the provisioning of credit and debit cards to the Apple Pay application was in time expected as fraudsters are the first group to find weaknesses. Evidence from issuers and analyst reports points to fraud as the result of established credit/debit cards compromised through data breaches or other means that are being enrolled into Apple Pay accounts – and being used to make large value purchases at large merchants. Keir Breitenfeld, our vice president of Fraud and Identity solutions said as much in a recent PYMNTS.com story where he was quoted about whether the Apple Watch will help grown Apple Pay. The challenge is that card issuers have no real controls over the provisioning or enrollment process so they currently only have an opportunity to authenticate their cardholder, but not the provisioning device. Fraud exposure can lie within call centers and online existing customer treatment channels due to: Identity theft and account takeover based on breach activity. Use of counterfeit or breached card data. Call center authentication process inadequacies. Capacity and customer experience pressures driving human error or subjectively lax due diligence. Existing customer/account authentication practices not tuned to this emerging scheme and level of risk. The good news is that positive improvements have been proven with bolstering risk-based authentication at the card provisioning process points by comparing the inbound provisioning device to the device that is on file for the cardholder account. This, in combination with traditional identity risk analytics, verifications, knowledge-based authentication, and holistic decisioning policies vastly improve the view afforded to card issuers for layered process point decisioning. Learn more on why emerging channels, like mobile payments, call for advanced fraud identification techniques.

The follow blog is by Kyle Enger, Executive Vice President of Finagraph With the surge of alternative lenders, competition among banks is stronger than ever. But what exactly does that mean for the everyday banker? It means business owners want more. If you’re only meeting your clients once a year on a renewal, it’s not good enough. In order to take your customer service to the next level, you need to become a trusted advisor. Someone who understands where your clients are going and how to help them get there. If you’re not investing in your clients’ business by taking the following actions, they may have one foot out the door. 1. Understand your clients’ business One of the biggest complaints from business owners is that bankers simply don’t understand their business. A good commercial banker should be well-versed in their borrower’s company, competitors and the industry. They should be willing to get to know their business, commit to them, stop by to check-in and provide a proactive plan to avoid future risks. 2. Utilize technology for your benefit The majority of recent bank innovations have been used to make the customer experience more convenient, but not necessarily the more helpful. We’ve seen everything from mobile remote deposit capture to online banking to mobile payments – all of which are keeping customers from interacting with the bank. Contrary to what many think, technology can be used to create strong relationships by giving bankers information about their customers to help serve them better. Using new software programs, bankers can see information like the current ratio, quick ratio, debt-to-equity, gross margin, net margin and ROI within seconds. 3. Heighten financial acumen Banks have access to a vast amount of customer financial data, but sometimes fail to use this information to its full potential. With insight into consumer purchasing behavior and business’ financial history, banks should be able to cater products and services to clients in a personalized manner. However, many lenders walk into prospect meetings without knowing much about the business. Their mode of operation is solely focused on trying to secure new clients by building rapport – they are what we call surface bankers. A good banker will educate clients on what they need to know such as equity, inventory, cash flow, retirement planning and sweep accounting. They should also know about new technology and consult borrowers on intermediate financing, terming out loans that are not revolving, or locking in with low interest rates. Following, they will bring in the right specialist to match the product according to their clients’ needs. 4. Go beyond the price Many business owners make the mistake of comparing banks based on cost, but the value of a healthy banking relationship and a financial guide is priceless. So many bankers these days are application gatherers working on a transactional basis, but that’s not what business owners need. They need to stop looking at the short-term convenience of brands, price and location, and start considering the long-term effects a trusted financial advisor can make on their business. 5. A partner in your business, not a banker “Sixty percent of businesses are misfinanced using short-term money for long-term use,” according to the CEB Business Banking Board. In other words, there are many qualified candidates in need of a trusting banker to help them succeed. Unbeknownst to many business owners, bankers actually want to make loans and help their clients’ business grow. Making this known is the baseline in building a strong foundation for the future of your career. Just remember to ask yourself – am I being business-centric or bank-centric? To view the original blog posting, click here. To read more about the collaboration between Experian and Finagraph, click here.

By: Mike Horrocks Experian has announced a new agreement with Finagraph, a best-in-class automated financial intelligence tool provider, to provide the banking industry with software to evaluate small business financials faster. Loan automation is key in pulling together data in a meaningful manner and this bank offering will provide consistent formatted financials for easier lending assessment. Finagraph’s automated financial intelligence tool delivers advanced analytics and data verification that presents small business financial information in a consistent format, making it easier for lenders to understand the commercial customer’s business. Experian’s portfolio risk management platform addresses the overall risks and opportunities within a loan portfolio. The company’s relationship lending platform provides a framework to automate, integrate and streamline commercial lending processes, including small and medium-sized enterprise and commercial lending. Both data-driven systems are designed to accommodate and integrate existing bank processes saving time which results in improved client engagement “Finagraph connects bankers and businesses in a data-driven way that leads to better insights that strengthens customer relationships,” said John Watts, Experian Decision Analytics director of product management. “Together we are helping our banking clients deliver the trusted advisor experience their business customers desire in a new industry-leading way.” “The lending landscape is rapidly changing. With new competitors entering the space, banks need innovative tools that allow them to maintain an advantage,” said James Walter, CEO and President of Finagraph. “We are excited about the way that our collaboration with Experian’s Baker Hill Advisor gives banks an edge by enabling them to connect with their clients in a meaningful way. Together we are hoping to empower a new generation of trusted advisors.” Learn more about our portfolio risk management and lending solutions and for more information on Finagraph please visit www.finagraph.com.
Deposit accounts for everyone Over the last several years, the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB) has, not so quietly, been actively pushing for changes in how banks decision applicants for new checking accounts. Recent activity by the CFPB is accelerating the pace of this change for those managing deposits-gathering activities within regulated financial institutions. It is imperative banks begin adopting modern technology and product strategies that are designed for a digital age instead of an age before the internet even existed. In October 2014, the CFPB hosted the Forum On Access To Checking Accounts to push for more transparent account opening procedures, suggesting that bank’s use of “blacklists” that effectively “exclude” applicants from opening a transaction account are too opaque. Current regulatory trends are increasingly signaling the need for banks to bring checking account originations strategies into the 21st century as I indicated in Banking in the 21st Century. The operations and technology implications for banks must include modernizing the approach to account opening that goes beyond using different decision data to do “the same old thing” that only partially addresses broader concerns from consumers and regulators. Product features attached to check accounts, such as overdraft shadow limits, can be offered to consumers where this liquidity feature matches what the customer can afford. Banking innovation calls for deposit gatherers to find more ways to approve a basic transaction account, such as a checking account, that considers the consumer’s ability to repay and limit approving overdraft features for some checking accounts even if the consumer opts in. This doesn’t mean banks cannot use risk management principles in assessing which customers get that added liquidity management functionality attached to a checking account. It just means that overdraft should be one part of the total customer level exposure the bank considers in the risk assessment process. The looming regulatory impacts to overdraft fees, seemingly predictable, will further reduce bank revenue in an industry that has been hit hard over the last decade. Prudent financial institutions should begin managing the impact of additional lost fee revenue now and do it in a way that customers and regulators will appreciate. The CFPB has been signaling other looming changes for check account regulations, likely to accelerate throughout 2015, and portend further large impacts to bank overdraft revenue. Foreshadowing this change are the 2013 overdraft study by the CFPB and the proposed rules for prepaid cards published for commentary in December 2014 where prepaid account overdraft is “subject to rules governing credit cards under TILA, EFTA, and their implementing regulations”. That’s right, the CFPB has concluded overdraft for prepaid cards are the same as a loan falling under Reg Z. If the interpretation is applied to checking account debit card overdraft rules, it would effectively turn overdraft fees into finance charges and eliminate a huge portion of remaining profitability for banks from those fees. The good news for banks is that the solution for the new deposits paradigm is accomplished by bringing retail banking platforms into the 21st century that leverage the ability to set exposure for customers at the client level and apportioned to products or features such as overdraft. Proactively managing regulatory change, that is predictable and sure to come, includes banks considering the affordability of consumers and offering products that match the consumer’s needs and ability to repay. The risk decision is not different for unsecured lending in credit cards or for overdraft limits attached to a checking account. Banks becoming more innovative by offering checking accounts enabling consumers more flexible and transparent liquidity management functionality at a reasonable price will differentiate themselves in the market place and with regulatory bodies such as the CFPB. Conducting a capabilities assessment, or business review, to assess product innovation options like combining digital lines of credit with check accounts, will inform your business what you should do to maintain customer profitability. I recommend three steps to begin the change process and proactively manage through the deposit industry regulatory changes that lay ahead: First, assess the impacts of potential lost fees if current overdraft fees are further limited or eliminated and quantify what that means to your product profitability. Second, begin designing alternative pricing strategies, product offerings and underwriting strategies that allow you to set total exposure at a client level and apportion this exposure across lending products that includes overdraft lines and is done in a way that it is transparent to your customers and aligns to what they can afford. Third, but can be done in parallel with steps one and two, begin capability assessments of your financial institution’s core bank decision platform that is used to open and manage customer accounts to ensure your technology is prepared to handle future mandatory regulatory requirements without driving all your customers to your competitors. It is a given that change is inevitable. Deposit organizations are well served to manage this current shift in regulatory policy related to checking account acquisitions in a way consistent with guaranteeing your bank’s competitive advantage. Banks can stay out front of competitors by offering transparent and relevant financial products consumers will be drawn to buy and can’t afford to live without! Thank you for following my blog and insights in DDA best practices. Please accept my invitation to participate in a short market study. Click here to participate. Participants in this 5 minute survey will receive a copy of the results as a token of appreciation.

By: Scott Rhode This is the third and last of a three-part blog series focused on the residential solar market looking at; 1) the history of solar technology, 2) current trends and financing mechanisms, and finally 3) overcoming market and regulatory challenges with Experian’s help. As we’ve discussed in the two previous blogs, the residential solar industry in the US has experienced tremendous growth and much of that growth is attributed to financing. As the financing offers continue to evolve and mature, there are challenges that the industry faces. The first, and most obvious challenge, is that the Solar Investment Tax Credit is set to expire on December 31st, 2016. (To be clear, the credit is not eliminated on Dec. 31, 2016, it is simply planned to be reduced to 10%) Given the state of affairs in Washington, it is unlikely that the tax credit will get extended. This is unfortunate since this tax credit has been a catalyst for investment in this industry, greatly increasing affordability and adoption from the public. Once this incentive expires, the solar companies will need to acquire capital from more traditional sources (Debt markets, securitization, or other third party financing) to fund their growth since the Tax Equity community may no longer be willing to invest. In addition, the expiration of the credit means that panel manufactures must find ways to reduce the cost of production and that finance and installation companies must lower their customer acquisition cost since they are unsustainable in a post-ITC world. A benefit of moving towards other means of funding is that the sophistication level of pre-screening, scoring, and portfolio management should improve dramatically. Today, the Tax Equity community drives all of the credit strategies and those strategies are actually holding solar companies back because of their simplicity. For example, most of the TE investors require that the customer have a 680 FICO score or better in order to get approval. They do not require a debt to income threshold to be met, nor do they look at other attributes or data points. This overly simplistic approach is meant to keep the TE investor out of difficult conversations of being in the “sub-prime” space; however, it greatly limits growth and it turns away good customers. Additionally, this approach does not consider the “essential use” nature of the product. When a customer becomes seriously delinquent, their panels get disconnected and their costs for energy go up more than the cost of their monthly lease payment. This ensures that, unlike an unsecured loan or credit card, the customer is more likely to pay this obligation since it is actually saving them money. This does not mean that the industry can approve everyone; however, it does mean that, with the right decisioning logic and scorecards, they can go much deeper into the credit pool without taking on huge risks. Another challenge for the industry is the shear rate of growth. There are new players in the market every day and even established firms have a hard time keeping up with the growth. This leaves the individual organization and industry at risk for missing critical compliance steps in their operations. Given that these financial instruments are long term in nature and more consumers are adopting this as a means to get solar, it is only a matter of time before the regulators start to look into the practices and operating processes to ensure that all of the applicable regulations are being followed. The industry, as a whole, needs to ensure that they spend a little money now shoring up their compliance instead of paying a hefty fine later. Finally, what happens at the end of the lease? Many of the large players have taken a conservative approach as to how they price the residual amount at the end of term; however, no one really knows what these assets will be worth in 20 years. While many of the panel manufacturers warrant performance for 25, many panels have a shelf-life of 40 years, so how will consumers and the industry behave? What happens if there is a technological breakthrough in 10 years and those old panels are obsolete? At the moment, the industry’s answer to these questions is to set a very low residual which carries risk. Being too conservative here means that your customer’s payment is higher than it needs to be, pricing yourself out of certain markets where the cost of power is less than 20 cents / kwh. As the lease product continues to mature, more focus and emphasis on residual pricing will need to take place to find the right balance for the Consumer and the finance company. It should be said that while there are risks associated with this industry, all markets and new financing products carry risks. The goal of this particular blog is to highlight some of the larger risks that this industry faces. As these are identified, it is incumbent on the industry and partners of the industry to mitigate these risks so that consumers can continue to realize the power of solar. To close this series, I would be remiss if I didn’t offer up Experian’s Global Consultancy solutions to help address the challenges that the industry faces. Our knowledge of best practices in the financial services industry allows us to help those companies in the solar market grow originations responsibly, meet their regulatory requirements, and manage their long term risks with customers. While we cannot solve the funding issues, we can work with organizations and the tax equity community to educate them on the power of decisioning beyond a simple “one-size fits all” score. In addition, our products and data allow for flexibility and certainty, giving the industry an edge in acquiring new customers in a more efficient and less expensive manner. Finally, we can help provide advice and best practices in decisioning, risk management, and regulatory compliance so that the industry can continue to grow and thrive. All in all, we are advocates for the industry and can bring tremendous expertise and experience to help ensure continued success. Solar Financing – The current and future catalyst behind the booming residential solar market (Part II) Solar Financing — The current and future catalyst behind the booming residential solar market (Part I)

By: Mike Horrocks I was raised in an underbanked home! I have known this for a long time, but it feels great to say it and be proud of it. I was raised in Neola, Utah, a small cattle ranching community of at the time 500 or so people. I don’t recall as a kid ever feeling poor or on the edge financially, in fact it was quite the opposite. When I was a freshman in college I got my own banking accounts and my first major credit card that gave cash back, it all just seemed normal. I recall showing my dad my new found financial life. The concept of getting cash back for purchases was something he wanted in on. He made the call to get his own card and within minutes the representative on the other end of the call asked if I was willing to co-sign for my dad because he did not have a thick enough credit file. At this point of my dad’s life, he had developed and sold a couple of businesses, bought and managed a successful angus cattle ranch - but he had done most of it in cash and so he was “off the grid”. When I co – signed for my dad, it hit me, in terms of the banking system that I was studying at the university, we were an underbanked family! So what are the lessons learned here for a banker today: Underbanked does not equal poor. I never felt poor, the family business was going great, and my dad was always able to meet any obligation or need for the ranch and us kids. Bankers need to know their customers. When my dad did need access to more capital, there was a great banker at Zions Bank that knew my dad and stood by him even though the traditional file was thin. So know your customers by all means (traditional credit, alternative data, etc.) Don’t forget the family. By this I mean the associated products and what they can mean to the overall customer picture and relationship. Know what risks and opportunities are there as you try to optimize the relationship. If you want to read some more, American Banker just published a great set of articles on including consumers and how to retain them - it is worth a quick review. Don’t let great customers like my dad go through your business development net. Attract them, nurture them and build great relationships with them.

The evolution of identity verification Knowing who you are doing business with isn’t just a sound business practice to protect your bottom line. In many cases, it also is a legal requirement. Identity verification techniques have been evolving over the past few years to meet business priorities beyond fraud prevention, including customer experience, operational costs and regulatory compliance. We recently wrote about the challenges of customer authentication on mobile devices to meeting new business priorities. Fraud prevention tools have responded to these shifting priorities. While extremely fast and very accurate at detecting fraud, they also: Are less invasive to customers Provide a strong return on investment Ensure consistency in compliance and audit Listen to what Matt Ehrlich, Experian fraud and identity director of product management, has to say about how verification techniques have changed: Download our fraud prevention perspective paper to gain more insight on how you can prepare your business.

By: Scott Rhode This is the second of a three-part blog series focused on the residential solar market looking at; 1) the history of solar technology, 2) current trends and financing mechanisms, and finally 3) overcoming market and regulatory challenges with Experian’s help. Lets discuss the current trends in solar and, more importantly, the mechanisms used to finance solar in the US residential market. As I discussed in the last blog, the growth in this space has been astronomical. To illustrate this growth, there was a recent article in The Washington Post by Matt McFarland, highlighting that solar-related jobs are significantly outpacing the rest of labor market in terms of year over year growth. The article states that since 2010 the number of solar-related jobs has doubled in the US, bring the total number of jobs in this industry to 173,807. While this is still smaller in comparison to other sectors of our economy, it underscores how much growth has occurred in a short amount of time. So what is driving this explosive growth? There are a few factors that should be considered; however, in the residential solar market, financing, is the main catalyst. As you might expect, there are a variety of financial products in the market giving the consumer lots of choices. First, there are traditional loans like home improvement loans, home equity loans, or energy efficiency loans offered by a bank, credit union, or specialty finance company. For homeowners that do not choose to secure their loan against their property, there are a variety of specialty lenders that will offer long-term, unsecured loans that only file a UCC against the panels themselves. For these types of offerings, some specialty lenders will even have special credit plans for the 30% Solar Investment Tax Credit so that the homeowner can have a deferred interest plan with the expectation that once they get the tax credit from the federal government, they will pay off the special plan and all of the deferred interest will be waived. If the customer does not pay in full, the plan rolls to their regular loan plan and the customer has a higher cost of financing. Second, there is a lease product which offers zero to little down and a monthly payment that is less than the savings that the homeowner will experience on their utility bill. Of all the financing options, the lease has been the biggest driver of growth since it offers an inexpensive, no-hassle way to get all the benefits of going solar without breaking the bank. What is unusual to most people that are unfamiliar with this concept is the term of the lease, which is typically 20 years. However, when you consider that most manufacturers warrant their panels for 25 and many have a usable life of 40 years, this term does not seem all that unusual. The benefits of this program look something like this: The homeowner has an average electric utility bill of $350 / month A solar company quotes a customer a savings of $200 / month in the form of a net metering energy credit, so their bill after solar is now $150 / month The lease payment for the installed solar array, metering equipment, and monitoring software is $150 / month The homeowner’s net saving is an average of $50 / month with nothing out of pocket Over the life of the lease, energy prices will increase which will mean more savings over time so long as there are not escalators in the contract that exceed the increase in energy prices The lessor “owns” the equipment and is responsible for maintenance, performance, and insurance With this product comes complexity. Many companies offering this program do not have the cash or the appetite to take on massive debt, so they partner with Tax Equity investors to make this transaction possible. Because of the 30% ITC and accelerated depreciation, this transaction is very favorable for a Tax Equity investor like Google, US Bank, or Bank of America Merrill Lynch. There are a number of structures they can use; however, the Sale-Leaseback structure is the easiest and most efficient way to fund the transaction. While this is not “known” to the end customer, it is important because the Tax Equity Investor effectively owns the asset and has the final say in setting credit policy. This transaction does require that the developer have a stake as well; however, many of the developers go to the debt market for “back leverage” on their stake so that they can reduce the impact to their balance sheet. This complexity carries a cost, as the cost of capital is higher than most traditional loan products from established financial services firms. That said, the fact that the lease allows the customer to monetize the tax credit and accelerated depreciation in the amount financed, balances out the higher costs of capital. In the next blog we will touch more on the challenges this product, in particular, has in the market. Last, but not least, there is another mechanism gaining popularity in the market. This concept is known as community solar. One of the obstacles of the lease and Tax Equity arrangement is that the lease is only available to single family residence homeowners and, if they have multiple homes, only the homeowner’s primary residence. That means that people who rent, own a condo, own a vacation home, or own a small business do not qualify for this type of lease. As a result, community solar has become a great option. With community solar, the panels are put in an ideal location for maximum exposure to the sun and they often produce 10-15% more power than panels on a rooftop. Portions of this solar farm can be sold, rented, or sublet to consumers regardless of their living situation. As the panels produce electricity, that power gets sold to the local utility and the customer gets money from that utility that shows up as a credit on their next bill. In this structure, the customer is not required to put money down in most cases and they are signing up for a specific term. Like a rooftop lease, this structure often has a Tax Equity investor that funds the project. Again, this allows them to take the 30% ITC and accelerated depreciation which, in turn, gets monetized and lowers the costs of construction. In the final installment of this blog series, I will discuss some of the challenges that this market faces as the ITC expiration date approaches and the market becomes more mature. Leasing is driving the market, so if the ITC does not get renewed, the market will need to have a plan in place to find other innovative ways to keep solar affordable so more consumers can realize the benefits of going solar. Solar Financing — The current and future catalyst behind the booming residential solar market (Part 1)

Customer experience strategies for success Sometimes it’s easier to describe something as the opposite of something else. Being “anti-” something can communicate something meaningful. Cultural movements in the past have taken on these monikers: consider the “anti-establishment” or “anti-war” movements. We all need effective anti-virus protection. And there are loads of skin products marketed as “anti-aging”, “anti-wrinkle”, or “anti-blemish.” But when you think about a vision for the customer experience that your company aspires to deliver, this approach of the “anti-X” falls flat. Would you want to aspire to basically “not stink?” Would that inspire you and your team to run through walls to deliver on that grand aspiration? Would it motivate customers to stick with you, buy more of what you sell, and tell others about you? I think not…But it sure seems like many out there indeed do aspire to “not stink.” Sure, there are great companies out there who have a set a high standard for customer experience, placing it at the center of their strategies and their success. Some, like Zappos, started that way from the beginning. Others, like The Ritz-Carlton, realized that they had lost their way and made the commitment to do the hard work of reaching and sustaining excellence. On the other hand, there are hundreds of firms who have a weak commitment to or even understanding of the importance of customer experience to their strategy and performance. Their leaders may give lip service or just pay attention for a few days or hours following the release of reports from leading analysts and firms. They may have posters and slogans that talk about putting the customer first or similar platitudes. These companies probably even have talented and passionate professionals working tirelessly to improve the customer experience in spite of the fact that nobody seems to care much. What these firms lack is a clear customer experience strategy. As nature abhors a vacuum, customers and employees are free to infer or just guess at it. Focusing on customer experience only when a report comes out – and paying special attention only when weak results put the firm near the bottom of the ranking leads people to conclude that all that really matters is to “not stink.” In other words, don’t stand out for being bad…but don’t worry much about being good as it is not important to the company’s strategy or results. I think that this “don’t stink” implicit strategy helps explain a fascinating insight from a Forrester survey in 2013: “80% of executives believe their company is delivering a superior customer experience, yet in 2013 only 8% of companies surveyed received a top grade from their customers.” Many leaders simply have not invested the energy and commitment necessary to define a real customer experience vision that reflects a deep understanding of the role that it plays in the company’s strategy. Beyond setting that vision, there is a big and sustained commitment required to deliver on the vision, measure results, and continuously adjust as customer needs evolve. Like all journeys, a great customer experience starts with one step. Establishing a customer experience strategy is the first one – and “don’t stink” simply stinks as a strategy. Download our recent perspective paper to learn how exceptional customer experience can give companies the competitive edge they need in a market where price, products and services can no longer be a differentiator.