E-Verify is an internet-based system in the United States administered by the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) in partnership with the Social Security Administration (SSA) that allows employers to verify the employment eligibility of newly hired employees. When new employees are hired, they must complete Form I-9, which documents their employment eligibility, and employers are tasked with verifying that the prospective employee is eligible to work in the United States. The E-Verify system was created to make it easier for employers to verify employment authorization and avoid penalties related to hiring undocumented workers. While using the E-Verify system to verify the employment eligibility of workers is voluntary, states have the authority to set their own laws surrounding the E-Verify system. In this guide, we’ll walk through E-Verify requirements by state to help you better understand the laws centered around state-by-state mandates.
How E-Verify Works
When it comes to E-Verify by state, the process remains the same. Here’s what you can expect when using the federal E-Verify system to authorize the employment status of new hires:
- Form I-9 completion: To start the E-Verify process, Form I-9 needs to be completed by the employee and the employer, which is used to verify the identity and employment eligibility of the employee. Inclusion of an otherwise optional SSN is required if an employer uses E-Verify.
- Enrollment in E-Verify: After completing Form I-9, the employer can enroll in the E-Verify program by submitting an enrollment form to DHS, and once accepted, the employer can start the verification process.
- Verification: Employers can use the E-Verify system to input employee information from Form I-9 into the system, such as their name, date of birth, Social Security number and immigration status, if applicable. Once provided, the system will match that information to the records held by the DHS and SSA to determine the employee’s employment eligibility.
- Verification results: After the system checks are performed, employers will receive the results, which go as follows:
- Employment authorized: The employee’s information matched the DHS and SSA records.
- E-Verify needs more time: The DHS needs more time for further verification.
- Tentative nonconfirmation (mismatch): The information provided does not match the information contained by the DHS and/or SSA and additional action is required.
- Case in continuance: The employee has visited or contacted the SSA/DHS, but more time is needed to confirm the case results.
- Close case and resubmit: The DHS or SSA requires the employer to close the case and resubmit a new case for the employee, such as if the employee’s U.S. passport, passport card or driver’s license information is incorrect.
- Final nonconfirmation: The DHS or SSA cannot confirm the employee’s employment eligibility after being contacted by the employee.
Importance of E-Verify State Mandates
Now that you understand how the E-Verify process works let’s dive into E-Verify regulations by state. Understanding E-Verify state mandates is essential as an employer, as the rules and regulations can vary on a state-by-state basis. States can set laws and regulations at the state level regarding how employers use the E-Verify system. Below are some of the reasons why E-Verify state mandates are important:
- Employment eligibility compliance: E-Verify allows employers to verify the employment authorization of employees to maintain a legal workforce and prevent the employment of unauthorized workers, allowing employers to remain compliant with federal immigration laws.
- Preventing document fraud: The E-Verify system matches the documents provided by prospective employees with records maintained by the SSA and DHS, which can help prevent document fraud and identity theft.
- Federal funding compliance: Some states issue E-Verify mandates for employers to receive federal grants or funding, and the E-Verify system can help employers receive funding for projects and business growth.
How E-Verify Requirements and Laws Can Vary by State
E-Verify requirements by state can vary drastically, and understanding how these laws can vary is important in remaining compliant. For instance, mandate coverage can vary by state, as some states may make the E-Verify system mandatory for all public and private businesses. In contrast, others may only require public employers or employers hiring contractors to use the E-Verify system. The use of E-Verify in California and Illinois is voluntary, subject to specific state-imposed restrictions. In California, neither the State nor any of its cities, counties, or special districts may mandate the use of E-Verify, as outlined in California Assembly Bill 1236 (2011-2012). In Illinois, employers enrolled in E-Verify must attest, under penalty of perjury, on a form prescribed by the Illinois Department of Labor, that they have received E-Verify training and have posted the required E-Verify posters in a prominent location visible to both prospective and current employees, in accordance with Illinois Compiled Statutes, 820 ILCS 55/12.
Additionally, penalties and fines for noncompliance can vary on a state level. Some states may impose minor fines for noncompliance, whereas others may enforce business license suspension or revocation.
Lastly, when it comes to E-Verify laws by state, some states may make exemptions and exceptions for certain types of businesses, such as businesses with a limited number of employees or businesses in certain industries, such as agriculture or independent contractors.
States With Mandatory E-Verify for All or Most Businesses
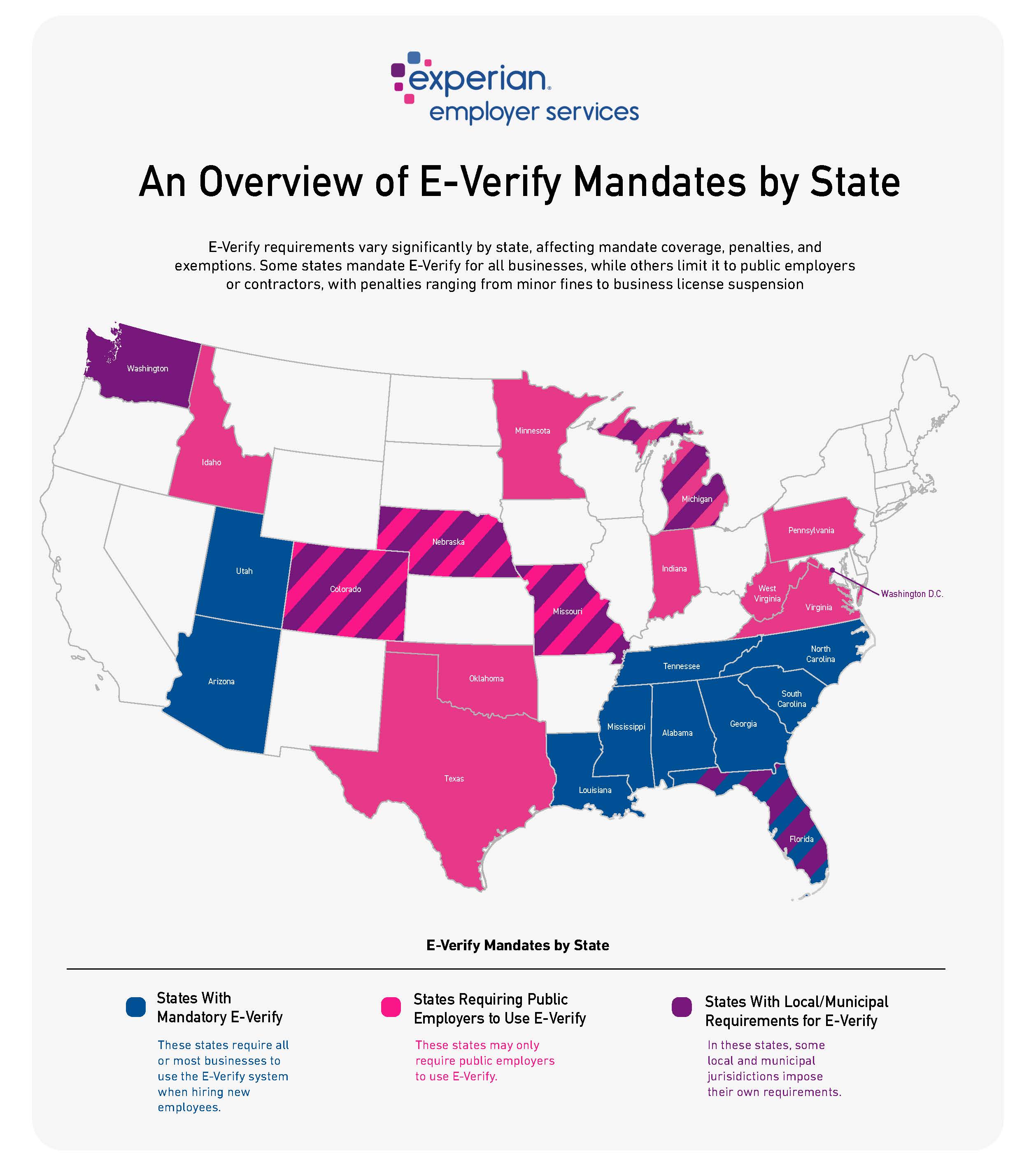
As stated, E-Verify requirements by state can vary when it comes to mandate coverage. Below are the states that require all or most businesses to use the E-Verify system when hiring new employees:
States Requiring Public Employers to Use E-Verify
In some cases, certain states may only require public employers to use E-Verify. These states include:
- Colorado
- Idaho
- Indiana
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Missouri
- Nebraska
- Oklahoma
- Pennsylvania
- Texas
- Virginia
- West Virginia
States With Local/Municipal Requirements for E-Verify
In addition to state-level E-Verify requirements, local and municipal jurisdictions may impose their own requirements. These states and their jurisdictions include:
- Colorado (Denver)
- Florida (Hernando County, Bonita Springs)
- Michigan (Ingham County, Macomb County, Oakland County)
- Missouri (O’Fallon)
- Nebraska (Fremont)
- Washington (Hoquiam, Pierce County, Woodland)
The Challenge of E-Verify State Mandates
There are pros and cons of using E-Verify. While E-Verify state mandates aim to improve employment eligibility verification compliance, there are a few challenges worth noting, such as:
- Outdated data: Due to the size and bandwidth of large federal agencies like the Department of Homeland Security and Social Security Administration, the information they have on file might be outdated, resulting in a delayed employment verification process that impacts employers and employees.
- Accuracy: While there are low levels of errors, the E-verify system isn’t perfect, which means there can be instances where identity theft, typographical errors and other issues aren’t detected, resulting in false positives that flag authorized employees as unauthorized or vice versa.
- Privacy and data security concerns: Because E-Verify requires collecting sensitive information like names, addresses and Social Security numbers, there are privacy and data security concerns, such as data breaches and the mishandling of personal information.
- Discrimination potential: There is potential for E-Verify to contribute to discriminatory practices during the hiring process, where employers use information, such as perceived immigration status or ethnicity, as grounds for hiring.
Why Use E-Verify?
While there are certain potential challenges of E-Verify, there are several reasons why employers should use this system. Overall, E-Verify can help employers maintain compliance with immigration laws by accurately verifying the employment authorization status of employees. Additionally, E-Verify can help reduce legal liability by offering a level of protection for employers exhibiting good faith when verifying employment eligibility. E-Verify can also help employers boost their images and reputations by showing their commitment to lawful employment practices and compliance with immigration laws. Additionally, and possibly most important, employers who wish to use the new alternate remote procedures must be E-Verify participants in good standing.
Streamlining E-Verify State Mandates With Experian Employer Services
At Experian Employer Services, our I-9 compliance and management solutions can help automate the I-9 verification process, eliminate potential risks and ensure consistency. E-Verify by state can be complex and time-consuming. With our team and I-9 solution on your side, you can stay ahead of missing data and potential issues and maintain federal and state compliance.


