Tag: payment stress

The COVID-19 pandemic has created unprecedented challenges for the utilities industry. This includes the need to plan for – and be prepared to respond to – changing behaviors and a sudden uptick in collections activities. As part of our recently launched Q&A perspective series, Mark Soffietti, Experian’s Senior Manager of Analytics Consulting and Tom Hanson, Senior Energy Consultant, provided insight on how utility providers can evolve and refine their collections and recovery processes. Check out what they had to say: Q: How has COVID-19 impacted payment behavior and debt collections? TH: Consumer payment behavior is changing. For example, those who paid as agreed, may not currently have the means to pay and are now distressed borrowers. Or those who were sloppy payers before the pandemic may now be defaulting on a more consistent basis. MS: As we saw with the last recession when faced with economic stress, consumer and commercial payment behavior changes based on their needs and current cash flow. For example, people prioritize their car, as they need it to get to and from work, so they’ll likely pay their auto bills on time. The same goes for their credit cards, which they need to make ends meet. We expect this will also be true with COVID-19. The commercial segment will face more dramatic and challenging circumstances, where complete or partial business closures and lack of federal relief could have severe ramifications. Q: What new restrictions have been put in place surrounding debt collection efforts and outbound calls? TH: To protect consumers who may be experiencing financial distress, most states have imposed new, stringent restrictions to prevent utilities from engaging in certain collections activities. Utilities are currently not charging any late payment fees and are instead structuring payment plans. Additionally, all outbound collections efforts have been suspended and there is fieldwork being executed of services for both commercial and consumer properties. As of now, consumer and commercial fieldwork will likely not commence until after the first year or when the winter moratorium concludes. MS: The new restrictions imposed upon collections activities will likely drive consumer payment behavior. If consumers know that their utilities (i.e. energy and water) will not be shut off if they miss a payment, they will make these bills less of a priority. This will dramatically increase the amount owed when these restrictions are lifted next year. Q: Can we predict how the utilities industry will fare post-COVID-19? TH: The volume of accounts in collections and eligible for disconnect will be overwhelming. Many utility providers fear the unpaid balances consumers and commercial entities accumulate will be nearly impossible to fit into a repayment schedule. Both analyzing internal payment segments and overlaying external factors may be the best way to optimize the most critical go-forward plan. MS: The amount of people who fall into collections is going to greatly increase and utility providers need to start planning for it now to weather the storm. They will need to use data, analytics and tools to help them optimize their tasks, so they can be more efficient with their resources. Like many other industries, the utilities sector will look to increasing digitalization of their processes and having less social interaction where possible. This could mean the need and drive for expediting current smart meter programs where possible to enable remote fieldwork to assist in managing this unprecedented level of activity that is sure to overwhelm field operations (where allowed by state regulators). Q: What should utility providers be doing to plan for an uptick in collections activities post-COVID-19? TH: With regulatory mandated suspensions of collections activities for utility providers and self-selected reductions due to stay at home orders and staff protection, the backlog of payments, calls and inquiries once business resumes as normal is set to overwhelm existing capacity. More than ever, self-service options (text/web), Q&A and alternative communication methods will be needed to shepherd consumers through the collections process and minimize the strain on call center agents. Many utility providers are asking for external data points to segment their consumers by industry or by those whose employment would have been adversely impacted by COVID-19. MS: Utility providers should be monitoring consumer data in order to prepare for when they are able to collect. This will help them strategize the number of resources they will need in their call centers and out in the field performing shut off activities. Given that the rise in cases will be more volume than their call centers can handle, they will need to use their resources wisely and plan to use them efficiently when they are able to resume collections. Q: How can Experian help utility providers reduce collections costs and maximize recovery? TH: Experian can help revise collections tactics and segmentation strategies by providing insight on how consumers are paying other creditors and identifying new segmentation opportunities as we emerge from the freeze on collections activities. Collections cases will be complex, and many factors and constraints will need to balanced against changing goals, making optimization key. MS: Utilizing Experian’s credit data and models can help ensure that resources are being used efficiently (i.e. making successful calls). There is also a need to leverage ability to pay models as well as prioritization models. By using these models and tools, utility providers can optimize their treatment strategies, reduce costs and maximize dollars collected. Learn more About our Experts: Tom Hanson, Senior Energy Consultant, Experian CEM, North America Tom is a Senior Consultant within the Energy Vertical at Experian, supporting regulated energy companies throughout the U.S. He brings over 25 years of experience in the energy field and supports his clients throughout the customer lifecycle, providing expertise in ID verification, account treatment, fraud solutions, analytics, consulting and final bill/field optimization strategies and techniques. Mark Soffietti, Analytics Consulting Senior Manager, Experian Decision Analytics, North America Mark has over 15 years of experience transforming data into actionable knowledge for effective decision management. Mark’s expertise includes solution development for consumer and commercial lending across the credit spectrum – from marketing to collections.

Article written by Alex Lintner, Experian's Group President of Consumer Information Services and Sandy Anderson, Experian's Senior Vice President of Client and Sales Operations Many consumers are facing financial stress due to unemployment and other hardships related to the COVID-19 pandemic. Not surprisingly, data scientists at Experian are looking into how consumers’ credit scores may be impacted during the COVID-19 national emergency period as financial institutions and credit bureaus follow guidance from financial regulators and law established in Section 4021 of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act (CARES Act). In a nutshell, Experian finds that if consumers contact their lenders and are granted an accommodation, such as a payment holiday or forbearance, and lenders report the accommodation accordingly, consumer scores will not be materially affected negatively. It’s not just Experian’s findings, but also those of the major credit scoring companies, FICO® and VantageScore®. FICO has reported that if a lender provides an accommodation and payments are reported on time consistent with the CARES Act, consumers will not be negatively impacted by late payments related to COVID-19. VantageScore® has also addressed this issue and stated that its models are designed to mitigate the impact of missed payments from COVID-19. At the same time, if as predicted, lenders tighten underwriting standards following 11 consecutive years of economic growth, access to credit for some consumers may be curtailed notwithstanding their score because their ability to repay the loan may be diminished. Regulatory guidance and law provide a robust response Recently, the Federal Reserve, along with the federal and state banking regulators, issued a statement encouraging mortgage servicers to work with struggling homeowners affected by the COVID-19 national emergency by allowing borrowers to defer mortgage payments up to 180-days or longer. The Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation stated that financial institutions should “take prudent steps to assist customers and communities affected by COVID-19.” The Office of the Comptroller of the Currency, which regulates nationally chartered banks, encouraged banks to offer consumers payment accommodations to avoid delinquencies and negative credit bureau reporting. This regulatory guidance was backed by Congress in passing the CARES Act, which requires any payment accommodations to be reported to a credit bureau as “current.” The Consumer Financial Protection Bureau, which has oversight of all financial service providers, reinforced the regulatory obligation in the CARES Act. In a statement, the Bureau said “the continuation of reporting such accurate payment information produces substantial benefits for consumers, users of consumer reports and the economy as a whole.” Moreover, the consumer reporting industry has a history of successful coordination during emergency circumstances, like COVID-19, and we’ve provided the support necessary for lenders to report accurately and consistent with regulatory guidance. For example, when a consumer faces hardship, a lender can add a code that indicates a customer or borrower has been “affected by natural or declared disaster.” If a lender uses this or a similar code, a notification about the disaster or other event will appear in the credit report with the trade line for the customer’s account and will remain on the trade line until the lender removes it. As a result, the presence of the code will not negatively impact the consumer credit score. However, other factors may impact a consumer’s score, such as an increase in a consumer’s utilization of their credit lines, which is a likely scenario during a period of financial stress. Suppression or Deletion of late payments will hurt, not help, credit scores In response to the nationwide impact of COVID-19, some lawmakers have suggested that lenders should not report missed payments or that credit bureaus should delete them. The presumption is that these actions would hold consumers harmless during the crisis caused by this pandemic. However, these good intentions end up having a detrimental impact on the whole credit ecosystem as consumer credit information is no longer accurately reflecting consumers’ specific situation. This makes it difficult for lenders to assess risk and for consumers to obtain appropriately priced credit. Ultimately, the best way to help is a consumer-specific solution, meaning one in which a lender reaches an accommodation with each affected individual, and accurately reflects that person’s unique situation when reporting to credit bureaus. When a consumer misses a payment, the information doesn’t end up on a credit report immediately. Most payments are monthly, so a consumer’s payment history with a financial institution is updated on a similar timeline. If, for example, a lender was required to suppress reporting for three months during the COVID-19 national emergency, the result would be no data flowing onto a credit report for three months. A credit report would therefore show monthly payments and then three months of no updates. The same would be true if a credit reporting agency were required to suppress or delete payment information. The lack of data, due to suppression or deletion, means that lenders would be blinded when making credit decisions, for example to increase a credit limit to an existing customer or to grant a new line of credit to a prospective customer. When faced with a blind spot, and unable to assess the real risk of a consumer’s credit history, the prudential tendency would be to raise the cost of credit, or to decrease the availability of credit, to cover the risk that cannot be measured. This could effectively end granting of credit to new customers, further stifling economic recovery and consumer financial health at a time when it’s needed most. Beyond the direct impact on consumers, suppression or deletion of credit information could directly affect the safety and soundness of the nation’s consumer and small business lending system. With missing data, lenders and their regulators would be flying blind as to the accurate information about a consumer’s risk and could result in unknowingly holding loan portfolios with heightened risk for loss. Too many unexpected losses threaten the balance of the financial system and could further seize credit markets. Experian is committed to helping consumers manage their credit and working with lenders on how best to report consumer-specific solutions. To learn more about what consumers can do to manage credit during the COVID-19 national emergency, we’ve provided resources on our website. For individuals looking to explore options their lenders may offer, we’ve included links to many of the companies and update them continuously. With good public policy and consumer-specific solutions, consumers can continue to build credit and help our economy grow.
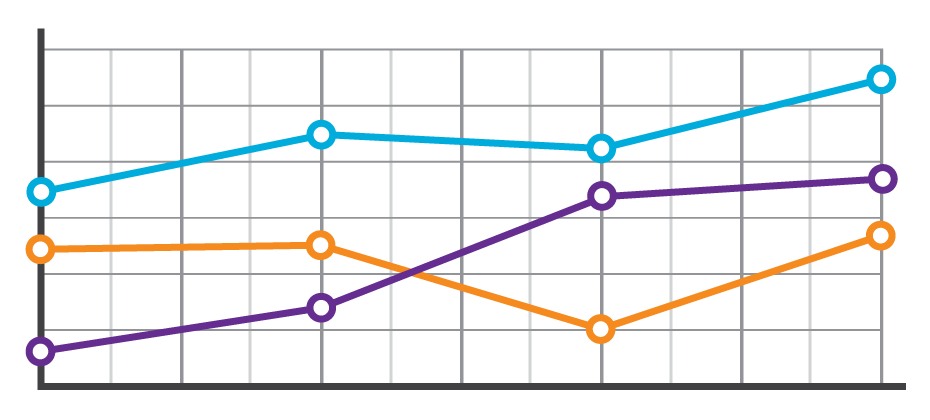
Sometimes life throws you a curve ball. The unexpected medical bill. The catastrophic car repair. The busted home appliance. It happens, and the killer is that consumers don’t always have the savings or resources to cover an additional cost. They must make a choice. Which bills do they pay? Which bills go to the pile? Suddenly, a consumer’s steady payment behavior changes, and in some cases they lose control of their ability to fulfill their obligations altogether. These shifts in payment patterns aren’t always reflected in consumer credit scores. At a single point in time, consumers may look identical. However, when analyzing their past payment behaviors, differences emerge. With these insights, lenders can now determine the appropriate risk or marketing decisions. In the example below, we see that based on the trade-level data, Consumer A and Consumer B have the same credit score and balance. But once we see their payment pattern within their trended data, we can clearly see Consumer A is paying well over the minimum payments due and has a demonstrated ability to pay. A closer look at Consumer B, on the other hand, reveals that the payment amount as compared to the minimum payment amount is decreasing over time. In fact, over the last three months only the minimum payment has been made. So while Consumer B may be well within the portfolio risk tolerance, they are trending down. This could indicate payment stress. With this knowledge, the lender could decide to hold off on offering Consumer B any new products until an improvement is seen in their payment pattern. Alternatively, Consumer A may be ripe for a new product offering. In another example, three consumers may appear identical when looking at their credit score and average monthly balance. But when you look at the trend of their historical bankcard balances as compared to their payments, you start to see very different behaviors. Consumer A is carrying their balances and only making the minimum payments. Consumer B is a hybrid of revolving and transacting, and Consumer C is paying off their balances each month. When we look at the total annual payments and their average percent of balance paid, we can see the biggest differences emerge. Having this deeper level of insight can assist lenders with determining which consumer is the best prospect for particular offerings. Consumer A would likely be most interested in a low- interest rate card, whereas Consumer C may be more interested in a rewards card. The combination of the credit score and trended data provides significant insight into predicting consumer credit behavior, ultimately leading to more profitable lending decisions across the customer lifecycle: Response – match the right offer with the right prospect to maximize response rates and improve campaign performance Risk – understand direction and velocity of payment performance to adequately manage risk exposure Retention – anticipate consumer preferences to build long-term loyalty All financial institutions can benefit from the value of trended data, whether you are a financial institution with significant analytical capabilities looking to develop custom models from the trended data or looking for proven pre-built solutions for immediate implementation.