Commercial Pulse Report
The bi-weekly Commercial Pulse provides a directional update on small business credit. It delivers a quick read on current market impacts, high level credit trends, score and attribute impacts, and other market related activities.
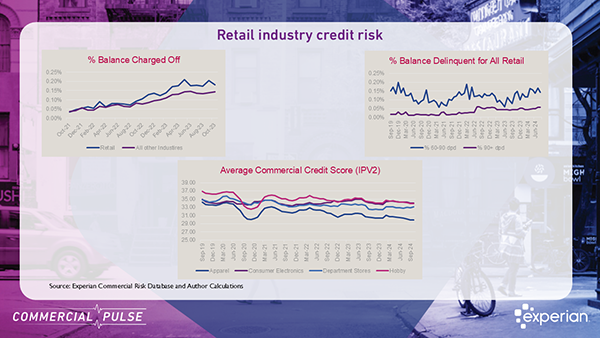
Commercial Pulse Report | 11/12/2024 Welcome to our November 12th, 2024 Commercial Pulse Report preview! Experian’s new Commercial Pulse Report highlights the economic trends shaping the retail landscape as we head into the holiday season. With 2.8% GDP growth in Q3 and steady unemployment at 4.1%, the economy shows resilience, yet retail businesses are navigating a mix of growth and caution in credit and spending trends. Watch Our Commercial Pulse Update This week as the holiday season gets under way, the team pulled together some interesting insights on the retail industry. With 2.8% GDP growth in Q3 and steady unemployment at 4.1%, the economy shows resilience, yet retail businesses are navigating a mix of growth and caution in credit and spending trends. Rising Credit Demand in Retail: Over the past year, commercial credit demand among retail businesses has surged by 25% as retailers boost inventory levels in anticipation of holiday sales. While demand is strong, businesses are finding that lending conditions are tighter than in previous years, especially in discretionary retail sectors. Lending Disparities Across Retail Sectors: Not all retailers benefit equally from this increased credit demand. Discretionary sectors like home goods are facing a drop in new commercial accounts and smaller loan sizes, reflecting a more cautious lending environment. Meanwhile, Consumer Electronics and Department Stores are seeing credit demand nearing pre-pandemic levels, indicating resilience in these areas. Higher Delinquency Rates Impacting Credit Scores: Rising financial pressures are pushing up delinquency rates, putting additional strain on commercial credit scores across the retail sector. This trend is a reminder for retailers to manage credit carefully, even as they position themselves for peak season sales. Slower Retail Sales Growth: Retail sales continue to grow but at a decelerating rate, with only 1.7% year-over-year growth from September 2023 to September 2024—a significant slowdown from previous years. Retailers are adjusting to a post-pandemic normalization as consumer demand steadies. With both opportunities and challenges ahead, this report offers insights to help retailers navigate the season. For more, check out Experian’s Commercial Insights Hub to see how these trends may impact your business. Download Commercial Pulse Report Commercial Insights Hub Related Posts
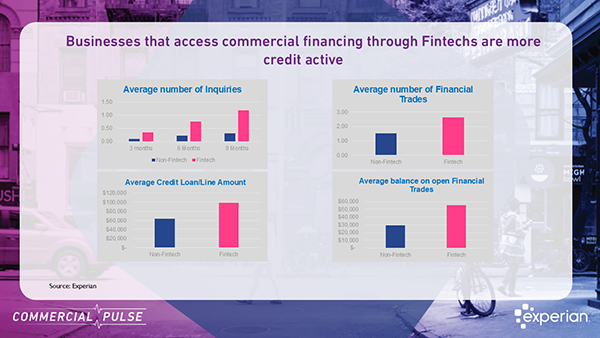
Explore how fintech growth impacts credit managers: increased credit activity, higher loan balances, but with greater delinquency risks in business financing decisions.

Get the latest Commercial Insights from Experian's October 2024 report—covering inflation, job growth, and why 75% of small businesses remain underinsured.

In this week’s Commercial Pulse report, we take a closer look at the burgeoning population of Women-owned businesses.

Population and business growth in the Southern U.S. have outpaced other regions since 2021, but both are now slowing.

I’m excited to share the current Experian Commercial Pulse Report with you. I have the opportunity each week to analyze data on the millions of U.S. small businesses in Experian’s database and discover actionable insights that benefit our clients. Making these discoveries is rewarding work, and we utilize these insights to guide our recommendations. I thought I would share what I am watching through Experian’s bi-weekly Commercial Pulse Report (just bookmark the link; we will update it on a bi-weekly basis). This week's report contains some compelling insight into commercial fraud. In 2002, a Trustpair Institute for Finance & Management survey reported 56% of businesses had reported some sort of fraud attempt, in 2023 the survey shows 96% of businesses reporting fraud attempts. What I'm watching: The growing financial fraud problem: Consumers lost a staggering $10 billion to fraud in 2022, marking a 14% increase from 2021. Already, a shocking 5 billion records were found on the dark web this year, matching the 2023 total. The economy grew 2.8% in Q2. The Fed leaves interest rates flat but leaves the door open for a potential cut at the September meeting. That’s a quick take – Download the latest report. Download Commercial Pulse Report Commercial Insights Hub Related Posts

New business formation strong, making accurate credit risk assessment crucial I’m excited to share the current Experian Commercial Pulse Report with you. I have the opportunity each week to analyze data on the millions of U.S. small businesses in Experian’s database and discover actionable insights that benefit our clients. Making these discoveries is rewarding work, and we utilize these insights to guide our recommendations. I thought I would share what I am watching through Experian’s bi-weekly Commercial Pulse Report (just bookmark the link; we will update it on a bi-weekly basis). This week’s report includes a study about the predictive nature of different credit scores, and how well a consumer risk score versus a commercial risk score or a blended risk score works to predict the future risk of a small business. What I am watching: Unemployment increased to 4.1% in June, the first time over 4% since November 2021. The U.S. economy added 206K new jobs in June while job-openings and job-quits continue to trend downward. 424K new businesses opened in May. The high level of new businesses opening makes it critical for lenders to accurately assess credit risk. That’s a quick take – Download the latest report. Download Commercial Pulse Report Commercial Insights Hub

Unemployment inches up as job growth slows I’m excited to share the current Experian Commercial Pulse Report with you. I have the opportunity each week to analyze data on the millions of U.S. small businesses in Experian’s database and discover actionable insights that benefit our clients. Making these discoveries is rewarding work, and we utilize these insights to guide our recommendations. I thought I would share what I am watching through Experian’s bi-weekly Commercial Pulse Report (just bookmark the link; we will update it on a bi-weekly basis). What I am watching: The U.S. population and labor force are experiencing a major transformation Aging Baby Boomers are changing the U.S. labor market. The only age group whose labor force participation rate is projected to rise are people 75 and older. Birth rates declined 50% since 1950. The median employment age is expected to grow from 39.9 in 2002 to 42.8 years old in 2032. That’s a quick take – Download the latest report. Download Commercial Pulse Report
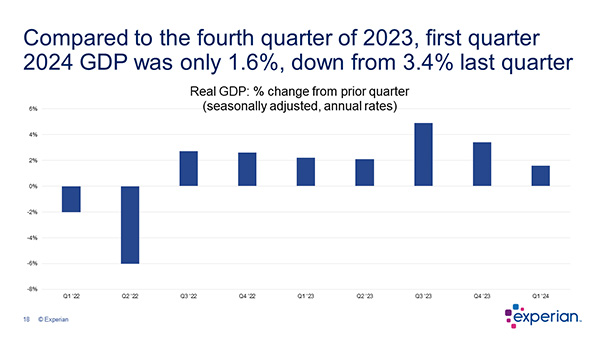
Here are a few quick small business insights from our latest Commercial Pulse Report.

