
Serving commercial Property & Casualty insurers is a major objective of 3rd parties in the analytics and data space. This industry vertical is one in which standard credit tools already apply to the carrier’s challenge in managing claims risk; there is continued investment within and beyond the industry in developing innovative tools for this purpose. However, a smooth roll out of such tools at scale requires a comprehensive understanding of the regulatory process and its constraints.
US Insurance industry- overall regulatory structure:
- Currently, US carriers are regulated primarily by the individual states, a result of the 1945 McCarran Ferguson Act (“MFA”). Less known is that the MFA was presaged by the Paul v Virginia decision (1869, later overturned by SCOTUS) that held that issuing an insurance policy was not a commercial transaction! [1]. Federal regulatory guidance, ultimately from the Office of the Controller of the Currency (OCC) and the Federal Reserve Board (FRB), is implemented via the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (“NAIC”; see below).
- NAIC organizes the insurance commissioners from all 50 states, Washington DC, and territories. NAIC maintains legislative databases, market conduct standards, industry financial reporting, conducts training, and many other functions.
- NAIC provides supervisory guidance for the use of models used to predict insurance loss risk. Among other functions, NAIC has created the Own Risk and Solvency Assessment (“ORSA”) framework which implements existing OCC and FRB guidance to the states.
Capital reserves needed for solvency as well as business conduct — including product definition and general business operations, licensing, maintaining a guaranty fund, underwriting, and rate setting– are determined primarily by the states in which the carrier operates [2]. Today’s system of state-by-state regulation is more challenging than an equivalent centralized regulating body; insurance carriers operate increasingly online, driving the need for multi-state operations which in turn require multistate licensing and complex regulatory compliance. The average property liability firm has 16 state licenses, while the average life insurance carrier has 25. The coordination of state insurance laws, as well as many other quasi-governmental insurance industry functions, falls under the aegis of the NAIC. We will focus our discussion here on the regulation of risk models.
How should third parties align the model building with regulatory requirements?
- Example 1: Basic filing and disclosure protocol: Responsibility to disclose to state regulators typically lies with the developer or the owner of the model. Disclosure responsibility for custom risk models built around the data of a specific client insurer resides with the insurer, while industry standard models used for multiple clients are typically disclosed by the model developer. Reporting and disclosure requirements vary by state. While the most central functions of interest by state regulators are underwriting and rate setting, any other use of models by insurers may be subject to regulatory disclosure. Models used to assess loss risk for rate setting or underwriting purposes are typically examined for discriminatory impact and use of prohibited data in addition to adequate risk performance and numerical stability. “Prohibited data” varies by state but may include certain data elements gleaned from in-state residents, federal crime data, certain credit data elements, traffic violations exceeding a specified age on the books, or other data; the section below deals with credit data. Finally, the requirement to disclose model details such as attributes and weightings also vary between states, and may require the developer to invoke trade secret status for the subject models to avoid disclosure to the public (implicit in many states). The adjudication of such claims is variable between states, as are all communications with regulators on this topic.
- Example 2: Use of consumer credit information to underwrite personal insurance policies: Using credit information in models to predict loss risk on personal insurance contracts also has a rich and extremely active history in the US. P&C insurers have generally found that credit risk and claims risk are positively correlated. They have used credit data on individual consumers to various degrees. Notably, the Consumer- Based Insurance Score (CBIS) employs consumer credit parameters and has been used across the insurance industry since 1993. Amid vigorous debate, states have seen active legislative attempts to restrict and define allowable use of consumer credit data by insurers. Credit information in some cases can outweigh a consumer’s driving record in setting rates- leading to the bitter but factual observation that excellent consumer credit can literally outweigh a DUI conviction in some states and conditions. In 2016 alone, the state legislative actions below were considered and/or enacted; note once again that the ability of individual states to regulate independently greatly complicates the picture for large carriers operating in multiple states:
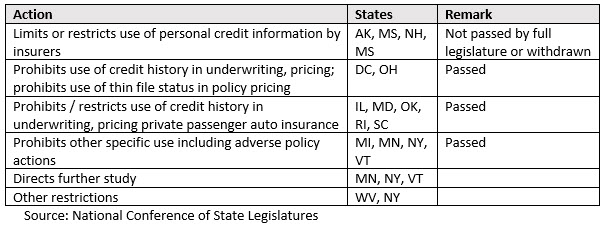
California, Hawaii, and Massachusetts do not appear in the table above. In those states, consumer credit information cannot be used to underwrite personal auto policies.
Example 3: Reporting channel: State regulators typically require use of the System for Electronic Rate and Form Filing (“SERFF”) database maintained by NAIC for formal submissions:
https://login.serff.com/serff/
What’s coming down the road?
We have seen examples of the dependence of applicable insurance regulations on individual state laws; the mechanics of model development requires understanding and working with these restrictions. Basic filing and disclosure, permissible model variables, the proprietary status of model detail, and the use of certain consumer information (e.g., credit scores, driving records) are all aspects of risk models whose successful execution depends on understanding the widely variable set of existing state regulations. Several authors have cited the need for a shift in the underlying regulatory structure of the industry from state-based to a national system, citing the inefficiency of the licensing process and the true interstate nature of today’s distribution system. A centralized federal insurance regulatory body would simplify interstate compliance by carriers, but would also introduce other complications. However, it appears prudent in the near-term for 3rd parties developing models to gain awareness of, and streamline, current requirements for regulatory compliance at the state level.
Conclusion: There is a considerable additional value that the next generation of models will contribute to the commercial P&C vertical. Insurers and 3rd party developers have demonstrated the applicability of their models and data reports, offering competitive added value with standard risk scores adapted from the credit domain. However, promoting these products more broadly and expanding the product offerings themselves into cyber risk, commercial linkages, and various other tools for insurers, the insurance industry faces efficiency hurdles from our 50-state regulatory framework. With any regulatory centralization unlikely near term, 3rd parties thus need to gain working fluency in NAIC and in the SERFF database, anticipate state-level documentation and disclosure requirements, and attain a level of familiarity with state regulatory machines that enables the management of the interests of their clients with confidence.
How Experian can help you
Experian provides analytical services for Property & Casualty as well as other insurance product verticals. To enable you to assess claims risk at the time of policy application (or renewal), we either apply standard risk models or develop custom risk models to your underwriting and rate-setting processes. To help you guard against cyber fraud, false identity, and reputation risk, we offer specialty products as well. We also offer special purpose, custom analyses on request, and we sell curated commercial data to your standards as well.
References:
[1] Brookings Institute. paper on future of regulation- Grace & Klein
[2] Insurance Information Institute: Regulation
[3] Grant Thornton: ORSA requirements: Model Risk Management for Insurance Companies
[4] Blueprint for a Modernized Financial Regulatory Structure, Dept. of Treas., 2008
